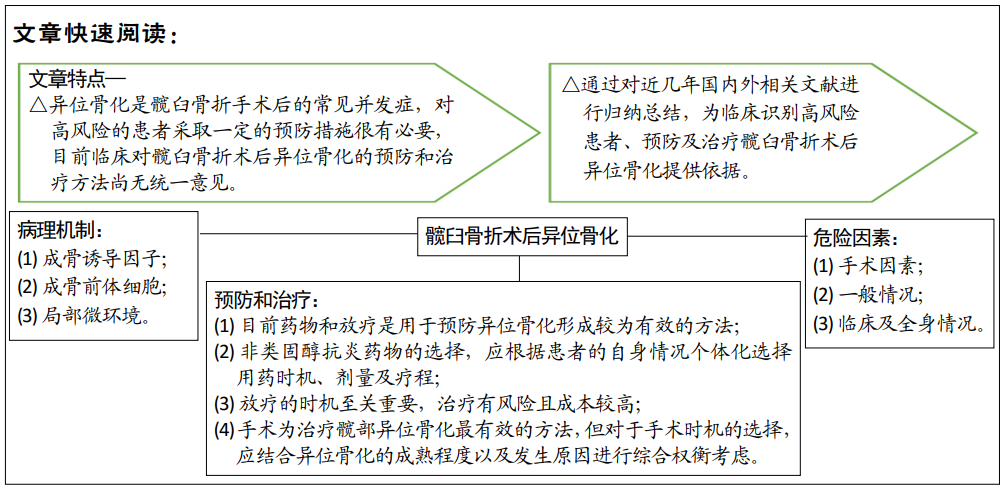
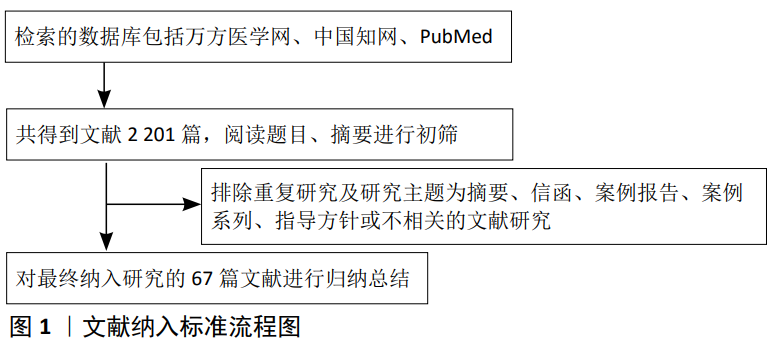
[1] RANGANATHAN K, LODER S, AGARWAL S, et al. Heterotopic ossification: basic-science principles and clinical correlates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(13):1101-1111.
[2] SHEHAB D, ELGAZZAR AH, COLLIER BD. Heterotopic ossification. J Nucl Med. 2002;43(3):346-353.
[3] MURPHY D, KALISZER M, RICE J, et al. Outcome after acetabular fracture. Prognostic factors and their inter-relationships. Injury. 2003;34(7):512-517.
[4] LAIRD A, KEATING JF. Acetabular fractures: a 16-year prospective epidemiological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(7):969-973.
[5] KITAYAMA K, KAWAKAMI Y, FUKUI T, et al. Rescue of ankylosing hip following open reduction and internal fixation of acetabular fracture by surgical resection of heterotopic ossification: A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2018;53:107-111.
[6] SIMONSEN LL, SONNE-HOLM S, KRASHENINNIKOFF M, et al. Symptomatic heterotopic ossification after very severe traumatic brain injury in 114 patients: incidence and risk factors. Injury. 2007; 38(10):1146-1150.
[7] WU XB, YANG MH, ZHU SW, et al. Surgical resection of severe heterotopic ossification after open reduction and internal fixation of acetabular fractures: a case series of 18 patients. Injury. 2014;45(10): 1604-1610.
[8] COLE PA, DUGARTE AJ, TALBOT M, et al. Early resection of ectopic bone in patients with heterotopic ossification about the hip after trauma. Injury. 2020;51(3):705-710.
[9] CHIU FY, CHEN CM, LO WH. Surgical treatment of displaced acetabular fractures - 72 cases followed for 10 (6-14) years. Injury. 2000;31(3): 181-185.
[10] DENORMANDIE P, DE L’ESCALOPIER N, GATIN L, et al.Resection of neurogenic heterotopic ossification (NHO) of the hip. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018;104(1S):S121-S127.
[11] BURD TA, LOWRY KJ, ANGLEN JO. Indomethacin compared with localized irradiation for the prevention of heterotopic ossification following surgical treatment of acetabular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83(12):1783-1788.
[12] BURNET NG, NASR P, YIP G, et al. Prophylactic radiotherapy against heterotopic ossification following internal fixation of acetabular fractures: a comparative estimate of risk. Br J Radiol. 2014;87(1042): 20140398.
[13] BLOKHUIS TJ, FRÖLKE JP. Is radiation superior to indomethacin to prevent heterotopic ossification in acetabular fractures?: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(2):526-530.
[14] NEGRIN LL, SELIGSON D. Results of 167 consecutive cases of acetabular fractures using the Kocher-Langenbeck approach: a case series. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):66.
[15] HARAN MJ, BHUTA T, LEE BS. WITHDRAWN: Pharmacological interventions for treating acute heterotopic ossification. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(5):CD003321.
[16] MAGILL P, MCGARRY J, QUEALLY JM, et al. Minimum ten-year follow-up of acetabular fracture fixation from the Irish tertiary referral centre. Injury. 2012;43(4):500-504.
[17] BASCHERA D, RAD H, COLLOPY D, et al. Incidence and clinical relevance of heterotopic ossification after internal fixation of acetabular fractures: retrospective cohort and case control study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:60.
[18] FIROOZABADI R, O’MARA TJ, SWENSON A, et al. Risk factors for the development of heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(11):3383-3388.
[19] DʼHEURLE A, ARCHDEACON MT, HIRATZKA S, et al. Do Surrogates of Injury Severity Influence the Occurrence of Heterotopic Ossification in Fractures of the Acetabulum? J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(4):213-216.
[20] HUANG Y, WANG X, LIN H. The hypoxic microenvironment: a driving force for heterotopic ossification progression. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18(1):20.
[21] EISENSTEIN N, STAPLEY S, GROVER L. Post-Traumatic Heterotopic Ossification: An Old Problem in Need of New Solutions. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(4):1061-1068.
[22] ZHANG Q, ZHANG Y, YAN M, et al. βig-h3 enhances chondrogenesis via promoting mesenchymal condensation in rat Achilles tendon heterotopic ossification model. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(8):7030‐7041.
[23] PEK CH, LIM MC, YONG R, et al. Neurogenic heterotopic ossification after a stroke: diagnostic and radiological challenges. Singapore Med J. 2014;55(8):e119-e122.
[24] ARDUINI M, MANCINI F, FARSETTI P, et al. A new classification of peri-articular heterotopic ossification of the hip associated with neurological injury: 3D CT scan assessment and intra-operative findings. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(7):899-904.
[25] ISAACSON BM, POTTER BK, BLOEBAUM RD, et al. Link Between Clinical Predictors of Heterotopic Ossification and Histological Analysis in Combat-Injured Service Members. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(8): 647-657.
[26] SHI WZ, JU JY, XIAO HJ, et al. Dynamics of MMP 9, MMP 2 and TIMP 1 in a rat model of brain injury combined with traumatic heterotopic ossification. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(4):2129-2135.
[27] BROOKER AF, BOWERMAN JW, ROBINSON RA, et al. Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55(8):1629-1632.
[28] MOED BR, SMITH ST. Three-view radiographic assessment of heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture surgery. J Orthop Trauma. 1996;10(2):93-98.
[29] MARY JIAYI T, LINDA P, MICHAEL P, et al. Potential discrepancy between plain films and CT scans in Brooker classification of heterotopic ossification. Br J Radiol. 2017;90(1080):20170263.
[30] DEBAUN MR, ZIINO C, LAPRADE C, et al. An anatomic classification for heterotopic ossification about the hip. J Orthop. 2020;21:228-231.
[31] PAPE HC, LEHMANN U, VAN GRIENSVEN M, et al. Heterotopic ossifications in patients after severe blunt trauma with and without head trauma: incidence and patterns of distribution. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(4):229-237.
[32] GIANNOUDIS PV, GROTZ MR, PAPAKOSTIDIS C, et al. Operative treatment of displaced fractures of the acetabulum. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(1):2-9.
[33] JOHNSON EE, KAY RM, DOREY FJ. Heterotopic ossification prophylaxis following operative treatment of acetabular fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(305):88-95.
[34] ALONSO JE, DAVILA R, BRADLEY E. Extended iliofemoral versus triradiate approaches in management of associated acetabular fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(305):81-87.
[35] BRAY TJ, ESSER M, FULKERSON L. Osteotomy of the trochanter in open reduction and internal fixation of acetabular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(5):711-717.
[36] ANTHONISSEN J, OSSENDORF C, HOCK JL, et al. The role of muscular trauma in the development of heterotopic ossification after hip surgery: An animal-model study in rats. Injury. 2016;47(3):613-616.
[37] RATH EM, RUSSELL GV JR, WASHINGTON WJ, et al. Gluteus minimus necrotic muscle debridement diminishes heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation. Injury. 2002;33(9):751-756.
[38] MATTA JM, MEHNE DK, ROFFI R. Fractures of the acetabulum. Early results of a prospective study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(205): 241-250.
[39] GHALAMBOR N, MATTA JM, BERNSTEIN L. Heterotopic ossification following operative treatment of acetabular fracture. An analysis of risk factors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(305):96-105.
[40] PENNAL GF, DAVIDSON J, GARSIDE H, et al. Results of treatment of acetabular fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;(151):115-123.
[41] ELHASSAN Y, ABDELHAQ A, PIGGOTT RP, et al. Heterotopic Ossification following acetabular fixation: Incidence and risk factors: 10-year experience of a tertiary centre. Injury. 2016;47(6):1332-1336.
[42] ANTHONISSEN J, STEFFEN CT, ALESSANDRI B, et al. Traumatic brain injury enhances the formation of heterotopic ossification around the hip: an animal model study [published online ahead of print, 2019 Dec 13]. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;10.1007/s00402-019-03326-0.
[43] 邹重文,陆焱,黄智.吲哚美辛预防髋臼骨折术后异位骨化的疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(10):870-873.
[44] SAGI HC, JORDAN CJ, BAREI DP, et al. Indomethacin prophylaxis for heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture surgery increases the risk for nonunion of the posterior wall. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(7):377-383.
[45] RUO REDDA MG, DE COLLE C, BIANCO L, et al. Heterotopic ossifications: role of radiotherapy as prophylactic treatment. Radiol Med. 2018;123(6):463-468.
[46] MATTA JM, SIEBENROCK KA. Does indomethacin reduce heterotopic bone formation after operations for acetabular fractures? A prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(6):959-963.
[47] KARUNAKAR MA, SEN A, BOSSE MJ, et al. Indometacin as prophylaxis for heterotopic ossification after the operative treatment of fractures of the acetabulum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(12):1613-1617.
[48] RATH E, WARSCHAWSKI Y, MAMAN E, et al. Selective COX-2 Inhibitors Significantly Reduce the Occurrence of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopic Surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(3):677-681.
[49] CHENG L, LONG HT, SUN BH, et al. The efficacy of a multimodal analgesia protocol in preventing heterotopic ossification after acetabular fractures surgery. Int J Clin Pharm. 2017;39(4):826-830.
[50] MONTGOMERY T, PEARSON J, AGARWAL A, et al. Thrombin Hemostatic Matrix Reduces Heterotopic Ossification in Acetabular Fractures fixed via the Kocher-Langenbeck Approach [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 13]. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;10.1097/BOT.0000000000001783.
[51] LEE DS, KIM Y, CHO HJ, et al. Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy for Progressive Heterotopic Ossification: The Relationship between Dose and Efficacy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020;106(5):993-997.
[52] ARCHDEACON MT, D’HEURLE A, NEMETH N, et al. Is preoperative radiation therapy as effective as postoperative radiation therapy for heterotopic ossification prevention in acetabular fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(11):3389-3394.
[53] MOURAD WF, PACKIANATHAN S, SHOURBAJI RA, et al. A prolonged time interval between trauma and prophylactic radiation therapy significantly increases the risk of heterotopic ossification. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82(3):e339-e344.
[54] ROOS DE, SMITH JG. Radiotherapy for the prophylaxis of heterotopic ossification: A single 7-8Gy fraction seems optimal. Radiother Oncol. 2015;116(1):1-3.
[55] SHEYBANI A, TENNAPEL MJ, LACK WD, et al. Risk of radiation-induced malignancy with heterotopic ossification prophylaxis: a case-control analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;89(3):584-589.
[56] 王一民,马云飞,姜楠,等.放射治疗与非甾体类抗炎药治疗预防髋部手术后异位骨化疗效比较的Meta分析[J].中国全科医学, 2012,15(36):4200-4204.
[57] PIATEK S, WESTPHAL T, ARBTER D, et al. Wertigkeit einer kombinierten Ossifikationsprophylaxe mit Indometacin und Bestrahlung bei Azetabulumfrakturen [Value of a combined ossification prophylaxis with indomethacin and radiotherapy for acetabular fractures]. Unfallchirurg. 2006;109(7):556-562.
[58] WANG Q, YANG Q, ZHANG A, et al. Silencing of SPARC represses heterotopic ossification via inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(11):BSR20191805.
[59] SORKIN M, HUBER AK, HWANG C, et al. Regulation of heterotopic ossification by monocytes in a mouse model of aberrant wound healing. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):722.
[60] KUSANO T, NAKATANI M, ISHIGURO N, et al. Desloratadine inhibits heterotopic ossification by suppression of BMP2-Smad1/5/8 signaling [published online ahead of print, 2020 Feb 11]. J Orthop Res. 2020; 10.1002/jor.24625.
[61] 张弛,纪方.SMAD7调控内皮间质转化可预防跟腱损伤后的异位骨化[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(8):1178-1185.
[62] ZHANG Q, ZHANG Y, YAN M, et al. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Molecular Mechanism of Late-Stage Heterotopic Ossification. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:5097823.
[63] SODEMANN B, PERSSON PE, NILSSON OS. Nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs prevent the recurrence of heterotopic ossification after excision. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1990;109(2):53-56.
[64] MACHERAS GA, LEPETSOS P, LEONIDOU A, et al. Results from the surgical resection of severe heterotopic ossification of the hip: a case series of 26 patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2017;27(8):1097-1102.
[65] WICK M, MÜLLER EJ, HAHN MP, et al. Surgical excision of heterotopic bone after hip surgery followed by oral indomethacin application: is there a clinical benefit for the patient?. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1999;119(3-4):151-155.
[66] GARLAND DE. A clinical perspective on common forms of acquired heterotopic ossification. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(263):13-29.
[67] ONG C, HALL M, YOUM T. Surgical technique: arthroscopic treatment of heterotopic ossification of the hip after prior hip arthroscopy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(4):1277-1282.
|