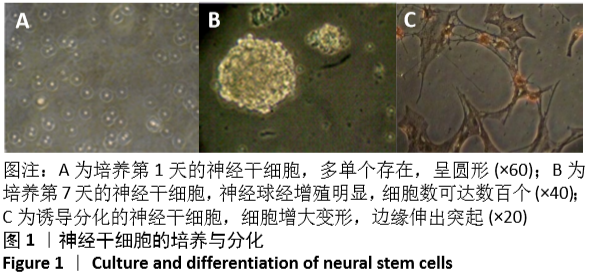
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 532-536.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2363
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
新型纳米支架对神经干细胞生物行为及相关基因表达的影响
周继辉1,姚 猛2,王岩松2,李新志1,周 游1,黄 卫1,陈文瑶1
- 1三峡大学附属仁和医院骨科,湖北省宜昌市 443001;2哈尔滨医科大学附属第二医院脊柱外科,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150086
Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression
Zhou Jihui1, Yao Meng2, Wang Yansong2, Li Xinzhi1, Zhou You1, Huang Wei1, Chen Wenyao1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Renhe Hospital of China Three Gorges University, Yichang 443001, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, Heilongjiang Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
MTT实验:是一种公认的检测生物材料细胞相容性的方法,吸光度值反映纳米支架对细胞数量的影响,可以判断支架的细胞毒性及对细胞增殖的影响。
Bcyclin与CDK基因:CDK在细胞周期的调控中占据核心地位,其表达水平增高促进细胞增殖;Bcyclin能够增高CDK的表达水平,通过对CDK正性调节促进细胞的增殖;细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶抑制因子能够降低CDK的表达水平,抑制细胞的增殖。
背景:利用纳米技术制备的支架可形成与天然生物体内基底膜结构相似的表面结构,对种子细胞的行为进行有效调节。
目的:观察平行与交错排列纳米纤维膜对神经干细胞增殖及分化等生物学行为的影响。
方法:以Ⅰ型胶原为材料,利用静电纺织技术制备平行排列纳米纤维膜与交错排列的纳米纤维膜。将新生大鼠神经干细胞接种于两种纳米纤维膜表面,以单独的细胞培养为对照,采用MTT法检测细胞增殖,流式细胞仪检测细胞增殖周期变化,免疫组化分析细胞神经元分化率,实时定量PCR技术检测Bcyclin D1及CDK2基因表达。
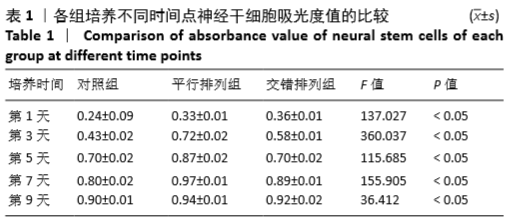
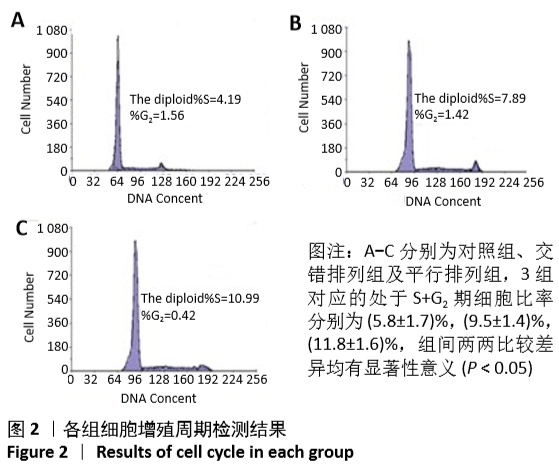
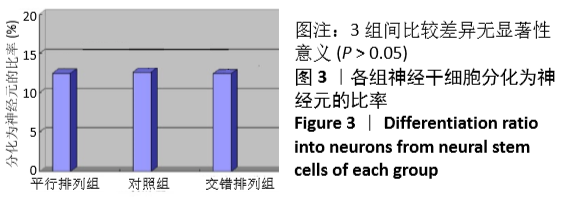
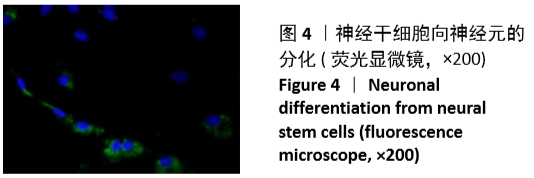
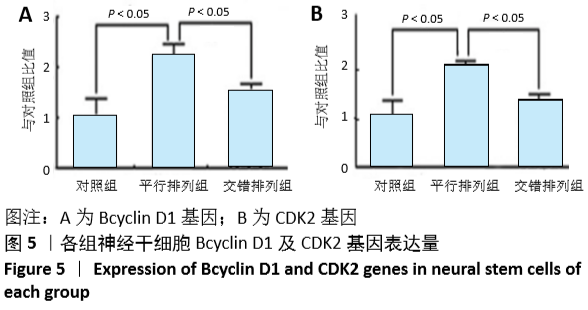
结果与结论:①平行排列组、交错排列组培养1,3,5,7,9 d的细胞增殖吸光度值均高于对照组(P < 0.05),平行排列组培养3,5,7,9 d的细胞增殖吸光度值高于交错排列组(P < 0.05);②平行排列组、交错排列组增殖期细胞比率高于对照组(P < 0.05),并且平行排列组高于交错排列组(P < 0.05);③免疫组化显示,3组细胞的神经元分化率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④实时定量PCR技术检测显示,平行排列组、交错排列组Bcyclin D1及CDK2基因表达量高于对照组(P < 0.05),并且平行排列组高于交错排列组(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,平行及交错排列纳米纤维膜可促进神经干细胞的增殖,对细胞分化无明显影响,能够从基因表达水平调节神经干细胞的生物学行为。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2646-5343 (周继辉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: