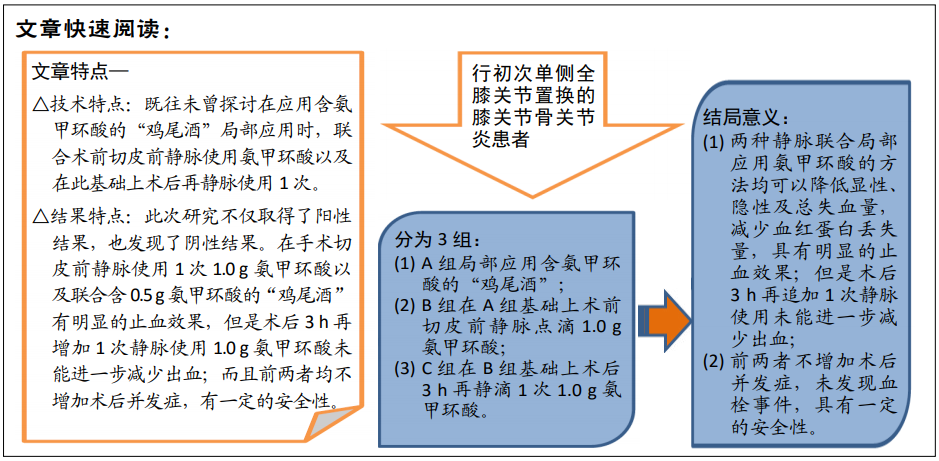
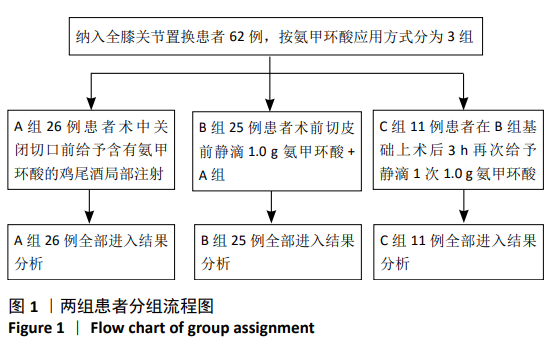
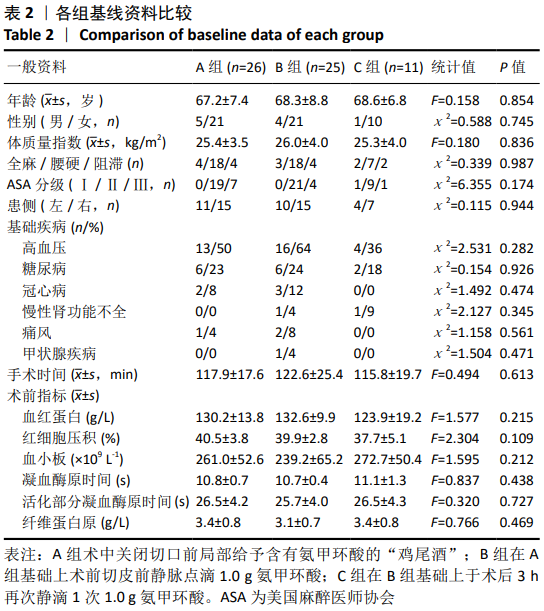
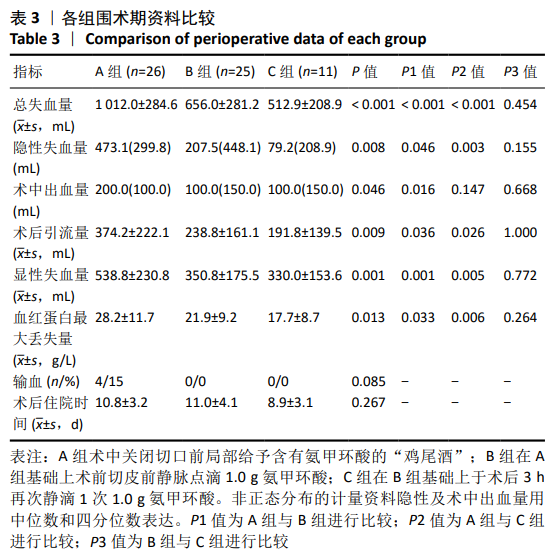
[1] LAWRIE CM, SCHWABE M, PIERCE A, et al. The cost of implanting a cementedversus cementless total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019; 101-B(7_Supple_C):61-63.
[2] KALAIRAJAH Y, SIMPSON D, COSSEY AJ, et al. Blood loss after total knee replacement: effects of computer-assisted surgery. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume, 2005,87(11):1480.
[3] 张岩,阚泉,张军伟,等. 重度膝骨关节炎患者全膝关节置换术中氨甲环酸静脉注射与关节腔内注射的止血效果对比观察[J]. 山东医药,2019,59(21): 58-60.
[4] BONG MR, PATEL V, CHANG E, et al. Risks associated with blood transfusion after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(3):281-287.
[5] GUERIN S, COLLINS C, KAPOOR H, et al. Blood transfusion requirement prediction in patients undergoing primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. Trans Med. 2007;17(1):37-43.
[6] KIM JL, PARK J, HAN S, et al. Allogeneic blood transfusion is a significant risk factor for surgical-site infection following total hip and knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(1):320-325.
[7] SHANDER A, HOFMANN A, OZAWA S, et al. Activity-based costs of blood transfusions in surgical patients at four hospitals. Transfusion. 2010;50(4):753-765.
[8] 薛晨曦, 姚运峰, 荆珏华. 全膝关节置换术中使用止血带的效果与安全性分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(6):626-628.
[9] 谢小伟, 岳辰, 黄泽宇, 等. 全膝关节置换术应用与不应用止血带的随机对照研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(17):1572-1576.
[10] 许宏, 张少云, 雷一霆, 等. 全膝关节置换术后多次静脉应用氨甲环酸的有效性及安全性[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2018,26(7):604-609.
[11] 蓝芳,林伟龙,林勇.静脉输注氨甲环酸对初次单侧全膝关节置换术后隐性出血的影响[J].现代实用医学,2018,30(7): 910-912.
[12] TENGBORN L, BLOMBÄCK M, BERNTORP E. Tranexamic acid - an old drug still going strong and making a revival. Thromb Res. 2015;135(2): 231-242.
[13] LEURCHARUSMEE P, SAWADDIRUK P, PUNJASAWADWONG Y, et al. The possible pathophysiological outcomes and mechanisms of tourniquet-induced ischemia-reperfusion injury during total knee arthroplasty. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2008:8087598.
[14] ARTHUR JR, SPANGEHL MJ. Tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2019;32:719-729.
[15] HUANG Z, XIE X, LI L, et al. Intravenous and topical tranexamic acid alone are superior to tourniquet use for primary total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2017;99(24):2053-2061.
[16] TILLE E, MYSLIWIETZ J, BEYER F, et al. Intraarticular use of tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rate after primary total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):341.
[17] ZHANG Y, YANG B, SUN X, et al. Combined intravenous and intra-articular tranexamic acid administration in total knee arthroplasty for preventing blood loss and hyperfibrinolysis. Medicine. 2019;98(7):e14458.
[18] LI J, MA Y, XIAO L. Postoperative Pain Management in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthop Surg. 2019; 11: 755-761.
[19] DANOFF JR, GOEL R, HENDERSON RA, et al. Periarticular Ropivacaine Cocktail Is Equivalent to Liposomal Bupivacaine Cocktail in Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:2455-2459.
[20] 何智超, 徐谦, 程兴旺, 等. 局部应用氨甲环酸复合镇痛鸡尾酒减少全膝关节置换术后出血的作用[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2017,33(7):640-645.
[21] 邱贵兴. 中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2009,3(3):380-383.
[22] GROSS JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983;58(3):277-280.
[23] NADLER SB, HIDALGO JH, BLOCH T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;51:224-232.
[24] ABDEL MP, CHALMERS BP, TAUNTON MJ, et al. Intravenous versus topical tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2018;100(12):1023-1029.
[25] MOSKAL J, CAPPS S. Intra-articular Tranexamic Acid in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: Meta-analysis. J Knee Surg. 2017;31(1):56-67.
[26] MI B, LIU G, LV H, et al. Is combined use of intravenous and intraarticular tranexamic acid superior to intravenous or intraarticular tranexamic acid alone in total knee arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):61.
[27] GUO P, HE Z, WANG Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty. Medicine. 2018;97(18):e587.
[28] PUA Y, POON CL, SEAH FJ, et al. Predicting individual knee range of motion, knee pain, and walking limitation outcomes following total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthopaedica. 2019;90(2):179-186.
[29] ZHAO J, DAVIS SP. An integrative review of multimodal pain management on patient recovery after total hip and knee arthroplasty. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019;98:94-106.
[30] 秦海江, 杨青, 张永战. 氨甲环酸联合“鸡尾酒”灌注在初次膝关节置换中的应用[J]. 实用医学杂志,2018,34(8):1343-1346.
[31] MORRISON RJM, TSANG B, FISHLEY W, et al. Dose optimisation of intravenous tranexamic acid for elective hip and knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(8):499-505.
[32] SUKEIK M, ALSHRYDA S, POWELL J, et al. The effect of tranexamic acid on wound complications in primary total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Surgeon. 2020;18: 53-61.
[33] 胡旭栋, 周宗科, 裴福兴, 等. 全膝关节置换围手术期氨甲环酸不同使用方法的有效性和安全性[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2014,34(6):599-604.
[34] XIE J, HU Q, MA J, et al. Multiple boluses of intravenous tranexamic acid to reduce hidden blood loss and the inflammatory response following enhanced-recovery primary total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(11):1442-1449.
[35] LEI Y, HUANG Q, HUANG Z, et al. Multiple-dose intravenous tranexamic acid further reduces hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(9):2940-2945.
|