[1] LEES RA, HENDRY BAK, BROOMFIELD N, et al. Cognitive assessment in stroke: feasibility and test properties using differing approaches to scoring of incomplete items. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2017;32(10):1072-1078.
[2] HILAL S, XU X, IKRAM MK, et al. Intracranial stenosis in cognitive impairment and dementia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37(6):2262-2269.
[3] PISCOPO P, LACORTE E, FELIGIONI M, et al. MicroRNAs and mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. 2019;50:131-141.
[4] HANSEN KF, KARELINA K, SAKAMOTO K, et al. MiRNA-132: a dynamic regulator of cognitive capacity. Brain Struct Funct. 2013;218(3):817-831.
[5] HUANG S, ZHAO J, HUANG D, et al. Serum miR-132 is a risk marker of post-stroke cognitive impairment. Neurosci Lett. 2016;615:102-106.
[6] YANG FW, WANG H, WANG C, et al. Upregulation of acetylcholinesterase caused by downregulation of microRNA-132 is responsible for the development of dementia after ischemic stroke. J Cell Biochem. 2020; 121(1):135-141.
[7] 徐珊珊,曾友华,包烨华.针灸通督法联合黄连温胆汤对脑卒中患者外周血miR-132、miR-134的影响[J].中国现代医生,2019,57(24):137-140, 144.
[8] STARY CM, SUN X, OUYANG Y, et al. miR-29a differentially regulates cell survival in astrocytes from cornu ammonis 1 and dentate gyrus by targeting VDAC1. Mitochondrion. 2016;30:248-254.
[9] RAGUSA M, BOSCO P, TAMBURELLO L, et al. miRNAs plasma profiles in vascular dementia: biomolecular data and biomedical implications. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10:51.
[10] BARBAGALLO C, MOSTILE G, BAGLIERI G, et al. Specific signatures of serum mirnas as potential biomarkers to discriminate clinically similar neurodegenerative and vascular-related diseases. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2019; 40(4):531-546
[11] ZHENG Y, WANG L, CHEN M, et al. Upregulation of miR-130b protects against cerebral ischemic injury by targeting water channel protein aquaporin 4 (AQP4). Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(7):3452-3461.
[12] WANG P, LIANG X, LU Y, et al. MicroRNA-93 downregulation ameliorates cerebral ischemic injury through the Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(10):2627-2635.
[13] 周凡萍,人血清microRNAs作为脑卒中后认知功能障碍生物标志物的研究[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2018.
[14] 黄墩兵,谷诗浓,王振杰,等.miR-93-5p联合BDNF蛋白检测卒中后认知功能障碍的诊断价值[J].按摩与康复医学,2019,10(9):44-47.
[15] DONG H, LI J, HUANG L, et al. Serum MicroRNA Profiles Serve as Novel Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Dis Markers. 2015; 2015:625659.
[16] DAS S, FERLITO M, KENT OA, et al. Nuclear miRNA regulates the mitochondrial genome in the heart. Circ Res. 2012;110(12):1596-1603.
[17] 张仕娟,刘月华,李乃坤,等.急性脑梗死患者血清miR-181c水平与认知功能受损的关系[J].山东医药,2016,56(38):90-92.
[18] 闫小菊,张羽,李勇,等.血清微小RNA-181c、甲基乙二醛和25羟基维生素D_3水平在评估老年高血压患者发生认知功能障碍中的价值[J].中华高血压杂志,2019,27(12):1137-1142.
[19] CHEN YL SHEN CK. Modulation of mGluR-dependent MAP1B translation and AMPA receptor endocytosis by microRNA miR-146a-5p. J Neurosci. 2013;33(21):9013-9020.
[20] 董瑞,许鑫,陆雅媛,等.术后认知功能障碍小鼠miR-146a表达的变化[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2017,33(10):1016-1020.
[21] MULLER M, KUIPERIJ HB, CLAASSEN JA, et al. MicroRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease: differential expression in hippocampus and cell-free cerebrospinal fluid. Neurobiol Aging. 2014;35(1):152-158.
[22] MARCHEGIANI F, MATACCHIONE G, RAMINI D, et al. Diagnostic performance of new and classic CSF biomarkers in age-related dementias. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(8):2420-2429.
[23] YASMEEN S, KAUR S, MIRZA AH, et al. miRNA-27a-3p and miRNA-222-3p as Novel Modulators of Phosphodiesterase 3a (PDE3A) in Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(8):5304-5314.
[24] OUYANG Y, LI D, WANG H, et al. MiR-21-5p/dual-specificity phosphatase 8 signalling mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of haem oxygenase-1 in aged intracerebral haemorrhage rats. Aging Cell. 2019;18(6):e13022.
[25] 欧阳烨彤.miR-21-5p在自发性脑出血患者血清中的表达及其与预后关系的研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2019.
[26] ZHOU J, ZHANG J. Identification of miRNA-21 and miRNA-24 in plasma as potential early stage markers of acute cerebral infarction. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10(2):971-976.
[27] SORENSEN SS, NYGAARD ABCHRISTENSEN T. miRNA expression profiles in cerebrospinal fluid and blood of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia - an exploratory study. Transl Neurodegener. 2016;5:6.
[28] 林洋,芮耀诚.脑缺血大鼠脑组织及血浆中microRNA-124a表达的变化[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2011,8(3):143-147.
[29] PONOMAREV ED, VEREMEYKO T, BARTENEVA N, et al. MicroRNA-124 promotes microglia quiescence and suppresses EAE by deactivating macrophages via the C/EBP-alpha-PU.1 pathway. Nat Med. 2011;17(1):64-70.
[30] SUN M, HOU X, REN G, et al. Dynamic changes in miR-124 levels in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Int J Neurosci. 2019;129(7):649-653.
[31] RAJASETHUPATHY P, FIUMARA F, SHERIDAN R, et al. Characterization of small RNAs in Aplysia reveals a role for miR-124 in constraining synaptic plasticity through CREB. Neuron. 2009;63(6):803-817.
[32] MALMEVIK J, PETRI R, KNAUFF P, et al. Distinct cognitive effects and underlying transcriptome changes upon inhibition of individual miRNAs in hippocampal neurons. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19879.
[33] MIAO W, BAO T-H, HAN J-H, et al. Neuroprotection induced by post-conditioning following ischemia/reperfusion in mice is associated with altered microRNA expression. Mol Med Report. 2016;14(3):2582-2588.
[34] YANG TT, LIU CG, GAO SC, et al. The Serum Exosome Derived MicroRNA-135a, -193b, and -384 Were Potential Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers. Biomed Environ Sci. 2018;31(2):87-96.
[35] PRABHAKAR P, CHANDRA SRCHRISTOPHER R. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for the identification of vascular dementia due to cerebral small vessel disease. Age Ageing. 2017;46(5):861-864.
[36] MA W, FU Q, ZHANG Y, et al. A Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism in 3’-Untranslated Region of Endothelin-1 Reduces Risk of Dementia After Ischemic Stroke. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:1368-1374.
[37] HU XL, WANG XX, ZHU YM, et al. MicroRNA-132 regulates total protein of Nav1.1 and Nav1.2 in the hippocampus and cortex of rat with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Behav Brain Res. 2019;366:118-125.
[38] OUYANG Y, LI D, WANG H, et al. MiR-21-5p/dual-specificity phosphatase 8 signalling mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of haem oxygenase-1 in aged intracerebral haemorrhage rats. Aging Cell. 2019;18(6):e13022.
[39] TOYAMA K, SPIN JM, DENG AC, et al. MicroRNA-Mediated Therapy Modulating Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption Improves Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38(6):1392-1406.
[40] VAN DEN BERG MMJ, KRAUSKOPF J, RAMAEKERS JG, et al. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Neurobiol. 2020;185:101732.
[41] WANG Z, LU G, SZE J, et al. Plasma miR-124 Is a Promising Candidate Biomarker for Human Intracerebral Hemorrhage Stroke. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(7):5879-5888.
[42] TSAI PC, LIAO YC, WANG YS, et al. Serum microRNA-21 and microRNA-221 as potential biomarkers for cerebrovascular disease. J Vasc Res. 2013;50(4): 346-354. |
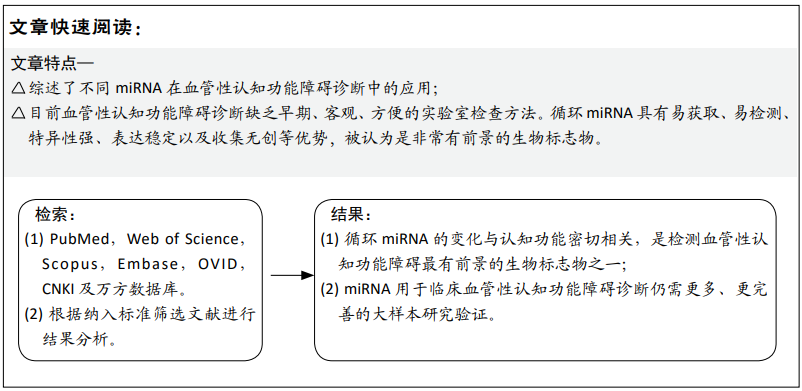

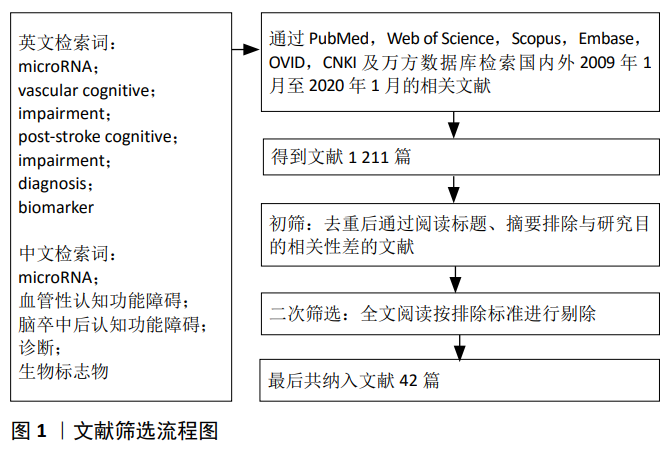
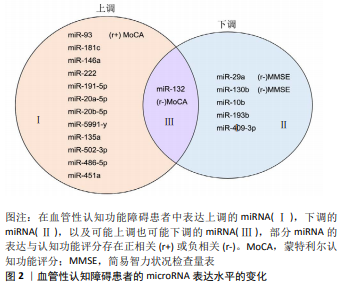 现有研究中循环microRNA在血管性认知功能障碍中的差异性表达方向不一致,有些表现为上调,有些表现为下调,或者无显著性差异,见表1。分析原因可能如下:第一,样本来源的不同,目前用于检测血管性认知功能障碍中循环microRNA差异性表达的样本主要来自于血清、血浆和脑脊液,Van DEN BERG等[40]报道microRNA在不同体液中的表达并无显著的相关性,甚至表达相反,可见不同体液样本的microRNA的表达并没有必然的联系;第二,样本采集时间的不同。脑出血损伤后,miR-124在24 h内的表达显著上调100倍,而后逐渐下降,在第30天可达正常健康人的表达水平[41],可见部分microRNA只在早期特异性表达,在后期和正常人群无显著性差异,在病程的不同时期microRNA的表达有不同的表达特点;第三,血管性认知功能障碍的纳入标准存在较大差异。不同的病因可导致microRNA的表达不同,例如,血清miR-21的表达在出血性脑卒中中显著上调[24],而在缺血性脑卒中则发现显著下调[42];第四,目前研究普遍样本量小,得到的结果需要在更大样本的研究中验证。
现有研究中循环microRNA在血管性认知功能障碍中的差异性表达方向不一致,有些表现为上调,有些表现为下调,或者无显著性差异,见表1。分析原因可能如下:第一,样本来源的不同,目前用于检测血管性认知功能障碍中循环microRNA差异性表达的样本主要来自于血清、血浆和脑脊液,Van DEN BERG等[40]报道microRNA在不同体液中的表达并无显著的相关性,甚至表达相反,可见不同体液样本的microRNA的表达并没有必然的联系;第二,样本采集时间的不同。脑出血损伤后,miR-124在24 h内的表达显著上调100倍,而后逐渐下降,在第30天可达正常健康人的表达水平[41],可见部分microRNA只在早期特异性表达,在后期和正常人群无显著性差异,在病程的不同时期microRNA的表达有不同的表达特点;第三,血管性认知功能障碍的纳入标准存在较大差异。不同的病因可导致microRNA的表达不同,例如,血清miR-21的表达在出血性脑卒中中显著上调[24],而在缺血性脑卒中则发现显著下调[42];第四,目前研究普遍样本量小,得到的结果需要在更大样本的研究中验证。 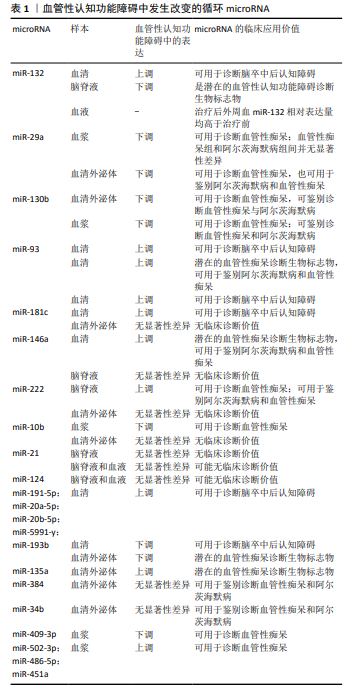 综上所述,循环microRNA可能是血管性认知功能障碍最有前景的诊断用新型生物标志物之一,但要确切诊断,仍然需要更多大样本、高质量的实验研究和临床试验结果来验证。同时,文章认为发掘更多在血管性认知功能障碍中特异性差异表达的microRNA,确定microRNA最佳的联合诊断方案,明确microRNA与样本种类、疾病病程及各血管性痴呆亚型之间的关系等是未来有待解决的研究方向。
综上所述,循环microRNA可能是血管性认知功能障碍最有前景的诊断用新型生物标志物之一,但要确切诊断,仍然需要更多大样本、高质量的实验研究和临床试验结果来验证。同时,文章认为发掘更多在血管性认知功能障碍中特异性差异表达的microRNA,确定microRNA最佳的联合诊断方案,明确microRNA与样本种类、疾病病程及各血管性痴呆亚型之间的关系等是未来有待解决的研究方向。