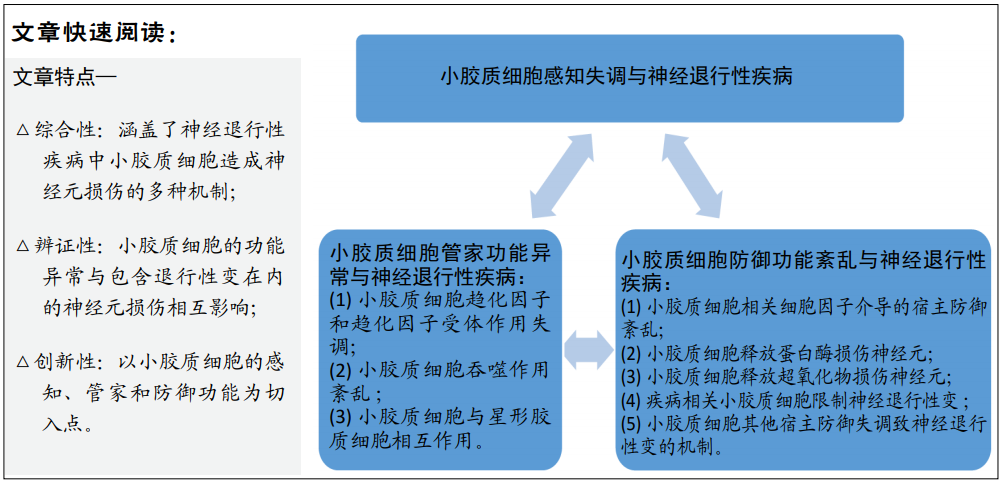
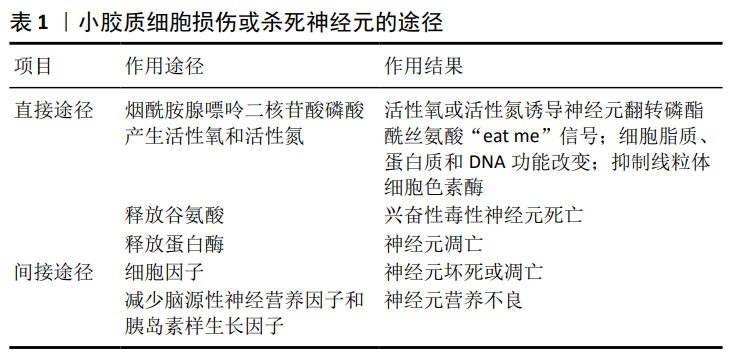
[1] HICKMAN S, IZZY S, SEN P, et al. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci. 2018; 21(10): 1359-1369.
[2] BEGGS S, SALTER MW. SnapShot: microglia in disease. Cell. 2016; 165(5): 1294-1294.e1.
[3] BRIGHT F, WERRY EL, DOBSON-STONE C, et al. Neuroinflammation in frontotemporal dementia. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(9): 540-555.
[4] BIBER K, OWENS T, BODDEKE E. What is microglia neurotoxicity (not). Glia. 2014; 62(6): 841-854.
[5] DECZKOWSKA A, KEREN-SHAUL H, WEINER A, et al. Disease-associated microglia: a universal immune sensor of neurodegeneration. Cell. 2018; 173(5): 1073-1081.
[6] VIOLA KL, KLEIN WL. Amyloid beta oligomers in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis, treatment, and diagnosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2015; 129(2): 183-206.
[7] BROWN GC, VILALTA A. How microglia kill neurons. Brain Res. 2015; 1628(Pt B): 288-297.
[8] CRUZ HERNÁNDEZ JC, BRACKO O, KERSBERGEN CJ, et al. Neutrophil adhesion in brain capillaries reduces cortical blood flow and impairs memory function in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Nat Neurosci. 2019; 22(3): 413-420.
[9] DRUMMOND RA, SWAMYDAS M, OIKONOMOU V, et al. CARD9(+) microglia promote antifungal immunity via IL-1beta- and CXCL1-mediated neutrophil recruitment. Nat Immunol. 2019; 20(5): 559-570.
[10] SPANGENBERG EE, LEE RJ, NAJAFI AR, et al. Eliminating microglia in Alzheimer’s mice prevents neuronal loss without modulating amyloid-beta pathology. Brain. 2016; 139(Pt 4): 1265-1281.
[11] PARAJULI B, HORIUCHI H, MIZUNO T, et al. CCL11 enhances excitotoxic neuronal death by producing reactive oxygen species in microglia. Glia. 2015; 63(12): 2274-2284.
[12] ZHU C, XU B, SUN X, et al. Targeting CCR3 to reduce amyloid-β production, tau hyperphosphorylation, and synaptic loss in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2017; 54(10): 7964-7978.
[13] EL KHOURY JB, MOORE KJ, MEANS TK, et al. CD36 mediates the innate host response to beta-amyloid. J Exp Med. 2003; 197(12): 1657-1666.
[14] ORIGLIA N, BONADONNA C, ROSELLINI A, et al. Microglial receptor for advanced glycation end product-dependent signal pathway drives beta-amyloid-induced synaptic depression and long-term depression impairment in entorhinal cortex. J Neurosci. 2010; 30(34): 11414-11425.
[15] GE X, ZHANG DM, LI MM, et al. Microglial LOX-1/MAPKs/NF-kappaB positive loop promotes the vicious cycle of neuroinflammation and neural injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019; 70: 187-200.
[16] CORNEJO F, VRUWINK M, METZ C, et al. Scavenger Receptor-A deficiency impairs immune response of microglia and astrocytes potentiating Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. Brain Behav Immun. 2018; 69: 336-350.
[17] GRICIUC A, PATEL S, FEDERICO AN, et al. TREM2 acts downstream of CD33 in modulating microglial pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2019; 103(5): 820-835.e7.
[18] WANG Y, ULLAND TK, ULRICH JD, et al. TREM2-mediated early microglial response limits diffusion and toxicity of amyloid plaques. J Exp Med. 2016; 213(5): 667-675.
[19] SONG WM, JOSHITA S, ZHOU Y, et al. Humanized TREM2 mice reveal microglia-intrinsic and -extrinsic effects of R47H polymorphism. J Exp Med. 2018; 215(3): 745-760.
[20] LEE CYD, DAGGETT A, GU X, et al. Elevated TREM2 gene dosage reprograms microglia responsivity and ameliorates pathological phenotypes in Alzheimer’s disease models. Neuron. 2018; 97(5): 1032-1048. e5.
[21] SCHLEPCKOW K, KLEINBERGER G, FUKUMORI A, et al. An Alzheimer-associated TREM2 variant occurs at the ADAM cleavage site and affects shedding and phagocytic function. EMBO Mol Med. 2017; 9(10): 1356-1365.
[22] ZHONG L, XU Y, ZHUO R, et al. Soluble TREM2 ameliorates pathological phenotypes by modulating microglial functions in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Nat Commun. 2019; 10(1): 1365.
[23] BOLAND B, YU WH, CORTI O, et al. Promoting the clearance of neurotoxic proteins in neurodegenerative disorders of ageing. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018; 17(9): 660-688.
[24] LEE EB, LEE VM, TROJANOWSKI JQ. Gains or losses: molecular mechanisms of TDP43-mediated neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011; 13(1): 38-50.
[25] PAOLICELLI RC, JAWAID A, HENSTRIDGE CM, et al. TDP-43 depletion in microglia promotes amyloid clearance but also induces synapse loss. Neuron. 2017; 95(2): 297-308.e6.
[26] TAKAHASHI H, KLEIN ZA, BHAGAT SM, et al. Opposing effects of progranulin deficiency on amyloid and tau pathologies via microglial TYROBP network. Acta Neuropathol. 2017; 133(5): 785-807.
[27] LUI H, ZHANG J, MAKINSON SR, et al. Progranulin deficiency promotes circuit-specific synaptic pruning by microglia via complement activation. Cell. 2016; 165(4): 921-935.
[28] LEMKE G. How macrophages deal with death. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019; 19(9): 539-549.
[29] HONG S, BEJA-GLASSER VF, NFONOYIM BM, et al. Complement and microglia mediate early synapse loss in Alzheimer mouse models. Science. 2016; 352(6286): 712-716.
[30] KIM T, VIDAL GS, DJURISIC M, et al. Human LilrB2 is a beta-amyloid receptor and its murine homolog PirB regulates synaptic plasticity in an Alzheimer’s model. Science. 2013; 341(6152): 1399-1404.
[31] LEE H, BROTT BK, KIRKBY LA, et al. Synapse elimination and learning rules co-regulated by MHC class I H2-Db. Nature. 2014; 509(7499): 195-200.
[32] GUNNER G, CHEADLE L, JOHNSON KM, et al. Sensory lesioning induces microglial synapse elimination via ADAM10 and fractalkine signaling. Nat Neurosci. 2019; 22(7): 1075-1088.
[33] LIU Z, CONDELLO C, SCHAIN A, et al. CX3CR1 in microglia regulates brain amyloid deposition through selective protofibrillar amyloid-β phagocytosis. J Neurosci. 2010; 30(50): 17091-17101.
[34] RIVEST S. A ‘don’t eat me’ immune signal protects neuronal connections. Nature. 2018; 563(7729): 42-43.
[35] WANG J, DING X, WU X, et al. SIRPalpha deficiency accelerates the pathologic process in models of Parkinson disease. Glia. 2019; 67(12): 2343-2359.
[36] VARNUM MM, KIYOTA T, INGRAHAM KL, et al. The anti-inflammatory glycoprotein, CD200, restores neurogenesis and enhances amyloid phagocytosis in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2015; 36(11): 2995-3007.
[37] HECKMANN BL, TEUBNER BJW, TUMMERS B, et al. LC3-associated endocytosis facilitates β-amyloid clearance and mitigates neurodegeneration in murine Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell. 2019; 178(3): 536-551.e14.
[38] KUTER K, OLECH L, GLOWACKA U. Prolonged dysfunction of astrocytes and activation of microglia accelerate degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the rat substantia nigra and block compensation of early motor dysfunction induced by 6-OHDA. Mol Neurobiol. 2018; 55(4): 3049-3066.
[39] JOSHI AU, MINHAS PS, LIDDELOW SA, et al. Fragmented mitochondria released from microglia trigger A1 astrocytic response and propagate inflammatory neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci. 2019; 22(10): 1635-1648.
[40] GLASS CK, SAIJO K, WINNER B, et al. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell. 2010; 140(6): 918-934.
[41] CHRISTOFFERSON DE, LI Y, YUAN J. Control of life-or-death decisions by RIP1 kinase. Annu Rev Physiol. 2014; 76(1): 129-150.
[42] YE L, HUANG Y, ZHAO L, et al. IL-1β and TNF-α induce neurotoxicity through glutamate production: a potential role for neuronal glutaminase. J Neurochem. 2013; 125(6): 897-908.
[43] MCNAMEE EN, RYAN KM, KILROY D, et al. Noradrenaline induces IL-1ra and IL-1 type II receptor expression in primary glial cells and protects against IL-1beta-induced neurotoxicity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010; 626 (2-3): 219-228.
[44] FERRO A, SHEELER C, CVETANOVIC M. Microglial self-recognition STINGs in A-T neurodegeneratio. Trends Neurosci. 2019; 42(11): 753-755.
[45] 石成奎,陈志强.小胶质细胞对中脑多巴胺能神经元铁代谢的影响及其机制:体外细胞学实验方案[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(8):1262-1267.
[46] NAZMI A, FIELD RH, GRIFFIN EW, et al. Chronic neurodegeneration induces type I interferon synthesis via STING, shaping microglial phenotype and accelerating disease progression. Glia. 2019; 67(7): 1254-1276.
[47] SWANSON KV, DENG M, TING JP. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019; 19(8): 477-489.
[48] GOLDMANN T, TAY TL, PRINZ M. Love and death: microglia, NLRP3 and the Alzheimer’s brain. Cell Res. 2013; 23(5): 595-596.
[49] ISING C, VENEGAS C, ZHANG S, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation drives tau pathology. Nature. 2019; 575(7784): 669-673.
[50] HENEKA MT, KUMMER MP, STUTZ A, et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature. 2013; 493(7434): 674-678.
[51] BROWN GC. Nitric oxide and neuronal death. Nitric Oxide. 2010; 23(3): 153-165.
[52] BAL-PRICE A, BROWN GC. Inflammatory neurodegeneration mediated by nitric oxide from activated glia-inhibiting neuronal respiration, causing glutamate release and excitotoxicity. J Neurosci. 2001; 21(17): 6480-6491.
[53] 陆明佳,王珊珊,朱沂.小胶质细胞介导帕金森病小鼠的氧化应激损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(11):2001-2006.
[54] SWEENEY MD, SAGARE AP, ZLOKOVIC BV. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018; 14(3): 133-150.
[55] LOU N, TAKANO T, PEI Y, et al. Purinergic receptor P2RY12-dependent microglial closure of the injured blood-brain barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016; 113(4): 1074-1079.
[56] LENG Y, MUSIEK ES, HU K, et al. Association between circadian rhythms and neurodegenerative diseases. Lancet Neurol. 2019; 18(3): 307-318.
[57] ERNY D, HRABE DE ANGELIS AL, JAITIN D, et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat Neurosci. 2015; 18(7): 965-977.
[58] D’ARGENIO V, SARNATARO D. Microbiome Influence in the Pathogenesis of Prion and Alzheimer’s Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4704.
[59] KIERDORF K, MASUDA T, JORDÃO MJC, et al. Macrophages at CNS interfaces: ontogeny and function in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019; 20(9): 547-562.
[60] HAMMOND TR, MARSH SE, STEVENS B. Immune signaling in neurodegeneration. Immunity. 2019; 50(4): 955-974. |