中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 1096-1103.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2126
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景
廖成成1,安家兴2,谭张雪1,王 倩3,刘建国1,3
- 1遵义医科大学口腔医学院,贵州省遵义市 563000;2遵义医科大学附属医院消化内科,贵州省遵义市 563000;3贵州省高等学校口腔疾病研究特色重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563000
-
收稿日期:2020-02-17修回日期:2020-02-25接受日期:2020-03-20出版日期:2021-03-08发布日期:2020-12-09 -
通讯作者:王倩,博士,副教授,贵州省高等学校口腔疾病研究特色重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563000 刘建国,博士,教授,遵义医科大学口腔医学院,贵州省遵义市 563000;贵州省高等学校口腔疾病研究特色重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563000 -
作者简介:廖成成,男,1995年生,浙江省江山市人,汉族,遵义医科大学在读硕士,主要从事头颈部鳞状细胞癌的研究。 -
基金资助:遵义医学院优秀青年人才项目(17zy-002);贵州省普通高等学校科技拔尖人才资助项目[黔教合KY(2016) 080];贵州省第六批人才基地《贵州省人才基地——医用生物材料研发》建设项目(RCJD2019-9)
Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells
Liao Chengcheng1, An Jiaxing2, Tan Zhangxue1, Wang Qian3, Liu Jianguo1, 3
- 1School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Gastroenterology, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 3Special Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research, Higher Education Institution in Guizhou Province, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2020-02-17Revised:2020-02-25Accepted:2020-03-20Online:2021-03-08Published:2020-12-09 -
Contact:Wang Qian, MD, Associate professor, Special Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research, Higher Education Institution in Guizhou Province, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China Liu Jianguo, MD, Professor, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Special Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research, Higher Education Institution in Guizhou Province, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Liao Chengcheng, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Outstanding Young Talent Project of Zunyi Medical University, No. 17zy-002; the Science and Technology Top Talent Support Project of Colleges and Universities in Guizhou Province, No. QIANJIAOHE KY(2016) 080; the Sixth Talent Foundation in Guizhou Province, No. RCJD2019-9
摘要:
文题释义:
口腔鳞状细胞癌:是最常见的口腔肿瘤,吸烟、饮酒和咀嚼槟榔是导致其发病的常见危险因素。在中国湖南等省份发病率较高,多见于40-60岁的成年男性,手术是其主要治疗方法。口腔鳞状细胞癌常常向区域淋巴结转移,晚期可发生远处转移,患者5年生存率较低。
肿瘤干细胞:是肿瘤细胞中数量较少的一类细胞,具有自我更新和分化为不同类型肿瘤细胞的能力。肿瘤干细胞对肿瘤的存活、增殖、转移及复发有着重要作用。从本质上讲,肿瘤干细胞通过自我更新和无限增殖维持着肿瘤细胞群的生命力。因此靶向干预肿瘤干细胞是治疗肿瘤的有效方法,也是目前肿瘤干细胞研究的热点之一。
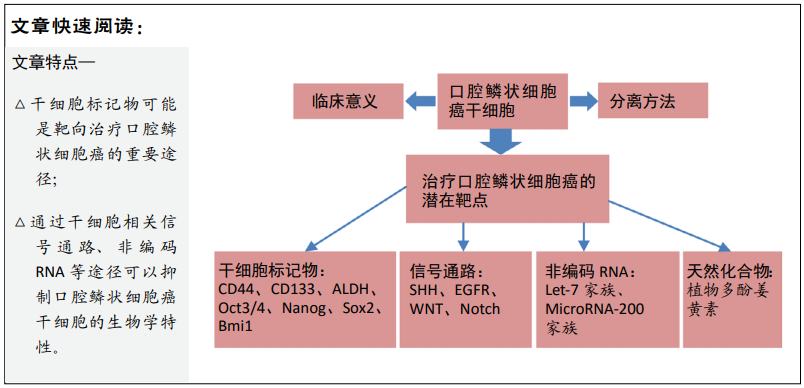
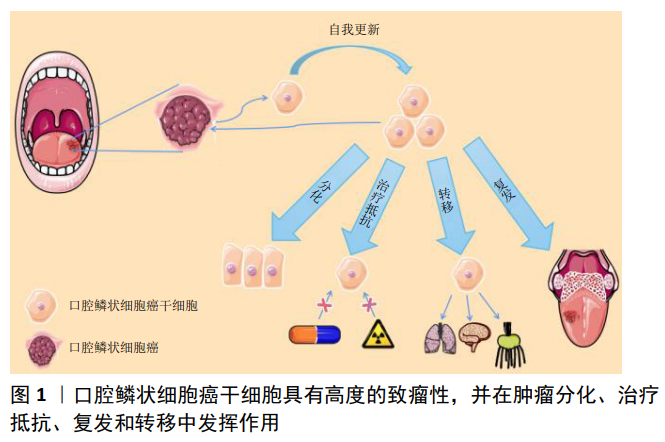
背景:肿瘤干细胞是肿瘤细胞中数量较少的一类细胞,具有自我更新和分化为不同类型肿瘤细胞的能力。口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞具有高度的致瘤性,并在肿瘤分化、治疗抵抗、复发和转移中发挥作用,同时肿瘤干细胞与正常干细胞具有极大的相似性,因此有必要建立有效、准确的肿瘤干细胞鉴定方法,设计对应的靶向治疗策略,这有助于口腔鳞状细胞癌患者的预后。
目的:总结目前文献中用于鉴定、分离口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的方法,分析针对口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞进行治疗的潜在靶点,并总结这些潜在靶点的研究进展。
方法:运用计算机检索中国期刊全文数据库和PubMed数据库,纳入建库以来至2020年发表的相关文献。检索英文关键词为“oral squamous cell carcinoma,OSCC,cancer stem cells,HNSCC,head and neck squamous carcinoma cell”,中文检索词为“口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞,口腔鳞状细胞癌,肿瘤干细胞,头颈部鳞状细胞癌”。对检索结果进行系统的归纳、总结和分析,并排除相关性低、重复文献和陈旧文献。
结果与结论:靶向干预口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞具有重要的临床意义。CD44、CD133和ALDH是目前最合适的鉴别、分离口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的生物标记物,与Oct3/4、Nanog、Sox2、Bmi1、EGFR信号通路、SHH信号通路、Notch信号通路、Wnt信号通路、Let-7家族、MicroRNA-200家族和天然化合物一起作为靶向治疗口腔鳞状细胞癌的潜在靶点。
中图分类号:
引用本文
廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103.
Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103.
肿瘤干细胞对现有的治疗方法通常表现出抗性,针对肿瘤干细胞的口腔癌治疗方法可能是一种新的途径[10]。目前,大多数肿瘤的治疗策略建立在传统的观点上,即肿瘤是由具有增殖潜能的细胞亚群引起的,治疗的首要策略包括手术切除等[11],然而肿瘤干细胞在手术治疗时可能已经转移,这些细胞对手术治疗乃至放化疗有着抵抗机制,在口腔鳞状细胞癌的转移和复发中起着重要的作用[12]。因此,针对口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞设计靶向治疗有着重要的临床意义。
2.2 分离口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的方法
2.2.1 体外分离口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的方法 主要有3种:①基于细胞表面标记(如CD44)表达的荧光激活细胞分选;②根据乙醛脱氢酶活性分离;③在非附着培养条件下进行肿瘤细胞成球实验[13]。
2.2.2 体内分离口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的方法 肿瘤干细胞是对肿瘤生长至关重要的癌细胞亚群,明确肿瘤干细胞在癌组织中的自然生态位对于理解它们的调控作用是很重要的。近年来,遗传谱系工具被应用于体内肿瘤干细胞的研究,最广泛使用的谱系追踪方法是 Cre-lox系统,其中Cre重组酶的表达由细胞特异性启动子驱动[14]。通过这种方法对研究癌症内环境稳定中的细胞层次结构非常有用。CHEN等[15]在致癌物诱导的未受干扰的头颈部鳞状细胞癌内对肿瘤细胞进行了克隆追踪,他们发现Bmi1+肿瘤干细胞参与了头颈部鳞状细胞癌的发生、发展和转移,有趣的是顺铂可以有效杀死增殖细胞,但不能杀死Bmi1+肿瘤干细胞,这可能是头颈部鳞状细胞癌复发的原因;Rosa26DTA小鼠在Bmi1+肿瘤干细胞消融后其肿瘤能力明显减弱。此外,在小鼠皮肤鳞状细胞癌模型中,通过Cre-lox系统发现表达转化生长因子β的肿瘤细胞负责加速肿瘤的生长[16]。
尽管这些小鼠模型有助于在体内研究肿瘤干细胞的表征,但小鼠和人类之间存在着差异。小鼠和人体内的一些细胞因子在功能上并不相同,这两个物种对肿瘤干细胞的调节可能遵循不同的方案。
2.3 治疗口腔鳞状细胞癌的可能靶点 在口腔癌分级的基础上,需要考虑肿瘤干细胞亚群的特性才能获得成功的癌症治疗,同时使用旨在消除肿瘤干细胞以降低肿瘤再生能力的方法可能会增强其他治疗的效果。
目前,发展肿瘤干细胞特异性治疗的努力正在不断增加。为了杀灭肿瘤干细胞,研究人员已经探索了多种分子靶点,如信号通路、细胞表面分子、凋亡途径、microRNA、干细胞标志物等[17]。通过调节这些靶点,可以消除肿瘤干细胞群,并有助于癌症治疗。此外天然化合物靶向肿瘤干细胞的研究也在逐渐增加,部分天然化合物具有毒性低、易获得、成本低廉等优点,在辅助放化疗等传统肿瘤治疗手段有着独特的优势。
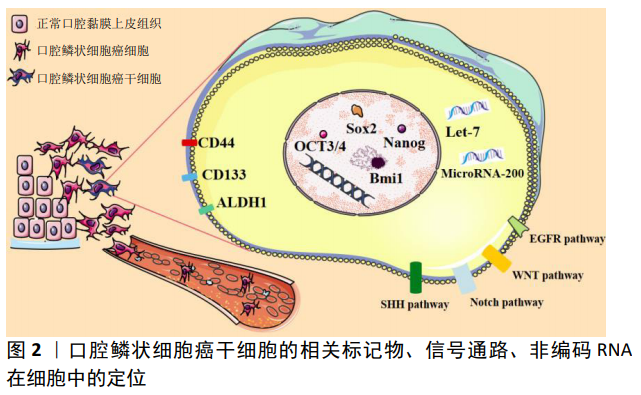
2.3.1 干细胞标记物可能是靶向治疗口腔鳞状细胞癌的重要途径 目前口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞鉴别、分离应用最多的分子标记物为CD44、ALDH和CD133。比较肿瘤干细胞和正常干细胞的分子特征,发现这两种不同的细胞群分子特征有大量的重叠;有趣的是,与自我更新、血管生成、迁移和抗凋亡相关的基因在这两个干细胞群中广泛共享,特别是在胚胎干细胞中高度富集的因子往往与口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的干细胞样特征有关[18],如Oct3/4(Octamerr结合转录因子4)、SOX2(性别决定区Y-box 2)、NANOG (NANOG Homeobox)和KLF4 (Kruppel-like factor 4)。越来越多的证据表明,CD44、ALDH、CD133、Oct3/4、Nanog、Sox2、KLF4等干细胞标记物在口腔鳞状细胞癌发生、发展及治疗中扮演重要角色,是口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞鉴别、分离及潜在的治疗靶点。
(1)CD44:CD44是位于11p13号染色体短臂上的CD44基因编码的糖蛋白,是一种细胞表面黏附分子。该基因由两组外显子组成,即常量外显子和可变外显子。该基因序列可以通过选择特定的外显子编码多种不同的蛋白质从而具有广泛的功能。由外显子1-5和16-20组成的一组被拼接在一起,形成一个标准CD44(CD44s)的转录本;其他10个变量外显子6-15也被称为v1-v10,它们交替剪接并包含在标准外显子中,含有可变外显子或其肽产物的分子称为CD44v;它们具有独特的细胞黏附特性,可导致2个不同的细胞或1个细胞与其周围细胞基质之间的相互作用,有助于肿瘤细胞的聚集和迁移[19]。
CD44在正常口腔黏膜上皮及口腔黏膜癌前病变、恶性病变中均有表达[20],口腔鳞状细胞癌患者肿瘤组织CD44的表达明显高于正常口腔黏膜上皮[21],并可作为口腔肿瘤干细胞识别的表面标志物[16]。事实上,CD44是口腔鳞癌肿瘤干细胞识别中被研究最多的细胞表面标志物,其表达已在多种实体恶性肿瘤如中枢神经系统肿瘤、乳腺癌、前列腺癌、结肠癌、胰腺癌以及包括口腔癌在内的头颈部鳞状细胞癌中得到确认[22]。CD44在许多癌症中激活一系列酪氨酸激酶受体[23],
通过激活PI3K/AKT通路增加肿瘤细胞的增殖和存活率[24]。在口腔癌中由MAPK/PI3K驱动的CD44变异体(v4和v6)表达与口腔癌侵袭性、耐药性和干性相关。CD44v4表达与ERK1/2激活和促进顺铂耐药性相关,而CD44v6表达主要与PI3K/Akt/GSK3β激活和驱动肿瘤侵袭、迁移相关[25]。
此外,CD44表达与口腔鳞状细胞癌浸润深度相关,并可能成为预测隐匿性淋巴结转移的指标[26]。唾液和血清中可溶性CD44水平的测定可能作为诊断患者是否有癌细胞浸润及早期癌症的有效方法[27]。
(2)ALDH:醛脱氢酶(Aldehyde Dehydrogenase,ALDH)有19个不同的ALDH蛋白亚型,不同蛋白亚型基因分别定位在不同的染色体区段上。与肿瘤干细胞最亲密的亚型是ALDH1家族,主要包括ALDH1A1、ALDH1A2、ALDH1A3、ALDH1B1、ALDH1L1和ALDH1L2。ALDH1A1、ALDH1A2、ALDH1A3是3种高度保守的同工酶,可将视黄醛催化成为细胞内的重要信号分子视黄酸,视黄酸对干细胞的发育、分化以及胞内醛的催化至关重要[28]。
ALDH在实体恶性肿瘤如结肠、乳腺、肝脏、肺肿瘤及头颈部鳞状细胞癌中均有表达[29]。与CD44相似,在口腔癌干细胞中也观察到ALDH的表达并与口腔癌分期、耐药及淋巴结转移相关[30-31]。在小鼠中,表达高水平ALDH标记的癌细胞具有更高的肿瘤发展潜力,而表达低水平ALDH标记的细胞则导致肿瘤发展受限[32]。因此,ALDH的表达可以用来预测口腔鳞状细胞癌的预后。
从头颈部鳞状细胞癌组织中提取的ALDH1+细胞具有自增殖能力、肿瘤形成能力、侵袭能力和成球能力[33]。ALDH1表达水平与口腔鳞状细胞癌的分期和发展呈正相关,与患者生存呈负相关;在动物模型中,ALDH1+细胞表现出更强的侵袭能力、转移能力、球状体形成能力和增加对治疗的抵抗力;ALDH1+细胞群与CD44+细胞群存在明显的重叠,其中50.6%-74.4%的ALDH1+细胞表达CD44,而只有9.8%-23.6%的CD44+细胞具有较高的ALDH活性[9,12,33],这些研究成果表明ALDH1可能是一个更有效的口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞标志物。
此外,ALDH抑制剂已被证实与传统的化疗、放疗在抑制疾病进展和预防肿瘤细胞耐药方面具有协同作用[34]。例如CHEN等[35]在头颈部鳞状细胞癌患者放化疗过程中抑制ALDH表达,观察到患者放化疗效果改善。
(3)CD133:人类CD133基因位于4号染色体上,包含至少37个外显子。CD133 (prominin-1)分子质量为115-
120 kD,包含850-865个氨基酸,n端暴露于细胞外环境,而c端暴露于细胞质。CD133有5个跨膜结构域,其中有2个较大的糖基化胞外环和2个较小的胞内环,分别包含约250和20个氨基酸残基[36]。
该标记已在神经组织的上皮细胞和干细胞以及脑癌、前列腺癌、结肠癌、肾癌、肺癌、肝癌、黑色素瘤和皮肤癌组织中观察到[37]。CD133在口腔癌中可能是一种独立预后标志物,与肿瘤进展和淋巴结转移相关[38]。在口腔癌细胞中,CD133+细胞比例为1%-2%,CD133+细胞具有更高的侵袭性、克隆原性和体内致瘤性;沉默CD133能够增强口腔癌细胞的化疗敏感性[39]。此外,CD133水平升高与口腔癌细胞上皮-间充质转化过程相关[40],并诱导细胞增殖[41]。
干细胞转录调节因子OCT4、SOX2和NANOG在肿瘤干细胞的转录和增殖中起关键作用,OCT4还可引起口腔癌变并作为口腔鳞状细胞癌发生的分子标记物[42]。OCT4和NANOG的表达与CD133的表达增加直接相关[43]。CD133还可能通过调节干细胞转录因子的表达启动口腔鳞状细胞癌,尽管它们具有自我更新和致瘤特性[44-45],但是CD133在一些肿瘤细胞中不表达,因此CD133不能单独作为鉴别实体肿瘤中肿瘤干细胞的可靠标志物。
(4)Oct3/4:Oct3/4在正常口腔黏膜、癌前病变、口腔鳞状细胞癌原发部位和转移部位均有表达,Oct4与Sox2共表达可能导致口腔黏膜恶性转化[46]。HABU等[47]研究发现Oct3/4的高表达增加了口腔鳞状细胞癌的恶性程度,当Oct3/4失活后其恶性成分减少;Oct3/4与其他肿瘤干细胞标记物一起通过增强迁移和侵袭能力促进口腔鳞状细胞癌转移病灶形成;此外,当原发癌细胞中存在Oct3/4时,易发生颈部淋巴转移。总的来说,Oct3/4可能促进口腔鳞状细胞癌恶性、转移,特别是当与其他肿瘤干细胞标志物共表达时。
(5)Nanog:HUANG等[48]研究了Nanog与口腔鳞状细胞癌之间的关系,发现Nanog阳性细胞具有标志性的肿瘤干细胞特性。Nanog翻译后磷酸化对调节Bmi1和促进头颈部鳞状细胞癌发生至关重要[49]。与其上游靶点Oct4一样,Nanog被认为有助于提高口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞的活性和侵袭性,并且是颈淋巴转移高危患者的预测因子[49]。NANOG的表达与口腔鳞癌的分化、转移和术前辅助治疗的耐药性相关[50]。SEINO等[51]研究发现Nanog高表达的口腔癌细胞对辐射等抗癌治疗具有抗性。总之,这些研究表明Nanog可作为口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的标志物,是对具有高远处颈部转移风险患者进行分层的预测因子,从而为这些患者的治疗规划提供信息。
(6)Sox2:研究发现4个转录因子(Sox2、Oct4、c-Myc、Klf4)的表达足以将分化的细胞重新编程为诱导多能干细胞,而Sox2在这个过程中扮演重要角色[52]。
Sox2通常与CD44共表达,这2种因子联合作用对肿瘤干细胞的自我更新能力有显著影响[53]。Sox2的表达是口腔白斑患者发生口腔癌风险的独立预测因子,并在早期口腔肿瘤发生中起到了重要作用[54]。Sox2的下调降低了口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的自我更新能力、耐药能力、侵袭能力及体内致瘤能力[55]。Sox2在体内以IFN-I依赖方式促进头颈部鳞状细胞癌的生长[56]。研究发现PI3K/mTOR可直接调控Sox2蛋白质含量[57],Sox2反过来激活ALDH1A1的表达和ALDH活力,Sox2表达通过诱导Cadherin 1来促进间叶细胞向上皮细胞的过渡和增殖,从而促进了肿瘤的进展。此外SOX2可诱导抗凋亡蛋白BCL-2的表达,增强对顺铂等凋亡诱导药物的耐药[58]。
综上所述,Sox2作为干细胞标记物在肿瘤发生发展中发挥重要作用,将来可能作为口腔鳞状细胞癌患者的预后指标。
(7)Bmi1:研究人员为了解口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的病理通路开展了相关研究,发现口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞中大量表达靶基因Bmi1[59-60]。下调Bmi1表达可以影响口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞成球能力和集落形成能力[61]。高Bmi1表达常与头颈部鳞状细胞癌的晚期、侵袭性临床病理行为、干细胞样特性、耐药性和不良预后相关[62-63]。以Bmi1为靶点,使用小分子抑制剂可显著降低头颈部鳞状细胞癌的肿瘤复发[64]。这些研究结果表明Bmi1具有成为干细胞标记物的潜力,并可能成为治疗口腔鳞状细胞癌的重要靶点。
2.3.2 影响口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的信号通路 SHH、Wnt、EGFR等信号通路控制着正常干细胞自我更新和分化,往往异常激活口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞。因此,识别口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞所需的关键途径(通路)可能是靶向口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的重要治疗途径。
(1)SHH信号通路:SHH(SonicHedgehog)信号通路是胚胎发育和成熟组织稳态的重要机制[65]。当SHH与PTCH受体结合时该通路被激活,PTCH受体进而抑制Smoothened(SMO)跨膜受体,而SMO的激活通过募集和激活GLI家族转录因子(包括GLI1、GLI2和GLI3)来触发SHH信号级联[66]。既往研究表明,SHH信号在多种肿瘤干细胞中上调,包括脑肿瘤、乳腺癌、肝癌和胃癌[67-70]。在口腔鳞状细胞癌中,与正常口腔黏膜相比,肿瘤组织中GLI、PTCH1、SMO和SHH表达水平均升高[71]。此外,GLI1的表达与口腔鳞状细胞癌淋巴结转移、复发、临床分期及预后不良有关,而SHH信号通路的阻断会抑制肿瘤生长和血管生成[72]。在口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞系中抑制GLI3表达后,减少了OCT4和Bmi1的表达,导致口腔鳞状细胞癌中肿瘤干细胞数量减少、成球能力下降[73]。
(2)WNT信号通路:WNT信号通路是干细胞自我更新和决定命运的进化保守通路[74]。基于β-catenin的依赖,WNT信号通路可分为2个,即经典和非经典途径。经典β-catenin/WNT信号通路的激活需要绑定WNT卷曲蛋白及其受体配体、脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5或6(LRP 5/6),收集β-catenin降解复合体并允许β-catenin积累在细胞质中。然后,β-catenin将易位到细胞核,通过绑定目标T细胞因子/淋巴增强因子(TCF/LEF)转录因子推动下游转录的氨基端[75]。
既往研究已经表明β-catenin/WNT信号通路维系口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的重要作用:WNT通路活化剂或WNT抑制剂可以改变口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞增殖率,而这种处理对亲代口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞的影响很小[76-78]。最近的一项研究表明,头颈部鳞状细胞癌中WNT通路的激活增加了肿瘤干细胞的成球能力和侵袭性[79]。
(3)EGFR信号通路:EGFR是一种跨膜蛋白,通过绑定特定的配体,包括表皮生长因子(EGF)和转化生长因子α(TGFα),进而激活细胞内的信号级联控制细胞生长、分化和生存[80]。在头颈部鳞状细胞癌中可以观察到EGFR表达水平升高,EGFR信号通路活性增加与治疗耐药性和临床预后不佳相关[81]。在高侵袭性人乳头瘤病毒16(HPV-16)阳性的头颈部鳞状细胞癌细胞系UM-SCC-104中,EGFR的高表达促进了肿瘤干细胞比例增加[82]。此外,肿瘤干细胞表面标志物CD44可与EGFR相互作用,促进头颈部鳞状细胞癌的进展[83]。
(4)Notch信号通路:Notch信号在干细胞增殖、分化和自我更新等过程中起着重要的作用[84]。在哺乳动物中已经报道了4个Notch受体(Notch 1-4)和5个Notch配体(Jagged-1、Jagged-2、Delta-1、Delta-3和Delta-4)。当Notch受体被激活时,在细胞内的Notch(NICD)将从质膜中释放并转移到细胞核中,NICD与CSL转录因子一起诱导其靶基因的表达,如HES1、Hey1[85]。利用抗体或抑制剂抑制Notch1表达可抑制多种肿瘤的生长和肿瘤干细胞功能[86-87]。此外,Notch1抑制可降低头颈部鳞状细胞癌的肿瘤发生和肿瘤干细胞的自我更新能
力[88]。然而,也有研究报道Notch1可能是头颈部鳞状细胞癌的抑癌基因[89]。
2.3.3 影响口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的非编码RNA 在与肿瘤干细胞相关的各种分子中,非编码RNA (ncRNAs)被认为是获得和维持癌症干性的关键分子。越来越多的研究表明,这些ncRNAs的异常表达可以作为癌症的替代诊断标记甚至治疗靶点。
(1)Let-7家族:目前已知有12种不同的人类let-7家族成
员[90]。两个关键的RNA结合蛋白(LIN28A和LIN28B)被证明直接与Let-7前体蛋白结合来抑制let-7家族的生物学功能[91]。
此前已有研究发现,Lin28B/Let-7通路可以正向调控Oct4和Sox2的表达;此外,Let-7还诱导正常口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞向具有肿瘤启动和自我更新特征的肿瘤干细胞转化[92],
并且Let-7a的过表达能够使ALDH1阳性的头颈部鳞状细胞癌细胞中Nanog表达下调[93];在口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞中异位过表达Let-7c和Let-7d可分别通过抑制IL-8和EMT标记物的表达来抑制肿瘤干细胞干性和肿瘤耐药[94-95]。总之,这些发现表明Let-7家族是口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的抑制因子。
(2)MicroRNA-200家族:miR-200的失调与肿瘤的形成有关。miR-200家族可通过直接靶向ZEB1或ZEB2调节肿瘤上皮-间充质转化[96]。长期以来,研究人员一直认为ZEB/miR-200反馈环控制着肿瘤干细胞的状态[97]。
在口腔鳞状细胞癌中,miR-200家族表达下调[98],在头颈部鳞状细胞癌中,miR-200c/miR-141与ZEB1相互作用,过表达miR-200c/miR-141可抑制迁移能力[99],减弱肿瘤的增殖和转移能力[100]。研究认为miR-200c、ZEB1/ZEB2和Bmi1之间的相互作用决定了口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的命运[101-102],而p53突变可能损害miR-200c下游转录的激活,导致口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞特征增强。
2.3.4 天然化合物靶向干预口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞 近几十年来,包括口腔鳞状细胞癌在内的多种癌症类型中,天然化合物被越来越多地认为是靶向肿瘤干细胞的有效药物[103]。
有研究分析了120种来自天然产物Set Ⅱ的化合物,以确定这些化合物对黑色素瘤肿瘤干细胞群体细胞活力、细胞周期阻滞、细胞凋亡、基因表达、克隆存活和标签保留的影响,细胞毒性不高的化合物,如苔藓虫素1、西霉素A、伊律丁M、米舍拉明B和戊酮昔芬林等,可显著降低ABCB5阳性细胞的数量,该研究中选择的化合物差异改变了黑素细胞/黑色素瘤特异性小邻苯二甲酸相关转录因子和原癌基因c-MYC的表达[104],对探讨天然化合物靶向治疗口腔鳞状细胞癌的研究具有重要的借鉴作用。
植物多酚姜黄素是一种有效的抗癌化合物,在体内外对顺铂诱导的头颈部鳞状细胞癌干细胞均有抑制作用[105],此外使用姜黄素还能通过靶向非小细胞肺癌的肿瘤干细胞亚群来增强顺铂的疗效[106]。然而,姜黄素抑制肿瘤干细胞的具体机制仍然未知,其临床引用价值还有待进一步研究。
| [1] ZHONG LP, ZHANG CP, REN GX, et al. Long-term results of a randomized phase III trial of TPF induction chemotherapy followed by surgery and radiation in locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6(21):18707-18714. [2] LIAN Q, MA DM, CHEN MG, et al. Silencing Rab14 represses the proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma, and enhances cisplatin sensitivity. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(9): 4195-4205. [3] COSTEA DE, TSINKALOVSKY O, VINTERMYR OK, et al. Cancer stem cells - new and potentially important targets for the therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Dis. 2006;12(5): 443-454. [4] BIANCHINI C, CIORBA A, STOMEO F, et al. Immunonutrition in head and neck cancer: have a look before surgery! Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;269(1):5-8. [5] DIANAT-MOGHADAM H, HEIDARIFARD M, JAHANBAN-ESFAHLAN R, et al. Cancer stem cells-emanated therapy resistance: Implications for liposomal drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 2018;288:62-83. [6] TABOR MH, CLAY MR, OWEN JH, et al. Head and neck cancer stem cells: the side population. Laryngoscope. 2011;121(3): 527-533. [7] STRANSKY N, EGLOFF AM, TWARD AD, et al. The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science. 2011; 333(6046):1157-1160. [8] PRINCE ME, SIVANANDAN R, KACZOROWSKI A, et al. Identification of a subpopulation of cells with cancer stem cell properties in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104(3):973-978. [9] PRINCE ME, AILLES LE. Cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(17):2871-2875. [10] SATPUTE PS, HAZAREY V, AHMED R, et al. Cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a review. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(10):5579-5587. [11] ZHANG Q, SHI S, YEN Y, et al. A subpopulation of CD133(+) cancer stem-like cells characterized in human oral squamous cell carcinoma confer resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2010; 289(2):151-160. [12] MAJOR AG, PITTY LP, FARAH CS. Cancer stem cell markers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Stem Cells Int. 2013; 2013:319489. [13] CHEN D, WANG CY. Targeting cancer stem cells in squamous cell carcinoma. Precis Clin Med. 2019;2(3):152-165. [14] KIM H, KIM M, IM SK, et al. Mouse Cre-LoxP system: general principles to determine tissue-specific roles of target genes. Lab Anim Res. 2018; 34(4):147-159. [15] CHEN D, WU M, LI Y, et al. Targeting BMI1+ Cancer Stem Cells Overcomes Chemoresistance and Inhibits Metastases in Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;20(5):621-634. [16] OSHIMORI N, ORISTIAN D, FUCHS E. TGF-β promotes heterogeneity and drug resistance in squamous cell carcinoma. Cell. 2015;160(5): 963-976. [17] PRASAD S, RAMACHANDRAN S, GUPTA N, et al. Cancer cells stemness: A doorstep to targeted therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(4):165424. [18] SCHEPERS AG, SNIPPERT HJ, STANGE DE, et al. Lineage tracing reveals Lgr5+ stem cell activity in mouse intestinal adenomas. Science. 2012; 337(6095):730-735. [19] MISHRA MN, CHANDAVARKAR V, SHARMA R, et al. Structure, function and role of CD44 in neoplasia. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2019;23(2): 267-272. [20] MONTEIRO LS, DELGADO ML, RICARDO S, et al. Prognostic significance of CD44v6, p63, podoplanin and MMP-9 in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Dis. 2016;22(4):303-312. [21] MĂRGĂRITESCU C, PIRICI D, SIMIONESCU C, et al. The utility of CD44, CD117 and CD133 in identification of cancer stem cells (CSC) in oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC). Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011; 52(3 Suppl):985-993. [22] MISHRA A, VERMA M. Cancer biomarkers: are we ready for the prime time? Cancers (Basel). 2010;2(1):190-208. [23] KAROUSOU E, MISRA S, GHATAK S, et al. Roles and targeting of the HAS/hyaluronan/CD44 molecular system in cancer. Matrix Biol. 2017;59:3-22. [24] SHERIDAN C, KISHIMOTO H, FUCHS RK, et al. CD44+/CD24- breast cancer cells exhibit enhanced invasive properties: an early step necessary for metastasis. Breast Cancer Res.2006;8(5): R59. [25] KASHYAP T, PRAMANIK KK, NATH N, et al. Crosstalk between Raf-MEK-ERK and PI3K-Akt-GSK3β signaling networks promotes chemoresistance, invasion/migration and stemness via expression of CD44 variants (v4 and v6) in oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2018;86:234-243. [26] MORAND GB, IKENBERG K, VITAL DG, et al. Preoperative assessment of CD44-mediated depth of invasion as predictor of occult metastases in early oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2019;41(4):950-958. [27] SEYEDMAJIDI S, SEYEDMAJIDI M, FOROUGHI R, et al. Comparison of Salivary and Serum Soluble CD44 Levels between Patients with Oral SCC and Healthy Controls. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018;19(11): 3059-3063. [28] SOBREIRA TJ, MARLÉTAZ F, SIMÕES-COSTA M, et al. Structural shifts of aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes were instrumental for the early evolution of retinoid-dependent axial patterning in metazoans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(1): 226-231. [29] MADJD Z, RAMEZANI B, MOLANAE S, et al. High expression of stem cell marker ALDH1 is associated with reduced BRCA1 in invasive breast carcinomas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(6): 2973-2978. [30] NOZAKI Y, TAMORI S, INADA M, et al. Correlation between c-Met and ALDH1 contributes to the survival and tumor-sphere formation of ALDH1 positive breast cancer stem cells and predicts poor clinical outcome in breast cancer. Genes Cancer. 2017; 8(7-8):628-639. [31] JAYASOORIYA P, FERNANDO C, SURAWEERA A, et al. Stem cell markers as a resource to predict prognosis of betel quid induced oral squamous cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical investigation. Stomatological Dis Sci 2017;1:29-34. [32] CANCER GENOME ATLAS NETWORK. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature. 2015;517(7536):576-582. [33] KRISHNAMURTHY S, NÖR JE. Head and neck cancer stem cells. J Dent Res. 2012;91(4):334-340. [34] DINAVAHI SS, BAZEWICZ CG, GOWDA R, et al. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Inhibitors for Cancer Therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019;40(10): 774-789. [35] CHEN YC, CHEN YW, HSU HS, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 is a putative marker for cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;385(3):307-313. [36] BARZEGAR BEHROOZ A, SYAHIR A, AHMAD S. CD133: beyond a cancer stem cell biomarker. J Drug Target. 2019;27(3):257-269. [37] HARPER LJ, PIPER K, COMMON J, et al. Stem cell patterns in cell lines derived from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36(10):594-603. [38] FUJII K, KUMAGAI K, HAMADA Y, et al. Clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of CD133 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol. 2015;27(2):176-182. [39] YU CC, HU FW, YU CH, et al. Targeting CD133 in the enhancement of chemosensitivity in oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived side population cancer stem cells. Head Neck. 2016;38 Suppl 1:E231-238. [40] MOON Y, KIM D, SOHN H, et al. Effect of CD133 overexpression on the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral cancer cell lines. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016;33(5):487-496. [41] SUN Y, HAN J, LU Y, et al. Biological characteristics of a cell subpopulation in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Dis. 2012; 18(2):169-177. [42] CAI J, HE B, LI X, et al. Regulation of tumorigenesis in oral epithelial cells by defined reprogramming factors Oct4 and Sox2. Oncol Rep. 2016; 36(2):651-658. [43] CHIOU SH, YU CC, HUANG CY, et al. Positive correlations of Oct-4 and Nanog in oral cancer stem-like cells and high-grade oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(13): 4085-4095. [44] REYA T, MORRISON SJ, CLARKE MF, et al. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414(6859):105-111. [45] SHEN G, SHEN F, SHI Z, et al. Identification of cancer stem-like cells in the C6 glioma cell line and the limitation of current identification methods. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008;44(7): 280-289. [46] QIAO B, HE B, CAI J, et al. The expression profile of Oct4 and Sox2 in the carcinogenesis of oral mucosa. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013; 7(1):28-37. [47] HABU N, IMANISHI Y, KAMEYAMA K, et al. Expression of Oct3/4 and Nanog in the head and neck squamous carcinoma cells and its clinical implications for delayed neck metastasis in stage I/II oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:730. [48] HUANG CF, XU XR, WU TF, et al. Correlation of ALDH1, CD44, OCT4 and SOX2 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma and their association with disease progression and prognosis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2014;43(7): 492-498. [49] XIE X, PIAO L, CAVEY GS, et al. Phosphorylation of Nanog is essential to regulate Bmi1 and promote tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2014; 33(16): 2040-2052. [50] WATANABE M, OHNISHI Y, INOUE H, et al. NANOG expression correlates with differentiation, metastasis and resistance to preoperative adjuvant therapy in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2014;7(1):35-40. [51] SEINO S, SHIGEISHI H, HASHIKATA M, et al. CD44(high)/ ALDH1(high) head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells exhibit mesenchymal characteristics and GSK3β-dependent cancer stem cell properties. J Oral Pathol Med. 2016;45(3): 180-188. [52] DALERBA P, CHO RW, CLARKE MF. Cancer stem cells: models and concepts. Annu Rev Med. 2007;58:267-284. [53] SAITO S, ONUMA Y, ITO Y, et al. Possible linkages between the inner and outer cellular states of human induced pluripotent stem cells. BMC Syst Biol. 2011;5 Suppl 1:S17. [54] DE VICENTE JC, DONATE-PÉREZ DEL MOLINO P, RODRIGO JP, et al. SOX2 Expression Is an Independent Predictor of Oral Cancer Progression. J Clin Med. 2019;8(10). pii: E1744. [55] LEE SH, OH SY, DO SI, et al. SOX2 regulates self-renewal and tumorigenicity of stem-like cells of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(11):2122-2130. [56] TAN YS, SANSANAPHONGPRICHA K, XIE Y, et al. Mitigating SOX2-potentiated Immune Escape of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma with a STING-inducing Nanosatellite Vaccine. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(17):4242-4255. [57] KEYSAR SB, LE PN, MILLER B, et al. Regulation of Head and Neck Squamous Cancer Stem Cells by PI3K and SOX2. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016;109(1):djw189. [58] SCHRÖCK A, BODE M, GÖKE FJ, et al. Expression and role of the embryonic protein SOX2 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(7):1636-1642. [59] CHEN YC, CHANG CJ, HSU HS, et al. Inhibition of tumorigenicity and enhancement of radiochemosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell cancer-derived ALDH1-positive cells by knockdown of Bmi-1. Oral Oncol. 2010;46(3):158-165. [60] HÄYRY V, MÄKINEN LK, ATULA T, et al. Bmi-1 expression predicts prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Br J Cancer. 2010; 102(5):892-897. [61] HE Q, LIU Z, ZHAO T, et al. Bmi1 drives stem-like properties and is associated with migration, invasion, and poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 2015;11(1):1-10. [62] NÖR C, ZHANG Z, WARNER KA, et al. Cisplatin induces Bmi-1 and enhances the stem cell fraction in head and neck cancer. Neoplasia. 2014;16(2):137-146. [63] KASEB HO, FOHRER-TING H, LEWIS DW, et al. Identification, expansion and characterization of cancer cells with stem cell properties from head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Exp Cell Res. 2016;348(1):75-86. [64] WANG Q, LI Z, WU Y, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of Bmi1 by PTC-209 impaired tumor growth in head neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2017;17:107. [65] MILLA LA, GONZÁLEZ-RAMÍREZ CN, PALMA V. Sonic Hedgehog in cancer stem cells: a novel link with autophagy. Biol Res. 2012;45(3): 223-230. [66] TICKLE C, TOWERS M. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Limb Development. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017;5:14. [67] XU Q, YUAN X, LIU G, et al. Hedgehog signaling regulates brain tumor-initiating cell proliferation and portends shorter survival for patients with PTEN-coexpressing glioblastomas. Stem Cells. 2008;26(12): 3018-3026. [68] ZHOU M, HOU Y, YANG G, et al. LncRNA-Hh Strengthen Cancer Stem Cells Generation in Twist-Positive Breast Cancer via Activation of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells. 2016; 34(1):55-66. [69] ZHANG C, LI C, HE F, et al. Identification of CD44+CD24+ gastric cancer stem cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137(11): 1679-1686. [70] ZHANG K, CHE S, PAN C, et al. The SHH/Gli axis regulates CD90-mediated liver cancer stem cell function by activating the IL6/JAK2 pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(7):3679-3690. [71] CAVICCHIOLI BUIM ME, GURGEL CA, GONÇALVES RAMOS EA, et al. Activation of sonic hedgehog signaling in oral squamous cell carcinomas: a preliminary study. Hum Pathol. 2011;42(10): 1484-1490. [72] FAN HX, WANG S, ZHAO H, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling may promote invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by activating MMP-9 and E-cadherin expression. Med Oncol.2014; 31(7): 41. [73] RODRIGUES MFSD, MIGUITA L, DE ANDRADE NP, et al. GLI3 knockdown decreases stemness, cell proliferation and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2018;53(6):2458-2472. [74] NUSSE R, CLEVERS H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985-999. [75] CLEVERS H, LOH KM, NUSSE R. Stem cell signaling. An integral program for tissue renewal and regeneration: Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Science. 2014;346(6205):1248012. [76] FELTHAUS O, ETTL T, GOSAU M, et al. Cancer stem cell-like cells from a single cell of oral squamous carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;407(1):28-33. [77] LIM YC, KANG HJ, KIM YS, et al. All-trans-retinoic acid inhibits growth of head and neck cancer stem cells by suppression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48(17):3310-3318. [78] WARRIER S, BHUVANALAKSHMI G, ARFUSO F, et al. Cancer stem-like cells from head and neck cancers are chemosensitized by the Wnt antagonist, sFRP4, by inducing apoptosis, decreasing stemness, drug resistance and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cancer Gene Ther. 2014;21(9):381-388. [79] LE PN, KEYSAR SB, MILLER B, et al. Wnt signaling dynamics in head and neck squamous cell cancer tumor-stroma interactions. Mol Carcinog. 2019;58(3):398-410. [80] WANG SJ, BOURGUIGNON LY. Hyaluronan and the interaction between CD44 and epidermal growth factor receptor in oncogenic signaling and chemotherapy resistance in head and neck cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;132(7):771-778. [81] ARGIRIS A, HARRINGTON KJ, TAHARA M, et al. Evidence-Based Treatment Options in Recurrent and/or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Front Oncol. 2017;7:72. [82] TANG AL, HAUFF SJ, OWEN JH, et al. UM-SCC-104: a new human papillomavirus-16-positive cancer stem cell-containing head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Head Neck. 2012;34(10):1480-1491. [83] PEREZ A, NESKEY DM, WEN J, et al. CD44 interacts with EGFR and promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma initiation and progression. Oral Oncol. 2013;49(4):306-313. [84] CHATTERJEE S, SIL PC. Targeting the crosstalks of Wnt pathway with Hedgehog and Notch for cancer therapy. Pharmacol Res. 2019;142: 251-261. [85] MEURETTE O, MEHLEN P. Notch Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2018;34(4):536-548. [86] CHU Q, ORR BA, SEMENKOW S, et al. Prolonged inhibition of glioblastoma xenograft initiation and clonogenic growth following in vivo Notch blockade. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(12):3224-3233. [87] PANNUTI A, FOREMAN K, RIZZO P, et al. Targeting Notch to target cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(12): 3141-3152. [88] ZHAO ZL, ZHANG L, HUANG CF, et al. NOTCH1 inhibition enhances the efficacy of conventional chemotherapeutic agents by targeting head neck cancer stem cell. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24704. [89] AGRAWAL N, FREDERICK MJ, PICKERING CR, et al. Exome sequencing of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma reveals inactivating mutations in NOTCH1. Science. 2011;333(6046): 1154-1157. [90] ROUSH S, SLACK FJ. The let-7 family of microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 2008;18(10):505-516. [91] BALZEAU J, MENEZES MR, CAO S, et al. The LIN28/let-7 Pathway in Cancer. Front Genet. 2017;8:31. [92] CHIEN CS, WANG ML, CHU PY, et al. Lin28B/Let-7 Regulates Expression of Oct4 and Sox2 and Reprograms Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells to a Stem-like State. Cancer Res. 2015;75(12):2553-2565. [93] YU CC, CHEN YW, CHIOU GY, et al. MicroRNA let-7a represses chemoresistance and tumourigenicity in head and neck cancer via stem-like properties ablation. Oral Oncol. 2011;47(3):202-210. [94] PENG CY, WANG TY, LEE SS, et al. Let-7c restores radiosensitivity and chemosensitivity and impairs stemness in oral cancer cells through inhibiting interleukin-8. J Oral Pathol Med. 2018;47(6): 590-597. [95] CHANG CJ, HSU CC, CHANG CH, et al. Let-7d functions as novel regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistant property in oral cancer. Oncol Rep. 2011;26(4): 1003-1010. [96] PARK SM, GAUR AB, LENGYEL E, et al. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev. 2008; 22(7): 894-907. [97] BRABLETZ S, BRABLETZ T. The ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop--a motor of cellular plasticity in development and cancer? EMBO Rep. 2010;11(9):670-677. [98] ARUNKUMAR G, DEVA MAGENDHRA RAO AK, MANIKANDAN M, et al. Dysregulation of miR-200 family microRNAs and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(1):649-657. [99] TAMAGAWA S, BEDER LB, HOTOMI M, et al. Role of miR-200c/miR-141 in the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33(4):879-886. [100] LO WL, YU CC, CHIOU GY, et al. MicroRNA-200c attenuates tumour growth and metastasis of presumptive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem cells. J Pathol. 2011;223(4): 482-495. [101] KIM T, VERONESE A, PICHIORRI F, et al. p53 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through microRNAs targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Exp Med. 2011;208(5):875-883. [102] KU TK, NGUYEN DC, KARAMAN M, et al. Loss of p53 expression correlates with metastatic phenotype and transcriptional profile in a new mouse model of head and neck cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2007; 5(4):351-362. [103] TSAI CF, HSIEH TH, LEE JN, et al. Curcumin Suppresses Phthalate-Induced Metastasis and the Proportion of Cancer Stem Cell (CSC)-like Cells via the Inhibition of AhR/ERK/SK1 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Agric Food Chem. 2015;63(48): 10388-10398. [104] SZTILLER-SIKORSKA M, KOPROWSKA K, MAJCHRZAK K, et al. Natural compounds’ activity against cancer stem-like or fast-cycling melanoma cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e90783. [105] JIANG P, XU C, ZHOU M, et al. RXRα-enriched cancer stem cell-like properties triggered by CDDP in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Carcinogenesis. 2018; 39(2):252-262. [106] BAHARUDDIN P, SATAR N, FAKIRUDDIN KS, et al. Curcumin improves the efficacy of cisplatin by targeting cancer stem-like cells through p21 and cyclin D1-mediated tumour cell inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 2016;35(1): 13-25. [107] CHAIB I, CAI X, LLIGE D, et al. Osimertinib and dihydroartemisinin: a novel drug combination targeting head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(22):651. |
| [1] | 林清凡, 解一新, 陈婉清, 叶振忠, 陈幼芳. 人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | 袁家威, 张海涛, 揭 珂, 曹厚然, 曾意荣. 基于网络药理学研究桃红四物汤治疗假体周围感染的潜在靶点和机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [4] | 张 超, 吕 欣. 髋臼骨折固定后的异位骨化:危险因素、预防及其治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [5] | 周继辉, 李新志, 周 游, 黄 卫, 陈文瑶. 髌骨骨折修复内植物选择的多重问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [6] | 王德斌, 毕郑刚. 尺骨鹰嘴骨折-脱位解剖力学、损伤特点、固定修复及3D技术应用的相关问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [7] | 顾 霞, 赵 敏, 王平义, 李一梅, 李文华. 低氧诱导因子1α与低氧相关疾病信号通路的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [8] | 姬志祥, 蓝常贡. 尿酸盐转运蛋白在痛风中的多态性和治疗相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [9] | 袁 美, 张新新, 郭祎莎, 毕 霞. 循环microRNA在血管性认知障碍诊断中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [10] | 李嘉程, 梁学振, 刘金豹, 许 波, 李 刚. 骨性关节炎mRNA差异表达谱及竞争性内源RNA调控的网络分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [11] | 柴 乐, 吕建兰, 胡劲涛, 胡华辉, 许庆军, 余进伟, 全仁夫. 诱导急性脊髓损伤模型大鼠炎症反应信号通路的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1218-1223. |
| [12] | 耿秋东, 葛海雅, 王和鸣, 李 楠. 基于网络药理学探讨龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨关节炎的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [13] | 张秀梅, 翟运开, 赵 杰, 赵 萌. 类器官模型国内外数据库近10年文献研究热点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [14] | 李中峰, 陈明海, 凡一诺, 魏秋实, 何 伟, 陈镇秋. 右归饮治疗激素性股骨头坏死作用机制的网络药理学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [15] | 刘 聪, 刘 肃. miR-17-5p调控低氧诱导因子1α介导脂肪细胞分化及血管生成的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
1.2 文献筛选标准 纳入内容相关性高,观点明确、证据充足可靠的文献,排除相关性差、内容重复、可信度低的文献。
1.3 质量评估及数据的提取 计算机初检得到327篇文献,经资料收集者互相评估纳入文献的有效性和适用性,通过阅读文题和摘要进行初步筛选;排除中英文文献重复性研究,以及内容不相关的文献,最后纳入107篇文献进行综述。
虽然针对不同肿瘤类型的肿瘤干细胞做了大量研究,但大多数分子靶点的效果有限,这可能是因为未能识别出真正的肿瘤干细胞亚群。为此,作者认为可使用遗传谱系追踪技术来进一步验证目前发现的干细胞标记物的有效性。此外,基于癌细胞的遗传不稳定性,肿瘤干细胞可能是异质性的,这增加了研究肿瘤干细胞的难度。在未来的研究中,可以根据CD44、ALDH、CD133、OCT3/4、Nanog、Sox2等干细胞标记物在肿瘤干细胞中的差异表达对口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞进行分类。
SHH、Wnt、EGFR等信号通路是靶向治疗口腔鳞状细胞癌又一重要途径,其中EGFR抑制药物已经发展到了第3代奥西替尼。有研究认为奥西替尼联合二氢青蒿素作为一种抗癌药物,是治疗复发性、转移性头颈部鳞状细胞癌患者的一种新的治疗策略[107],但是该研究并未说明奥西替尼是否通过抑制肿瘤干细胞来产生相应效果,也未进行临床试验。尽管如此,奥西替尼的出现为研究肿瘤干细胞相关的肿瘤恶性行为提供了便利,并有望成为治疗预后不良的口腔鳞状细胞癌患者的临床药物。
此外,Let-7家族和MicroRNA-200家族等非编码RNA、天然化合物靶向治疗口腔鳞状细胞癌的研究结果为根除口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞提供一些新策略。
目前,靶向干预肿瘤干细胞仍处于起步阶段,包括口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞免疫治疗在内的许多治疗途径仍未见文献报道。虽然对口腔鳞状细胞癌中肿瘤干细胞的特点和调节已经进行了深入的研究,但其中许多研究是基于体外数据,没有一项研究经历过早期临床阶段,并且肿瘤干细胞靶向治疗可能对正常干细胞有毒性。虽然存在以上的问题,但全面了解该文章介绍的干细胞标记物、信号通路、非编码RNA等仍会为不同肿瘤干细胞调节表现的口腔鳞状细胞癌患者提供很大的治疗价值。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程

文题释义:
口腔鳞状细胞癌:是最常见的口腔肿瘤,吸烟、饮酒和咀嚼槟榔是导致其发病的常见危险因素。在中国湖南等省份发病率较高,多见于40-60岁的成年男性,手术是其主要治疗方法。口腔鳞状细胞癌常常向区域淋巴结转移,晚期可发生远处转移,患者5年生存率较低。
肿瘤干细胞:是肿瘤细胞中数量较少的一类细胞,具有自我更新和分化为不同类型肿瘤细胞的能力。肿瘤干细胞对肿瘤的存活、增殖、转移及复发有着重要作用。从本质上讲,肿瘤干细胞通过自我更新和无限增殖维持着肿瘤细胞群的生命力。因此靶向干预肿瘤干细胞是治疗肿瘤的有效方法,也是目前肿瘤干细胞研究的热点之一。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程肿瘤干细胞存在于肿瘤微环境中不同的解剖区域,这些小环境维持了肿瘤干细胞的基本特性,保持了它们的表型可塑性,保护它们不受免疫系统的影响,并促进了它们的转移潜能。肿瘤微环境中的关键成分作为治疗肿瘤干细胞的靶点具有广阔的前景。但是,目前以肿瘤微环境为切入点研究靶向治疗肿瘤干细胞的相关文献仍然较少,而这可能成为研究口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的下一个热点。
值得一提的是,癌症患者的免疫系统可能识别出肿瘤干细胞并杀死肿瘤干细胞,设计以免疫检查点为靶点的靶向治疗肿瘤干细胞策略是一个值得关注的领域,遗憾的是口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的相应研究仍未形成体系。不过研究者们仍然对口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞与人体免疫的相关研究充满期待。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||