中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 1393-1397.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.4009
• 脊柱植入物Spinal implants • 上一篇 下一篇
减压植骨融合内固定治疗退变性腰椎滑脱:基于脊柱骨盆参数预测患者的功能预后
王海莹,吕 冰,李 辉,王顺义
- 河北省保定市第一中心医院骨一科,河北省保定市 071000
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters
Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi
- First Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Baoding No.1 Central Hospital, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
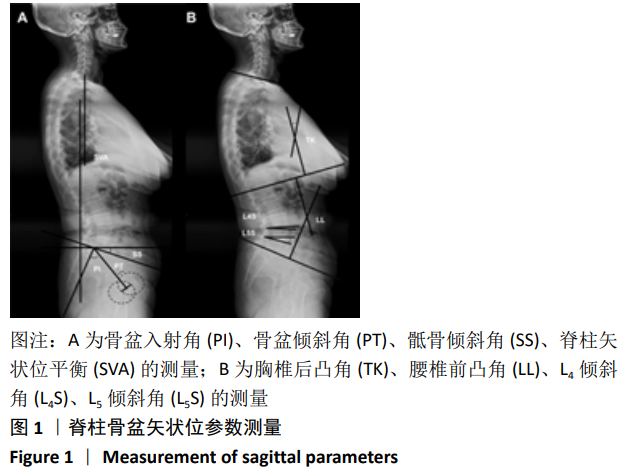
脊柱骨盆参数:脊柱骨盆矢状面平衡对维持正常的脊柱生物力学至关重要,相应的脊柱骨盆参数为脊柱疾病的诊断、治疗提供重要的参考依据。站立位脊柱骨盆全长X射线片检查是评估脊柱骨盆参数的主要测量方法,主要包括腰椎前凸角、胸椎后凸角、矢状位垂直轴、骶骨倾斜角、骨盆投射角、骨盆倾斜角等相关参数。
生活质量评价:生活质量是不同文化和价值体系中个体对他们的目标、期望、标准、所关心的事情及生存状况的体验。目前,生活质量评价已成为一种重要的医疗评价技术。SF-36量表是目前评价健康生活质量的通用量表,该表已在全球范围内广泛应用。SF-36量表包含8个维度,每个维度的测试不仅包含生理成分,还包括心理成分。该量表对于健康生活质量的评价更全面,在临床应用上具有很高的效度和信度。
背景:手术是治疗退变性腰椎滑脱的常用方式,但是部分患者出现术后健康生活质量改善不良,而患者术前脊柱骨盆参数与术后患者健康生活质量的关系尚不明确。
目的:基于脊柱骨盆参数探讨退变性腰椎滑脱患者术后健康生活质量改善不良的术前预测因素。
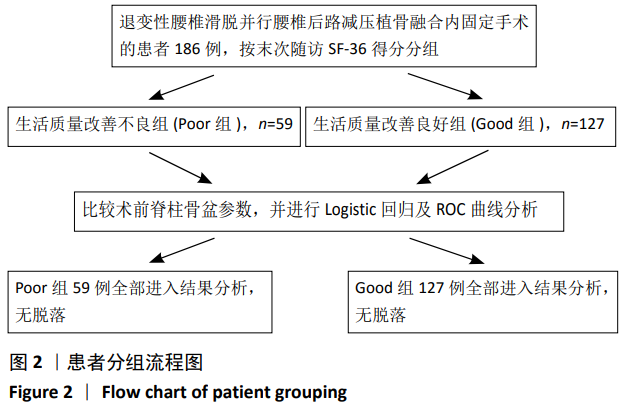
方法:回顾性分析2014年6月至2017年9月符合标准的退变性腰椎滑脱症患者186例,均行腰椎后路减压植骨融合内固定术,其中男 87 例,女 99例。①所有患者术前拍摄站立位脊柱全长X射线片,并测量矢状面脊柱骨盆参数:胸椎后凸角、腰椎前凸角、骨盆投射角、骨盆倾斜角、骶骨倾斜角、L4倾斜角、L5倾斜角和脊柱矢状位平衡。②末次随访采用SF-36量表对患者进行健康生活质量评定,并根据评分分为生活质量改善良好组(Good组)和生活质量改善不良组(Poor组)。比较两组患者的基本资料及脊柱骨盆参数,并应用Logistic回归及ROC曲线分析患者健康生活质量差的术前预测因素。
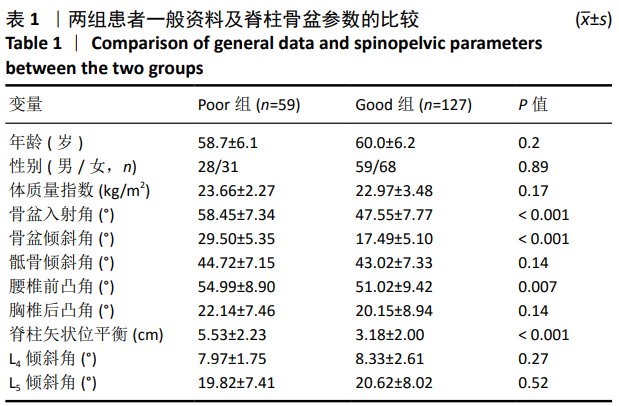
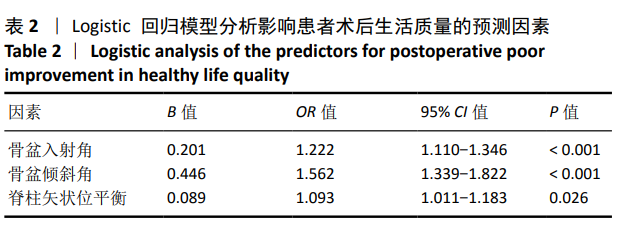
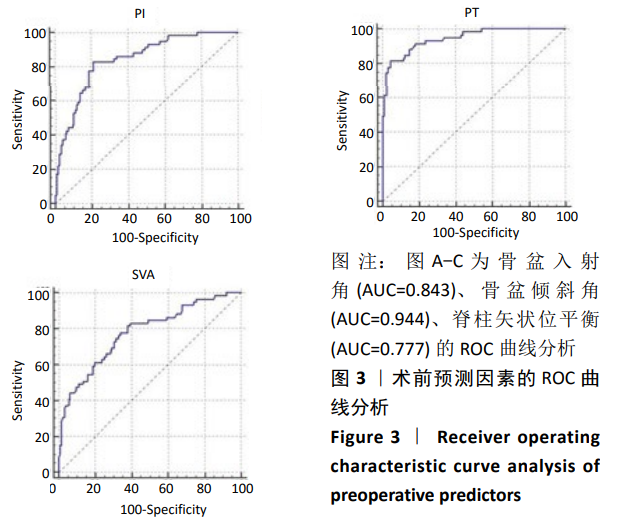
结果与结论:①全部病例均获得随访,随访时间20-26个月,平均24个月。②Good组127例,Poor组59例,生活质量改善不良患者占32%。组间比较显示Poor组的骨盆入射角、骨盆倾斜角、腰椎前凸角、脊柱矢状位平衡均大于Good组(P < 0.05),两组患者骶骨倾斜角、L4倾斜角、L5倾斜角及胸椎后凸角无统计学差异(P > 0.05)。③Logistic回归分析确定了3个术前预测因素:盆投射角(P < 0.001)、骨盆倾斜角(P < 0.001)和脊柱矢状位平衡(P=0.026)。④ROC曲线分析显示盆投射角> 52.18°,骨盆倾斜角> 25.23°,脊柱矢状位平衡> 3.84 cm 是术后患者生活质量改善不良的危险因素,其中骨盆倾斜角的AUC值(0.944)最大。提示对于术前伴有危险因素的患者应该引起足够的重视。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0404-672X (王海莹)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: