中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 1290-1298.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3039
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
尿酸盐转运蛋白在痛风中的多态性和治疗相关性
姬志祥1,2,蓝常贡3
- 1右江民族医学院附属医院临床学院,广西壮族自治区百色市 533000;2右江民族医学院研究生学院,广西壮族自治区百色市 533000;3右江民族医学院附属医院脊柱外科,广西壮族自治区百色市 533000
-
收稿日期:2020-05-18修回日期:2020-05-20接受日期:2020-07-09出版日期:2021-03-18发布日期:2020-12-14 -
通讯作者:蓝常贡,硕士,主任医师,教授,右江民族医学院附属医院脊柱外科,广西壮族自治区百色市 533000 -
作者简介:姬志祥,男,1994年生,山西省阳城县人,汉族,右江民族医学院在读硕士,主要从事关节炎及痛风的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学地区基金项目(81660369);广西自然科学基金面上项目(2016GXNSFAA380173); 广西卫生计生委项目(Z2016411)
Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment
Ji Zhixiang1, 2, Lan Changgong3
- 1Clinical School of the Affiliated Hospital of YouJiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Graduate School of YouJiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Spinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of YouJiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2020-05-18Revised:2020-05-20Accepted:2020-07-09Online:2021-03-18Published:2020-12-14 -
Contact:Lan Changgong, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Spinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of YouJiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Ji Zhixiang, Master candidate, Clinical School of the Affiliated Hospital of YouJiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Graduate School of YouJiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Regional Project), No. 81660369; Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (General Project), No. 2016GXNSFAA380173: Guangxi Health and Family Planning Commission Project, No. Z2016411
摘要:
文题释义:
全基因组关联研究(Genome-Wide Association Studies,GWAS):是指在全基因组层面上,开展多中心、大样本、反复验证的基因与疾病的关联研究,是通过对大规模的群体DNA样本进行全基因组高密度遗传标记(如SNP或CNV等)分型,从而寻找与复杂疾病相关的遗传因素的研究方法,全面揭示疾病发生、发展与治疗相关的遗传基因。
尿酸盐转运蛋白:主要位于肾脏和肠道,负责调节人的血清尿酸水平。如近端小管细胞的基底外侧膜中的GLUT9和顶端膜中的URAT1介导肾尿酸重吸收。部分尿酸盐转运蛋白的变体会增加血清尿酸盐水平和痛风风险,这些蛋白的基因多态性研究和药物相关性研究对于痛风的个体化高效治疗有重要意义。
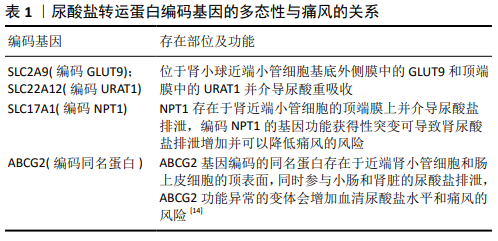
背景:研究表明,GLUT9、URAT1、NPT1和ABCG2等尿酸盐转运蛋白直接参与人的血清尿酸水平调节,其编码基因的多态性与痛风的发生发展密切相关。因此,尿酸盐转运蛋白的针对性治疗成为一种临床治疗痛风的新思路。
目的:总结近几年尿酸盐转运蛋白在痛风中的多态性表达及与临床药物的相关性研究进展,为进一步探究痛风及高尿酸血症的个性化治疗提供文献和理论基础。
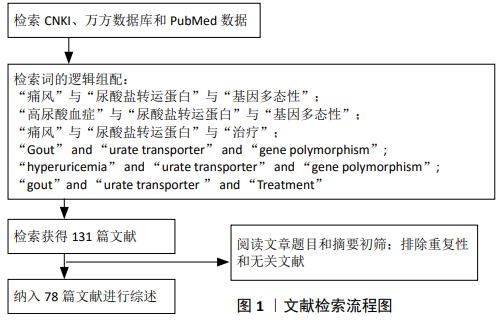
方法:由第一作者以“痛风、尿酸盐转运蛋白、高尿酸血症、基因多态性、治疗”为中文检索词,以“Gout,Urate transporter,Hyperuricemia,Polymorphism,GWAS,Therapy”为英文检索词,通过计算机检索CNKI、万方数据库和PubMed数据,检索出相关文献131篇,根据纳入与排除标准,并进行文献增减,筛选出78篇文献进行汇总、归纳,主要包括尿酸盐转运蛋白在痛风中的基因多态性及痛风药物作用机制与尿酸盐转运蛋白的相关性等内容。
结果与结论:大量研究表明,尿酸盐转运蛋白的多态性与尿酸稳态密切相关,以GLUT9、URAT1、NPT1和ABCG2最为重要。这些蛋白在不同人群中的差异性表达,并且与痛风药物的反应机制密切相关。在未来诊疗中,这些研究结果可以帮助评估高尿酸血症患者有无治疗必要,并帮助痛风患者制定个体化高效的治疗方案。通过激活BCRP增强肠道对尿酸的清除来治疗高尿酸血症可能是一种可行方案。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6318-2348 (姬志祥)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程中图分类号:
引用本文
姬志祥, 蓝常贡. 尿酸盐转运蛋白在痛风中的多态性和治疗相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298.
Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298.
2.1.1 SLC2A9基因多态性与痛风的关系 SLC2A9基因编码的GLUT9蛋白是GLUT家族独特的成员,在转运尿酸的过程中具有电压依赖性。GLUT9有2个同工型GLUT9L(长同工型)和GLUT9S(短同工型),分别位于肾近曲小管细胞的基底外侧膜和顶端膜,区别仅在于N端结构域的前29个残基[16]。GLUT9S的尿酸转运能力更高,具有重吸收尿酸的作用,而GLUT9L主要负责尿酸的排出。研究已证明,SLC2A9是最突出的尿酸盐转运蛋白编码基因之一,与ABCG2共同解释了6.9%以上的血清尿酸盐变异[17],且在女性中更为常见[1],突变可降低血清尿酸盐水平,并造成2型肾性低尿酸血症[18]。GLUT9功能的丧失是SLC2A9基因36kb缺失导致231个氨基酸的蛋白被截断所致[19]。
在近几年的全基因组关联研究中,SLC2A9的SNP风险等位基因(如rs1014290的C/T等位基因)对临床参数的影响在不同类型痛风的病例对照OR比值中呈显著的线性关系[17, 20]。这提示GLUT9的多态性不仅会影响尿酸水平,还与痛风特定亚型(肾脏排泄不足型和肾脏超负荷型)存在差异性关联。MATSUO等[17]的全基因组关联研究研究表明,SLC2A9(rs3775948)与肾脏排泄不足型痛风的关联性(OR=1.94)明显强于肾脏超负荷型痛风(OR=1.38);病例亚型异质性检验显示OR值有显著性差异(P=2.7×10?4) 。
尿酸浓度异常的个体与SLC2A9的SNP密切相关[16],主要体现在基因型不同的人种存在不同的临床表型。TU等[21]对中国台湾的原住民和汉族的基因型研究表明,参与研究的汉族人高风险基因型SLC2A9(rs1014290 [AA])和痛风的发生密切相关,此基因型在原住民参与者中并不显著,而另一项在日本男性门诊患者中的研究也证明了此基因型与痛风的关联性[20]。WRIGLEY等[22]使用对数变量进行多元调整的逻辑回归和线性回归方法分析了1 699例欧洲痛风病例和14 350例正常尿酸和高尿酸对照组的基因型,证明欧洲高尿酸血症患者SLC2A9 rs11942223的T等位基因与痛风相关;类似的研究还证明新西兰人的相关性并排除了波西尼亚人的相关性风险[23];而在高加索人中,该基因在果糖负载增加的情况下会表达上调,减少尿酸排泄[24];还有研究证明了此基因型与痛风石的发病无关[25]。CHEN等[26]在非洲大陆进行了第一个全基因组关联研究测定血清尿酸,共有4 126位非洲人和5 007位非裔美国人参与研究。确定了非洲人与血清尿酸相关的2个重要基因座:4p16.1(SLC2A9)和11q13.1(SLC22A12)。SLC2A9中关联最紧密的SNP为新发现的rs7683856(P=1.60×10-44),其次为rs6838021(P=5.75×10-17)。SUN等[27]测试了中国新疆维吾尔族人SLC2A9中的5个SNP(rs938557,rs7679916,rs7349721,rs13101785和rs13137343),结果正常血尿酸组中,rs938557与尿酸显著相关,其中具有T等位基因的个体尿酸水平明显高于C等位基因的个体;rs7679916和rs13137343有一定相关性;在高尿酸血症组中,未发现可能影响尿酸浓度的SNP。YANG等[28]从中国东南沿海地区1 056例高尿酸血症患者中随机选择300例受试者鉴定基因多态性,SLC2A9 rs11722228多态性(CC,CT和TT)据报道分别为49.3%,40.3%和10.3%;而DAS GUPTA等[29]在针对马来西亚人的研究表明也提示,相对于CT基因型和TT基因型,SLC2A9 rs11722228的CC基因型的痛风受试者的血尿酸水平明显较高(P=0.002),同时还具有更高的有痛风家族史概率(P < 0.050)和肾结石发生率(P=0.026);早前类似的研究还表明此基因型与墨西哥人、日本人的高尿酸血症发生密切相关[30- 31]。ZHOU等[32]在中国大陆进行了低尿酸血症、高尿酸血症例和正常对照的3组队列研究,共鉴定出84个高质量变体。在低尿酸血症患者中发现2种SLC2A9的罕见变体p.T21I和p.G13D,而高尿酸血症例和正常对照组则未发现。
总体而言,阐明GLUT9多态性对血清尿酸的作用是一项复杂的工作,因为种族、性别以及物种等多种因素可能会影响基因多态性。因此,阐明GLUT9与尿酸代谢之间的相互作用机制将具有重要意义。由于工作量多而繁杂,目前针对不同基因型的具体治疗仍未开展广泛研究,并且针对特定等位基因型的跨种族研究相对较少,仍需要继续开展相关研究。
2.1.2 SLC22A12基因多态性与痛风的关系 SLC22A12基因编码的尿酸盐/阴离子交换剂(URAT1)在2002年首先被证明主要位于肾脏近端小管细胞的顶端膜中,它是与肾脏中尿酸重吸收有关的最重要的转运蛋白[33]。URAT1由555个氨基酸残基组成,形成12个跨膜结构域,其中亲水基由4个跨膜结构域组成。URAT1在12个跨膜结构域中具有一个亲水环。在人类肾脏中,URAT1负责通过跨膜电位梯度将尿酸盐经由近端小管细胞的顶端膜转运到近端肾小管管腔。URAT1具有高容量,但对尿酸的亲和力低,Km为(371±28)μmol/L[34]。所以URAT1在调节人类血液尿酸水平中起着重要的作用,它也已被证明是高尿酸血症的重要靶标,其氨基酸的变化对尿酸吸收有很强的影响[35],而SLC22A12突变可降低血清尿酸盐水平,并造成1型肾性低尿酸血症[18]。URAT1功能失调的患者常常因运动累积过多自由基导致肾动脉痉挛,进而引起急性肾功能衰竭。早前的研究已表明,SLC22A12基因包含多个与高尿酸血症相关的多态性位点,第1外显子C258T位点SNP可提高尿酸排泄率并降低尿酸的重吸收,第2外显子C426T的SNP可能与减少尿酸排泄相关。此外,URAT1中的SNP与肥胖、胆固醇、原发性高血压等代谢综合征的发病机制有关。
研究还发现较高的CADD Phred得分与SLC22A12变体中对血清尿酸盐的实质性不良影响相关[36]。而MISAWA等[35]的研究中未发现CADD Phred评分与URAT1的功能变化之间有任何显著相关性,这可能与后者的基因座数量少有关。MISAWA等[35]还通过微基因实验证明,SLC22A12的rs58174038等位基因G突变为A时,将出现终止密码子TGA进而导致URAT1功能丧失。对URAT1吸收尿酸有显著改变的SNP还包括rs552232030、rs145738825和rs201136391,表明罕见变异体是解释血清尿酸盐水平“缺失遗传力”的重要部分。
TU等[21]对中国台湾的原住民和汉族的基因型研究表明,参与研究的汉族人高风险基因型SLC22A12(rs475688[CC])和痛风的发生密切相关,此基因型在原住民参与者中并不显著;ZOU等[37]进行的Meta分析也证明了该基因型的易感性。TIN等[36]报道了在19 517名欧洲裔和非洲裔美国人的大规模全基因组关联研究,发现尿酸盐转运蛋白SLC22A12和SLC2A9中低频破坏变异的聚集关联,同时还找到了SLC22A12中2个罕见的独立错义变异体rs150255373和rs147647315携带者的痛风风险减半,rs150255373变异仅在欧洲裔美国人参与者中观察到,而rs147647315主要在非裔美国人参与者中观察到;CHEN等[26]在非洲大陆进行的第一个全基因组关联研究也证明rs147647315是与非洲人群的血清尿酸关联最紧密的SNP(P=6.65×10-25)。 ZHOU等[32]在中国大陆进行了低尿酸血症、高尿酸血症例和正常对照的3组队列研究,共鉴定出84个高质量变体。在低尿酸血症患者中发现4种SLC22A12的罕见变体p.W50fs,p.Q382L,p.V547L和p.E458K,而高尿酸血症例和正常对照组则未发现。IM等[38]为了确定韩国受试者中血清尿酸浓度的致病性遗传变异,进行了全基因组关联研究(1 902名男性)和验证研究(2 912名男性和女性),发现11号染色体上的SLC22A12-NRXN2具有全基因组意义,处于弱或中度连锁不平衡(LD)状态(r2=0.02-0.68)。SLC22A12基因rs121907892(c.774G>A,p.W258*)表达与附近全基因组关联研究信号相关存在显著变异。目前为止仅在韩国和日本受试者中发现了这种变体,已知该变体可降低普通人群中的血清尿酸浓度[39- 40]。在SLC22A12的SNP对儿童的影响方面,LEE等[41]通过出生与成长队列研究评估了3-9岁儿童的2个SNP(rs3825017和rs16890979)对尿酸浓度的影响,并用混合模型分析来估计rs3825017(SLC22A12 c.246C> T)和rs16890979(SLC2A9 c.844G> A)基因型引起的血清尿酸浓度的纵向关联。结果表明rs3825017对尿酸浓度的影响仅在男孩中很明显,其中rs3825017 T等位基因的男孩比同龄人的浓度更高;此基因型在早前的韩国成人群体研究中也被证明会提高个体的高尿酸血症风险[39]。DUONG等[42]评估了SLC22A12基因多态性与越南人痛风易感性之间的关系,结果rs11231825,rs7932775均符合Hardy-Weinberg平衡,其中rs11231825的C等位基因相对于T等位基因可以降低痛风风险(OR=0.712;95%CI:0.526-0.964,P=0.030 2)。这表明SLC22A12 rs11231825的其中T等位基因可能是越南人群痛风易感性的危险因素,而此基因型在中国台湾汉族的基因型研究中则未表现出与痛风发生密切相关[21]。
值得一提的是,URAT1在其羧基末端具有一个PDZ基序,与PDZ结构域结合在一起,该结构域由80-90个氨基酸组成,这些氨基酸在PDZ蛋白中以多个拷贝特异性表达。PDZK1于1997年从大鼠肾脏中首次发现,它具有4个串联的PDZ域。在PDZK1中的第一、第二和第四PDZ域与URAT1相互作用是必要的,揭示了PDZK1也定位于肾近端小管细胞如URAT1的顶端膜。进一步的研究表明,PDZK1和URAT1在人类胚胎肾293细胞(HEK293细胞)中的共表达比无PDZ基序的URAT1具有更高的尿酸转运能力,这表明PDZK1通过PDZ相互作用调节URAT1转运活性。随后,一项复制研究也证明了rs12129861与痛风易感性之间存在显着关联[34]。此外,其他报道汉族痛风与PDZK1多态性之间相关性的研究也显示出与上述研究结果一致的正相关性[43-44]。URAT1的多态性或基因变异可能与综合征密切相关的发现可能为个体化临床治疗和新药开发提供新的线索。
2.1.3 SLC17A1基因多态性与痛风的关系 SLC17A1编码肾脏尿酸分泌转运蛋白钠离子依赖磷酸盐转运体1(Na+ dependent phosphate transporter 1,NPT1),该蛋白主要位于人类肾脏中近端肾小管细胞的顶端膜上。NPT1有多种底物,例如对氨基马尿酸(PAH)和尿酸[45]。NPT1是一种分泌性转运蛋白,可以将尿酸盐从肾小管转运到尿液中[46]。与早期的研究一样,尽管没有足够的研究来证明NPT1与痛风之间的联系,但是NPT1的突变被认为是肾分泌不足(renal under excretion,RUE)型痛风的另一种致病因素[47-49]。随后,全基因组关联研究表明NPT1/SLC17A1的SNP与血清尿酸水平密切相关。与上述两个基因相比,SLC17A1的SNP与痛风或高尿酸血症的相关性研究相对较少,部分研究还证明此基因的多态性与Dent病和红细胞水平调控相关[50-51]。
URANO等[47]证明NTP1变体rs1165196显著提升了血清尿酸,这有加重痛风发生与进展的风险。此后,研究证明了NPT1 I269T的另一个突变增加了尿酸盐的最大转运能力,而不是通过脂质体体外诱导Km的变化来促进尿酸排泄。这可能是因为就转运蛋白的交替进入模型而言,变体269T的化学结构变化可能比变体269I快,或者原因可能是由于苏氨酸具有比异亮氨酸更小的疏水性侧链[46]。在日本患者中进行的另一项研究进一步证实了这一现象,该研究表明在尿酸排泄分数(FEUA)低的肾分泌不足痛风患者中,rs1165196(I269T)导致肾近曲小管中尿酸排泄增加(5.5%),该结果表明常见的错义变体NTP1-rs1165196(I269T)是功能获得性突变。因此,变异rs1165196对肾分泌不足痛风患者可能是有益的突变[52]。已经有人提出,NPT1中这种常见的功能获得突变对于评估其他人群中肾分泌不足痛风的风险也可能很重要[47-48]。值得一提的是,Hap Map数据库中rs1165196的次要等位基因频率在不同地区之间有所不同,即东京的日本人为16.7%,伊巴丹的约鲁巴人为4.2%,北京的汉族人为14.4%,表明NPT1的rs1165196突变不仅在日本人中很普遍,在其他人群中也很普遍。这一有价值的发现可能为肾分泌不足痛风的基因治疗提供潜在的靶标。
ZHOU等[53]在中国汉族男性中选择622例痛风患者和917名健康对照者进行基因分型,证实了SLC17A1的rs1183201与痛风性关节炎和尿酸浓度相关;ROMAN等[54]在美国明尼苏达州非苗族人群中的研究也表明,rs1183201等位基因(A)的发生频率比高加索人(16.4% vs. 50%,P < 0.001)低3倍。但是,苗族之间等位基因的发生频率同汉族相比没有差异(16.4% vs. 13.3%,P=0.54)。该SNP(rs1183201)在不同种族中的广泛验证及其对肾尿酸排泄的直接作用为苗族可能有较高的痛风风险做出合理解释,这些一致的发现在一定程度上为苗族与非苗族在明尼苏达州的患病率差异提供了一个可能的遗传基础。考虑到人群之间的遗传差异和痛风性关节炎的复杂发病机制,未来研究方向应继续选择在独立人群中进行更多的验证试验和相关的功能实验。
2.1.4 ABCG2基因多态性与痛风的关系 ATP结合盒(ABC)转运蛋白2(ABCG2/BCRP)属于亚家族G,其编码基因位于4q11染色体上痛风易感基因座(MIM 138,900)。ABCG2蛋白是一种ATP依赖的多功能转运体,负责调节各种物质的排泄。ABCG2表达于肾近端小管的刷状膜,并参与顶端尿酸盐的分泌。该转运体也表达于小肠和肝脏的上皮细胞顶端膜,提示其在肾外调节尿酸分泌的作用。BHATNAGAR等[55]还发现,主要在肠中表达的肾外ABCG2可以补偿由于肾脏功能下降而导致的人体主要尿酸水平升高。据报道,伴有代偿性尿酸肠排泄的患者肾小球滤过率(GFR)较低。
研究已证明,在欧洲、非洲和亚洲人群中,ABCG2与高尿酸血症和痛风的最强关联位点均在SNP rs2231142,该位点引起ABCG2蛋白141位谷氨酰胺转变为赖氨酸(Q141K)。其中WRIGLEY等[22]使用对数变量进行多元调整的逻辑回归和线性回归方法分析了1 699例欧洲痛风病例和14 350例正常尿酸和高尿酸对照组的基因型,证明欧洲高尿酸血症患者ABCG2 141K(T)等位基因与痛风相关联,141K对欧洲人的高尿酸血症具有决定性影响,而对波利尼西亚人则无影响;而在高尿酸血症的条件下,141K等位基因与rs10011796 CC基因型结合可增加痛风风险,西波里尼西亚人(P=0.009)为21.5倍,欧洲人(P=9.9×10-6)为2.6倍。WANG等[16]发现中国汉族男性人群中rs2231142位点AA基因型携带者痛风发病率远高于CC基因型携带者,表明rs2231142位点多态性与中国汉族男性原发性痛风的发病密切相关;而YANG等[28]在中国东南沿海地区人群中的研究则给出不同结果,1 056例高尿酸血症患者中随机选择的300例受试者鉴定基因多态性的结果表明ABCG2 rs2231142多态性(CC,CA和AA)的患病率分别为44.4,44.8和11.8。在最近研究中,rs2231142被证明与中国汉族男性人群中的肾结石、CKD等痛风合并症相关(P=0.014,P=0.026)[56],且在菲律宾怀孕女性中,也发现该基因型的痛风风险等位基因(T)患病率(46%)明显高于高加索人、汉族和非裔美国人[57]。DUONG等[42]评估了Q126X(rs72552713)基因多态性与越南人痛风易感性之间的关系,结果ABCG2基因的rs72552713均符合Hardy-Weinberg平衡,且T等位基因与痛风的风险增加相关(OR=21.19;95%CI:3.00-918.96;P < 0.001)。此外,NAKASHIMA等[58]针对1 214例血液透析患者的前瞻性队列研究还表明,CC基因型的ABCG2功能最好,而Q126X(rs72552713)的TT/TC分型和Q141K(rs2231142)CC/CA分型为≤1/4功能类型;最终有220例患者死亡,遗传变异估计的ABCG2功能障碍与血清尿酸水平显著正相关。在早前TAKADA等[59]进行的研究中,也通过尿毒症小鼠模型证明了ABCG2是尿毒症毒素硫酸吲哚的主要转运体。这些研究表明ABCG2在尿酸排泄中起着重要的生理作用,而ABCG2功能障碍是血液透析患者死亡的危险因素。
由于ABCG2在不少器官和组织中均有表达,因此其遗传突变可能会在内源性尿酸的排泄中产生很大的差异。ABCG2的多态性研究表明,该基因在调节血清尿酸水平中起重要作用,这表明通过激活ABCG2增强肠道对尿酸的排泄来降低血清尿酸水平进而达到治疗高尿酸血症可能是未来研究的一个思路。
2.2 尿酸盐转运蛋白在痛风治疗中的研究进展 近年来有大量的关于高尿酸血症和痛风的遗传研究、基因与环境相互作用研究以及降低尿酸盐疗法的药物遗传学研究出现,这些新的研究和发现增加了在临床实践中为痛风患者提供个性化医学方法的可行性。临床实际中基因检测费用昂贵,且仅仅应用于对诊断或药物基因组学有强烈临床需求的情况下,但个人的基因组序列测序成本不足1 000美元,且仍在不断降低[60],在未来的个性化医疗保健中有巨大的应用空间。RISTIC等[61]认为未来可以通过PPARγ,PPARα,NRF2和AhR等4个转录因子靶向诱导ABCG2表达,研究的要点在于找到这些转录因子的激活剂,并评估此类药物治疗痛风性关节炎的功效。作者将围绕尿酸盐转运蛋白,综述近几年与痛风治疗相关的细胞、动物和临床药物研究,讨论高尿酸血症和痛风个性化治疗方法的潜力。
2.2.1 糖皮质激素与尿酸盐转运蛋白的关系 糖皮质激素广泛用于治疗痛风,该药物与尿酸稳态及尿酸盐转运蛋白的相关研究较少。LI等[62]在痛风小鼠模型的研究表明,3种NSAID(布洛芬、双氯芬酸和吲哚美辛)治疗1周对小鼠尿酸稳态的影响很小,而低剂量地塞米松的1周低剂量(1 mg/kg和5 mg/kg)显著降低血清尿酸(降低约15%)。研究表明,低剂量的地塞米松会诱导肝脏产生黄嘌呤氧化还原酶(XOR),并下调肾脏中的URAT1,进而帮助降低血清尿酸盐。体外细胞研究还表明,糖皮质激素受体参与了地塞米松介导的URAT1下调,糖皮质激素受体通过其与核因子κB和AP-1信号通路的相互作用来调节URAT1[62]。这些研究证明痛风治疗常用药物的反应机制尚未完成清楚,需要进一步研究以帮助指导未来的个性化医疗服务。
2.2.2 尿酸合成抑制剂与尿酸盐转运蛋白的关系 除去最早在临床上应用于痛风治疗的秋水仙碱、糖皮质激素以及非类固醇甾体类抗炎药物(如布洛芬、双氯芬酸钠和塞来昔布),近年来别嘌醇、非布司他等尿酸合成抑制类药物也广泛地应用于临床。
别嘌醇是次黄嘌呤的结构异构体,最早开发于19世纪60年代,最初认为别嘌醇可与次黄嘌呤和黄嘌呤竞争性抑制剂,但其作用机制却更为复杂[63]。别嘌呤醇通过黄嘌呤氧化还原酶羟基化为羟嘌呤醇,与还原的钼原子形成共价键,该共价键对于限制尿酸盐的产生至关重要,共价键消失后作用较弱。GRAHAM等[64]通过临床试验发现,每日剂量100-300 mg的别嘌呤醇仅能在约40%的痛风患者中充分降低血清尿酸,而非布司他80 mg的每日剂量在约70%的痛风患者中充分降低血清尿酸;研究表明别嘌醇的作用效果与患者的ABCG2基因型相关,ABCG2转运蛋白功能丧失的次要等位基因(r2231142)携带者比主要等位基因(野生型)的携带者反应更差。另一项研究比较了此SNP(r2231142)在反应不佳患者(别嘌呤醇使用剂量>300 mg/d,但尿酸水平仍>0.36 mmol/L)中的基因频率与反应良好患者(尿酸含量< 0.36 mmol/L且别嘌呤醇的剂量<300 mg/d)中的基因频率,排除依从性差或反应未分类的患者;结果表明反应不佳患者的等位基因(rs2231142)的平均频率为62%,而反应良好患者中则仅为32%[65]。WALLACE等[66]对痛风患者(n=299)进行了别嘌醇的长期安全性研究,相关性回归分析结果表明ABCG2 rs2231142(Q141K)与别嘌醇产生的不良反应密切相关(OR=2.35,P=7.3×10-4)。上述研究表明,别嘌醇对于ABCG2基因型为r2231142的痛风患者效果较差,且该基因型患者使用别嘌醇将有更高的概率出现不良反应。
非布司他可以与黄嘌呤氧化还原酶的黄嘌呤结合位点结合,并通过各种复杂的相互作用表现出极强的抑制作用,包括与酶分子形成的离子键、氢键、疏水键和范德华力,机制不涉及钼的氧化态。因此,与别嘌醇不同,非布司他主要在肝脏中代谢,适合肾功能不全的患者使用,减少了不良反应风险[63]。在中国健康受试者中的研究表明,非布司他的药代动力学(PKs)因人而异,UGT1A1*6(c.211G> A,rs4148323)的杂合子和纯合子的血浆浓度-时间曲线(AUC)下的面积显著高于野生型,且清除率(CL/F)下降了22.2%[67]。这些结果表明,UGT1A1*6是影响患者体内药物处置的重要因素,为中国受试者非布司他药代动力学的个体差异提供了可能的解释。
2.2.3 促尿酸盐排泄药与尿酸盐转运蛋白的关系 丙磺舒和苯溴马隆是临床常见的促尿酸排泄药。丙磺舒开发之初是为了竞争性地抑制药物的肾脏排泄,从而增加其血药浓度并延长其作用持续时间。后来的研究中偶然发现了丙磺舒是一种URAT1抑制剂,可抑制近端小管的尿酸盐重吸收作用,此外丙磺舒还可以非选择性地抑制有机阴离子转运体(Organic anion transporter,OAT)。苯溴马隆是19世纪70年代第一个作为促尿酸排泄药物开发的化合物,尽管分子机制未阐明,但已明确其通过抑制URAT1而作用于肾近端小管的管腔膜,后者可重新吸收排泄到尿液中的尿酸盐。
近年来,关于促尿酸盐排泄药的研究主要集中在Lesinurad和Dotinurad等新型药物。Lesinurad是一种新型降尿酸剂,于2015年12月获得美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)的批准,并于2016年2月获得欧盟的批准上市,目前尚未在国内上市。它可以选择性地抑制肾脏URAT1和OAT4,不抑制GLUT9,并且对ABCG2没有影响;与苯溴马隆相比,Lesinurad的线粒体毒性和PPARγ诱导风险也较低;与丙磺舒相比,Lesinurad不抑制OAT1或OAT3[68]。YANG等[69]通过体外细胞实验表明,Lesinurad的单个阻转异构体在调节尿酸摄入表达这些转运蛋白的稳定细胞系中时,对URAT1具有立体特异性药理活性,但对OAT4不具有立体特异性,因此将Lesinurad发展为单独的阻转异构药物将是昂贵且不切实际的。ALGHAMDI等[70]通过小鼠实验证明,Lesinurad和别嘌醇联合使用,可以降低高尿酸血症小鼠的血尿酸、血尿素氮、黄嘌呤氧化酶活性谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶等指标,同时抑制炎性反应,并在一定程度上逆转了含氧酸盐诱导的肾脏mURAT-1、mGLUT-9、mOAT-1和mOAT-3的表达,抑制转化生长因子β1免疫反应,帮助肾脏尿酸的排泄增加。Dotinurad与Lesinurad类似,是一种新型的URAT1抑制剂,于2019年11月在日本获得批准上市,Dotinurad是苯溴马隆的结构衍生物。Hosoya等[71-72]的2次临床对照研究证明,Dotinurad的降尿酸作用明显大于非布司他,且无明显的不良发育发生。
2.2.4 中药及其提取物与尿酸盐转运蛋白的关系 近年来,中日韩3国在痛风治疗的研究中广泛涉及各种中药及其提取物。其中LEE等[73]通过将野菊花提取物和肉桂皮提取物相混合获得DKB114,在正常大鼠和高尿酸血症大鼠的对照实验中证明DKB114能够降低hURAT1的卵母细胞和HEK293细胞中尿酸的摄取,从而降低URAT1和GLUT9的蛋白表达水平,减少肾脏中尿酸的重吸收;此外DKB114还可以通过抑制肝脏黄嘌呤氧化酶活性来减少尿酸的产生。LIN等[74]在鼠麴草中提取了木犀草素和木犀草素-4’-O-葡萄糖苷,并通过高尿酸血症小鼠模型证明,这2种黄酮可降低mURAT1的水平和抑制黄嘌呤氧化酶活性,从而帮助尿酸排泄并改善高尿酸血症引起的肾功能不全;此外,木犀草素和木犀草素4’-O-葡萄糖苷还可减轻单钠尿酸盐晶体引起的足爪肿胀和炎症症状。TASHIRO等[75]制备了107种不同原料药的提取物,发现蛇床花的提取物蛇床子素(osthol)可以非竞争性抑制URAT1,从而减少尿酸的吸收。LEE等[76]通过高尿酸血症的小鼠模型研究了日本汉方药物Yokuininto,证明该药物可在不影响URAT1的情况下显著提高OAT3表达水平,降低GLUT9水平,达到促进尿酸排泄和抑制尿酸再吸收的效果,在研究中可使高尿酸血症小鼠的血尿酸降低44%。LEE等[77]通过大鼠模型及细胞对照实验,证明益智种子提取物在体外不抑制黄嘌呤氧化酶,但低剂量的益智种子提取物会显著降低hURAT1的表达,从而降低尿酸重吸收率。WANG等[78]建立了Sprague Dawley大鼠模型,分别用富含黄酮的土茯苓根茎和别嘌醇进行喂养,结果表明富含黄酮的土茯苓根茎可通过增加ABCG2、OAT1和OCT2表达,从而促进尿酸排泄。传统中医药及其提取物在尿酸盐转运蛋白相关的痛风治疗研究前景广阔,但仍需要大量的动物、细胞学实验和临床研究,在未来的痛风个体化诊疗中有机会发挥重要作用。
| [1] DALBETH N, MERRIMAN TR, STAMP LK. Gout.Lancet. 2016;388(10055): 2039-2052. [2] LIN CY, HSIEH MC, KOR CT, et al. Association and risk factors of chronic kidney disease and incident diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Diabetologia.2019; 62(3): 438-447. [3] CHRISTENSEN JL, YU W, TAN S, et al. Gout Is Associated With Increased Coronary Artery Calcification and Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging.2020;13(3): 884-886. [4] TATSUMI Y, ASAYAMA K, MORIMOTO A, et al. Hyperuricemia predicts the risk for developing hypertension independent of alcohol drinking status in men and women: the Saku study. Hypertens Res.2020;43(5): 442-449. [5] OH TR, CHOI HS, KIM CS, et al. Hyperuricemia has increased the risk of progression of chronic kidney disease: propensity score matching analysis from the KNOW-CKD study . Sci Rep.2019; 9(1): 6681. [6] CHEN-XU M, YOKOSE C, RAI SK, et al. Contemporary Prevalence of Gout and Hyperuricemia in the United States and Decadal Trends: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007-2016. Arthritis Rheumatol.2019; 71(6): 991-999. [7] RAI SK, AVINA-ZUBIETA JA, MCCORMICK N, et al. The rising prevalence and incidence of gout in British Columbia, Canada: Population-based trends from 2000 to 2012. Semin Arthritis Rheum.2017; 46(4): 451-456. [8] ZOBBE K, PRIETO-ALHAMBRA D, CORDTZ R, et al. Secular trends in the incidence and prevalence of gout in Denmark from 1995 to 2015: a nationwide register-based study. Rheumatology (Oxford).2019; 58(5): 836-839. [9] BARDIN T, BOUEE S, CLERSON P, et al. Prevalence of Gout in the Adult Population of France. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken).2016; 68(2): 261-266. [10] DEHLIN M, DRIVELEGKA P, SIGURDARDOTTIR V, et al. Incidence and prevalence of gout in Western Sweden. Arthritis Res Ther.2016;18:164. [11] 陈晓波, 李诺利, 陈樱君,等. 钦州地区痛风和高尿酸血症影响因素流行病学研究 [J]. 检验医学与临床, 2017, 14(23): 3470-3472. [12] 刘新琼, 王晓朋, 关黎清,等. 新疆伊犁哈萨克自治州不同民族中高尿酸血症与痛风患病率及相关危险因素分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2016,14(7):1186-1188,1192. [13] 谭立夫, 朱君, 严妙娟,等. 惠州市惠阳区2008~2014年痛风和高尿酸血症的流行病学调查[J]. 现代诊断与治疗,2016,27(10): 1919-1920. [14] DALBETH N, CHOI HK, JOOSTEN LAB, et al. Gout. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019; 5(1): 69. [15] NAKAYAMA A, NAKAOKA H, YAMAMOTO K, et al. GWAS of clinically defined gout and subtypes identifies multiple susceptibility loci that include urate transporter genes. Ann Rheum Dis.2017;76(5): 869-877. [16] WANG Z, CUI T, CI X, et al. The effect of polymorphism of uric acid transporters on uric acid transport. J Nephrol. 2019; 32(2): 177-187. [17] MATSUO H, YAMAMOTO K, NAKAOKA H, et al. Genome-wide association study of clinically defined gout identifies multiple risk loci and its association with clinical subtypes. Ann Rheum Dis.2016; 75(4): 652-659. [18] MANCIKOVA A, KRYLOV V, HURBA O, et al. Functional analysis of novel allelic variants in URAT1 and GLUT9 causing renal hypouricemia type 1 and 2. Clin Exp Nephrol.2016;20(4):578-584. [19] DINOUR D, GRAY NK, CAMPBELL S, et al. Homozygous SLC2A9 mutations cause severe renal hypouricemia. J Am Soc Nephrol.2010; 21(1): 64-72. [20] KAWAMURA Y, NAKAOKA H, NAKAYAMA A, et al. Genome-wide association study revealed novel loci which aggravate asymptomatic hyperuricaemia into gout. Ann Rheum Dis.2019;78(10): 1430-1437. [21] TU HP, MIN-SHAN KO A, LEE SS, et al. Variants of ALPK1 with ABCG2, SLC2A9, and SLC22A12 increased the positive predictive value for gout. J Hum Genet.2018;63(1):63-70. [22] WRIGLEY R, PHIPPS-GREEN AJ, TOPLESS RK, et al. Pleiotropic effect of the ABCG2 gene in gout: involvement in serum urate levels and progression from hyperuricemia to gout . Arthritis Res Ther.2020; 22(1):45. [23] NARANG RK, VINCENT Z, PHIPPS-GREEN A, et al. Population-specific factors associated with fractional excretion of uric acid. Arthritis Res Ther.2019;21(1):234. [24] DALBETH N, HOUSE ME, GAMBLE GD, et al. Population-specific influence of SLC2A9 genotype on the acute hyperuricaemic response to a fructose load. Ann Rheum Dis.2013;72(11):1868-1873. [25] HE W, PHIPPS-GREEN A, STAMP LK, et al. Population-specific association between ABCG2 variants and tophaceous disease in people with gout. Arthritis Res Ther.2017;19(1):43. [26] CHEN G, SHRINER D, DOUMATEY AP, et al. Refining genome-wide associated loci for serum uric acid in individuals with African ancestry. Hum Mol Genet.2020; 29(3): 506-514. [27] SUN YP, XU FL, YAN DD, et al. Association between SLC2A9 Genetic Variants and Risk of Hyperuricemia in a Uygur Population. Curr Med Sci.2019; 39(2): 243-249. [28] YANG X, XIAO Y, LIU K, et al. Prevalence of hyperuricemia among the Chinese population of the southeast coastal region and association with single nucleotide polymorphisms in urateanion exchanger genes: SLC22A12, ABCG2 and SLC2A9. Mol Med Rep.2018;18(3): 3050-3058. [29] DAS GUPTA E, SAKTHISWARY R, LEE S L, et al. Clinical significance of SLC2A9/GLUT9 rs11722228 polymorphisms in gout. Int J Rheum Dis.2018; 21(3): 705-709. [30] SUMA S, NAITO M, OKADA R, et al. ASSOCIATIONS BETWEEN BODY MASS INDEX AND SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS IN A JAPANESE POPULATION WERE SIGNIFICANTLY MODIFIED BY LRP2 rs2544390. Nagoya J Med Sci.2014;76(3-4): 333-339. [31] RIVERA-PAREDEZ B, MACIAS-KAUFFER L, FERNANDEZ-LOPEZ JC, et al. Influence of Genetic and Non-Genetic Risk Factors for Serum Uric Acid Levels and Hyperuricemia in Mexicans. Nutrients.2019;11(6): 1336. [32] ZHOU Z, WANG K, ZHOU J, et al. Amplicon targeted resequencing for SLC2A9 and SLC22A12 identified novel mutations in hypouricemia subjects. Mol Genet Genomic Med.2019;7(7): e00722. [33] TAN P K, FARRAR J E, GAUCHER E A, et al. Coevolution of URAT1 and Uricase during Primate Evolution: Implications for Serum Urate Homeostasis and Gout. Mol Biol Evol.2016;33(9): 2193-2200. [34] HIGASHINO T, MATSUO H, SAKIYAMA M, et al. Common variant of PDZ domain containing 1 (PDZK1) gene is associated with gout susceptibility: A replication study and meta-analysis in Japanese population.Drug Metab Pharmacokinet.2016; 31(6): 464-466. [35] MISAWA K, HASEGAWA T, MISHIMA E, et al. Contribution of Rare Variants of the SLC22A12 Gene to the Missing Heritability of Serum Urate Levels. Genetics.2020;214(4):1079-1090. [36] TIN A, LI Y, BRODY J A, et al. Large-scale whole-exome sequencing association studies identify rare functional variants influencing serum urate levels. Nat Commun.2018; 9(1): 4228. [37] ZOU Y, DU J, ZHU Y, et al. Associations between the SLC22A12 gene and gout susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Clin Exp Rheumatol.2018; 36(3):442-447. [38] IM SW, CHAE J, SON HY, et al. A population-specific low-frequency variant of SLC22A12 (p.W258*) explains nearby genome-wide association signals for serum uric acid concentrations among Koreans. PLoS One. 2020;15(4):e0231336. [39] CHO SK, KIM S, CHUNG JY, et al. Discovery of URAT1 SNPs and association between serum uric acid levels and URAT1 . BMJ Open. 2015;5(11):e009360. [40] SAKIYAMA M, MATSUO H, SHIMIZU S, et al. The effects of URAT1/SLC22A12 nonfunctional variants, R90H and W258X, on serum uric acid levels and gout/hyperuricemia progression. Sci Rep.2016; 6:20148. [41] LEE HA, PARK BH, PARK EA, et al. Long-term effects of the SLC2A9 G844A and SLC22A12 C246T variants on serum uric acid concentrations in children. BMC Pediatr.2018;18(1): 296. [42] DUONG NT, NGOC NT, THANG NTM, et al. Polymorphisms of ABCG2 and SLC22A12 Genes Associated with Gout Risk in Vietnamese Population. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019;55(1):8. [43] LI M, LI Q, LI C G, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in the PDZK1 gene and susceptibility to gout in male Han Chinese: a case-control study. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(8):13911-13918. [44] PHIPPS-GREEN AJ, MERRIMAN ME, TOPLESS R, et al. Twenty-eight loci that influence serum urate levels: analysis of association with gout. Ann Rheum Dis.2016;75(1):124-130. [45] IHARADA M, MIYAJI T, FUJIMOTO T, et al. Type 1 sodium-dependent phosphate transporter (SLC17A1 Protein) is a Cl(-)-dependent urate exporter. J Biol Chem.2010;285(34):26107-26113. [46] CHIBA T, MATSUO H, KAWAMURA Y, et al. NPT1/SLC17A1 Is a Renal Urate Exporter in Humans and Its Common Gain-of-Function Variant Decreases the Risk of Renal Underexcretion Gout. Arthritis Rheumatol.2015;67(1):281-287. [47] URANO W,TANIGUCHI A,ANZAI N,et al.Sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter type 1 sequence polymorphisms in male patients with gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69(6): 1232-1234. [48] HOLLIS-MOFFATT JE, PHIPPS-GREEN AJ, CHAPMAN B,et al. The renal urate transporter SLC17A1 locus: confirmation of association with gout. Arthritis Res Ther.2012;14(2): R92. [49] YANG Q, KOTTGEN A, DEHGHAN A, et al. Multiple genetic loci influence serum urate levels and their relationship with gout and cardiovascular disease risk factors. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.2010; 3(6): 523-530. [50] GIANESELLO L, CEOL M, BERTOLDI L, et al. Genetic Analyses in Dent Disease and Characterization of CLCN5 Mutations in Kidney Biopsies . Int J Mol Sci.2020; 21(2):516. [51] TIMMER T, TANCK MWT, HUIS IN ‘T VELD EMJ, et al. Associations between single nucleotide polymorphisms and erythrocyte parameters in humans: A systematic literature review. Mutat Res.2019; 779:58-67. [52] SAKIYAMA M, MATSUO H, NAGAMORI S, et al. Expression of a human NPT1/SLC17A1 missense variant which increases urate export. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2016;35(10-12):536-542. [53] ZHOU Z W, CUI L L, HAN L, et al. Polymorphisms in GCKR, SLC17A1 and SLC22A12 were associated with phenotype gout in Han Chinese males: a case-control study. BMC Med Genet.2015;16:66. [54] ROMAN YM, CULHANE-PERA KA, MENK J,et al. Assessment of genetic polymorphisms associated with hyperuricemia or gout in the Hmong. Per Med.2016;13(5): 429-440. [55] BHATNAGAR V, RICHARD EL, WU W, et al. Analysis of ABCG2 and other urate transporters in uric acid homeostasis in chronic kidney disease: potential role of remote sensing and signaling . Clin Kidney J.2016; 9(3): 444-453. [56] ZHANG K, LI C. ABCG2 gene polymorphism rs2231142 is associated with gout comorbidities but not allopurinol response in primary gout patients of a Chinese Han male population. Hereditas.2019;156:26. [57] ROMAN Y, TIIRIKAINEN M, PROM-WORMLEY E. The prevalence of the gout-associated polymorphism rs2231142 G>T in ABCG2 in a pregnant female Filipino cohort. Clin Rheumatol. 2020;39(8):2387-2392. [58] NAKASHIMA A, ICHIDA K, OHKIDO I, et al. Dysfunctional ABCG2 gene polymorphisms are associated with serum uric acid levels and all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients. Hum Cell. 2020 ;33(3): 559-568. [59] TAKADA T, YAMAMOTO T, MATSUO H, et al. Identification of ABCG2 as an Exporter of Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate in Mice and as a Crucial Factor Influencing CKD Progression. Sci Rep.2018; 8(1):11147. [60] DALBETH N, STAMP LK, MERRIMAN TR. The genetics of gout: towards personalised medicine?. BMC Med.2017;15(1):108. [61] RISTIC B, SIKDER MOF, BHUTIA YD, et al. Pharmacologic inducers of the uric acid exporter ABCG2 as potential drugs for treatment of gouty arthritis. Asian J Pharm Sci.2020;15(2):173-180. [62] LI G, HAN L, MA R, et al. Glucocorticoids Increase Renal Excretion of Urate in Mice by Downregulating Urate Transporter 1. Drug Metab Dispos. 2019;47(11):1343-1351. [63] OTANI N, OUCHI M, KUDO H, et al. Recent approaches to gout drug discovery: an update. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2020;15(8):943-954. [64] GRAHAM GG, STOCKER SL, KANNANGARA DRW, et al. Predicting Response or Non-response to Urate-Lowering Therapy in Patients with Gout. Curr Rheumatol Rep.2018; 20(8):47. [65] ROBERTS RL, WALLACE MC, PHIPPS-GREEN AJ, et al. ABCG2 loss-of-function polymorphism predicts poor response to allopurinol in patients with gout. Pharmacogenomics J. 2017;17(2):201-203. [66] WALLACE MC, ROBERTS RL, NANAVATI P, et al. Association between ABCG2 rs2231142 and poor response to allopurinol: replication and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford).2018; 57(4): 656-660. [67] LIN M, LIU J, ZHOU H, et al. Effects of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of febuxostat in healthy Chinese volunteers. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2017; 32(1): 77-84. [68] MINER JN, TAN PK, HYNDMAN D, et al. Lesinurad, a novel, oral compound for gout, acts to decrease serum uric acid through inhibition of urate transporters in the kidney. Arthritis Res Ther.2016; 18(1): 214. [69] YANG C, ZHOU D, SHEN Z, et al. Characterization of Stereoselective Metabolism, Inhibitory Effect on Uric Acid Uptake Transporters, and Pharmacokinetics of Lesinurad Atropisomers. Drug Metab Dispos. 2019;47(2): 104-113. [70] ALGHAMDI Y S, SOLIMAN M M, NASSAN M A. Impact of Lesinurad and allopurinol on experimental Hyperuricemia in mice: biochemical, molecular and Immunohistochemical study. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020;21(1): 10. [71] HOSOYA T, FURUNO K, KANDA S. A clinical pharmacology study of the novel, selective urate reabsorption inhibitor dotinurad in outpatients. Clin Exp Nephrol.2020;24(Suppl 1): 103-111. [72] HOSOYA T, FURUNO K, KANDA S. A non-inferiority study of the novel selective urate reabsorption inhibitor dotinurad versus febuxostat in hyperuricemic patients with or without gout. Clin Exp Nephrol.2020;24(Suppl 1):71-79. [73] LEE Y S, KIM S H, YUK H J, et al. DKB114, A Mixture of Chrysanthemum Indicum Linne Flower and Cinnamomum Cassia (L.) J. Presl Bark Extracts, Improves Hyperuricemia through Inhibition of Xanthine Oxidase Activity and Increasing Urine Excretion. Nutrients.2018;10(10): [74] LIN Y, LIU P G, LIANG W Q, et al. Luteolin-4’-O-glucoside and its aglycone, two major flavones of Gnaphalium affine D. Don, resist hyperuricemia and acute gouty arthritis activity in animal models. Phytomedicine.2018;41:54-61. [75] TASHIRO Y, SAKAI R, HIROSE-SUGIURA T, et al. Effects of Osthol Isolated from Cnidium monnieri Fruit on Urate Transporter 1. Molecules. 2018; 23(11):2837. [76] LEE SH, LEE HS, PARK G, et al. Dual actions on gout flare and acute kidney injury along with enhanced renal transporter activities by Yokuininto, a Kampo medicine . BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019; 19(1): 57. [77] LEE Y S, SUNG Y Y, YUK H J, et al. Anti-hyperuricemic effect of Alpinia oxyphylla seed extract by enhancing uric acid excretion in the kidney. Phytomedicine.2019; 62:152975. [78] WANG S, FANG Y, YU X, et al. The flavonoid-rich fraction from rhizomes of Smilax glabra Roxb. ameliorates renal oxidative stress and inflammation in uric acid nephropathy rats through promoting uric acid excretion.Biomed Pharmacother.2019; 111:162-168. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 张 超, 吕 欣. 髋臼骨折固定后的异位骨化:危险因素、预防及其治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [3] | 周继辉, 李新志, 周 游, 黄 卫, 陈文瑶. 髌骨骨折修复内植物选择的多重问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | 王德斌, 毕郑刚. 尺骨鹰嘴骨折-脱位解剖力学、损伤特点、固定修复及3D技术应用的相关问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [5] | 袁 美, 张新新, 郭祎莎, 毕 霞. 循环microRNA在血管性认知障碍诊断中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [6] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [7] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [8] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [9] | 赵 敏, 冯柳祥, 陈 垚, 顾 霞, 王平义, 李一梅, 李文华. 低氧环境下外泌体可作为疾病的标志物[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [10] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [11] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [12] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [13] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [14] | 曾燕华, 郝延磊. 许旺细胞体外培养及纯化的系统性综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [15] | 宋成杰, 常恒瑞, 石明鑫, 孟宪中. 侧方入路腰椎融合治疗后的生物力学稳定性的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
病理高尿酸血症指血清尿酸浓度高于408 μmol/L,高于此浓度时在生理pH值和温度下体外可形成单钠尿酸盐结晶。血清尿酸盐浓度的升高与环境因素及遗传因素相关[1]。环境因素包括摄入啤酒,肉类和海鲜等富含嘌呤的食物,摄入会增加嘌呤核苷酸降解的果糖,自身的体质量指数(BMI)过高以及有利尿药物服用史,最终导致尿酸产生过剩[14]。遗传因素对血清尿酸盐浓度变化的影响大于环境因素,主要是相关易感基因的单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphism,SNP)影响肾脏和肠道中尿酸盐转运蛋白的功能,造成尿酸排泄不足。
尿酸盐转运蛋白主要位于肾脏和肠道,负责调节人的血清尿酸水平,如近端小管细胞的基底外侧膜中的GLUT9蛋白和顶端膜中的URAT1介导肾尿酸重吸收。部分尿酸盐转运蛋白的多态性变体会增加血清尿酸盐水平和痛风风险,这些蛋白的基因多态性研究和药物相关性研究对于痛风的个体化高效治疗有重要意义。文章旨在探讨尿酸盐转运蛋白编码基因多态性和综述相关药物治疗的最新研究进展。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1.1 数据库 第一作者通过计算机检索CNKI、万方数据库和PubMed数据。
1.1.2 检索词 中文检索词:痛风、尿酸盐转运蛋白、高尿酸血症、基因多态性、治疗;英文检索词:Gout,Urate transporter,Hyperuricemia,Polymorphism,GWAS,Therapy。
1.1.3 检索词的逻辑组配 “痛风”与“尿酸盐转运蛋白”与“基因多态性”;“高尿酸血症”与“尿酸盐转运蛋白”与“基因多态性”;“痛风”与“尿酸盐转运蛋白”与“治疗”;“Gout” and“urate transporter”and“gene polymorphism”;“hyperuricemia” and “urate transporter”and “gene polymorphism”; “gout”and “urate transporter ” and “Treatment”;
1.1.4 检索的时间范围 2010至2020年发表的文献。
1.2 文献筛选标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与转运蛋白GLUT9,URAT1,NPT1和ABCG2在痛风的多态性表达相关的研究;②糖皮质激素、尿酸合成抑制剂、促尿酸盐排泄药、中药及其提取物等痛风药物与转运蛋白相关的研究。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与文章内容关联性弱、参考价值不高的文章;②重复的文献;③研究方法有明显漏洞、缺乏可靠论据的文章。
1.3 质量评估及数据的提取 计算机检索获得131篇文献,经过作者评价纳入文献的有效性和适用性,通过阅读文章题目和摘要初次筛选;排除重复性研究和无关文献,最后纳入78篇文献进行综述。文献检索流程图见图1。
在肾脏中,肾小球滤过的尿酸盐通过位于肾近曲小管基底外侧膜上的URAT1和GLUT9S有效地重新吸收回血流中,携带这些基因的功能丧失突变的个体具有部分尿酸重吸收缺陷,从而导致低尿酸血症。但值得注意的是,功能获得性突变可能诱发高尿酸血症。这些新发现可能有帮助评估高尿酸血症患者的痛风风险,并为基因治疗提供理想的线索。最近的研究表明,GLUT9可能也是高尿酸血症和痛风的有希望的治疗靶标。另一方面,BCRP和NPT1参与了尿酸的分泌,这些转运蛋白的SNP功能异常可能导致尿酸排泄减少,从而引起高尿酸血症和痛风。与此同时,某些功能获得性突变[例如NPT1中的rs1165196(I269T)]会导致尿酸排泄增加,这在肾分泌不足痛风的发生中起促进作用。这提示通过激活BCRP增强肠道对尿酸的清除来治疗高尿酸血症可能是一种可行方案。从以上分析和综述中可以容易地推断出,尿酸转运蛋白的多态性对尿酸的稳态具有重要作用。
此次综述还进一步证明,快速进步的技术和针对疾病的遗传发现使得个性化的药物治疗在痛风管理中成为现实。如ABCG2基因型为r2231142的痛风患者采取别嘌醇治疗的有效率低且不良反应的发生率高,野生型的应用效果则较好。另外还可以根据痛风患者的尿酸盐转运蛋白功能异常类型,个性化地选择针对ABCG2、URAT1、GLUT9、OAT1等蛋白特异反应的药物。尽管通过全基因组关联研究已经取得了重大进展,但仍然需要大型、特征明确的数据集来丰富数据,完善不同的疾病状态、药理学(包括剂量信息,治疗反应,药物不良反应)和生活方式等信息。为了避免增加痛风治疗中已经明显的差异,对不同人群的研究至关重要,尤其是对于那些患有严重疾病的人群而言。
总之,尿酸盐转运蛋白编码多态性的研究是复杂且技术密集的,所以仍有大量工作要做。随着分子生物学技术的不断发展,未来将进一步发展以阐明高尿酸血症和其他代谢紊乱的遗传基础。肾脏和肾外组织中尿酸转运行为和基因多态性的研究不仅对了解尿酸转运机制具有重要意义,而且在基因水平上更准确地指出与尿酸有关的疾病的发病机制,这可能提供他们个性化临床管理和治疗指导。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程

文题释义:#br# 全基因组关联研究(Genome-Wide Association Studies,GWAS):是指在全基因组层面上,开展多中心、大样本、反复验证的基因与疾病的关联研究,是通过对大规模的群体DNA样本进行全基因组高密度遗传标记(如SNP或CNV等)分型,从而寻找与复杂疾病相关的遗传因素的研究方法,全面揭示疾病发生、发展与治疗相关的遗传基因。#br# 尿酸盐转运蛋白:主要位于肾脏和肠道,负责调节人的血清尿酸水平。如近端小管细胞的基底外侧膜中的GLUT9和顶端膜中的URAT1介导肾尿酸重吸收。部分尿酸盐转运蛋白的变体会增加血清尿酸盐水平和痛风风险,这些蛋白的基因多态性研究和药物相关性研究对于痛风的个体化高效治疗有重要意义。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程痛风是一组遗传性或获得性嘌呤代谢紊乱和(或)尿酸排泄障碍所致的综合征,临床表现主要是关节部位出现的疼痛、水肿、红肿和炎症。痛风主要病理学特征是在尿酸浓度逐渐升高的条件下尿酸钠结晶的慢性沉积,单钠尿酸盐沉积的形成依赖高尿酸血症,而血清尿酸盐浓度的升高受到环境因素及遗传因素的影响,且后者更为重要,直接影响了肠道和肾脏对尿酸的代谢过程。高尿酸血症患者是否会出现痛风以及最佳治疗方案仍需进一步研究。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||