中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 1318-1323.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3751
• 骨与关节生物力学Bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
骶骨精准切除影响骨盆稳定性的冯米斯应力特征及临床验证
姜 勇1,罗 翼2,丁永利1,周 勇2,闵 理2,唐 凡2,张闻力2,段 宏2,屠重棋2
- 1河南中医药大学第一附属医院骨伤科,河南省郑州市 450000;2四川大学华西医院骨科,四川省成都市 610041
Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation
Jiang Yong1, Luo Yi2, Ding Yongli1, Zhou Yong2, Min Li2, Tang Fan2, Zhang Wenli2, Duan Hong2, Tu Chongqi2
- 1Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
冯米斯应力:是针对塑性材料或弹塑性材料的强度理论,即材料力学中的第四强度理论,该理论认为形状改变比能是引起材料破坏的主要原因,也就是认为无论是复杂应力状态或简单应力状态,形状改变比能都是引起流动(即塑性)破坏的主要因素。
骶骨肿瘤:主要是指骶骨的原发性肿瘤,以原发性恶性肿瘤为主,最常见的是脊索瘤。
背景:骶骨切除现已成为公认的骶骨恶性肿瘤首选治疗方案。关于单纯骶骨切除后是否会发生骨折或骶髂关节滑脱的生物力学相关研究较少,对于骶骨次全切除后能否完全负重与何时重建等相关问题尚未达成共识。
目的:通过对完整骨盆和不同平面骶骨切除后的新鲜骨盆模型行生物力学测试,分析冯米斯应力变化,并结合临床试验,以明确高位骶骨切除至何种程度时无需行腰骶髂重建。
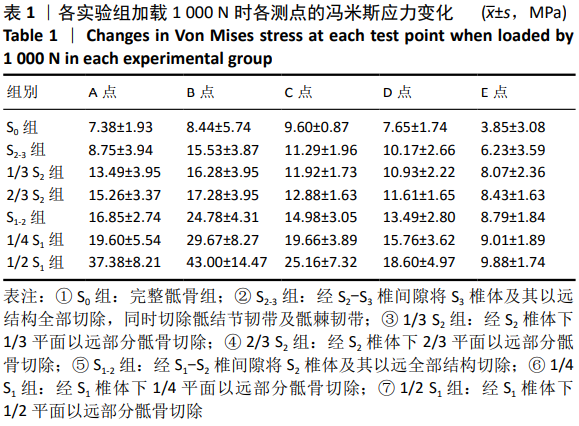
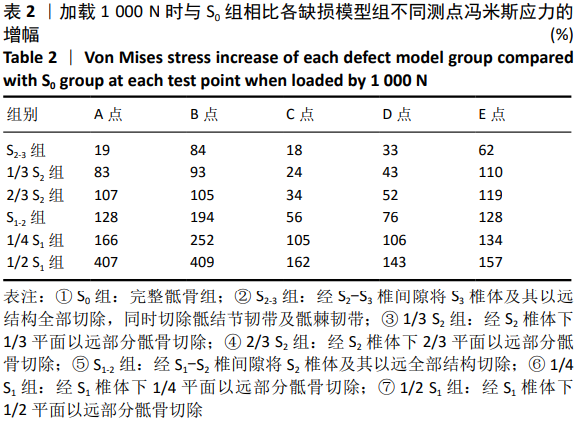
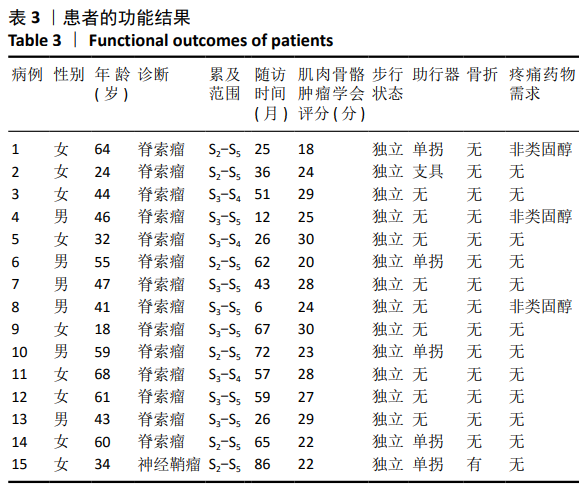
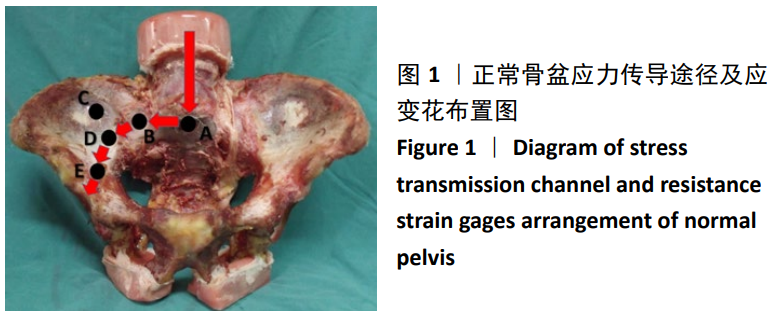
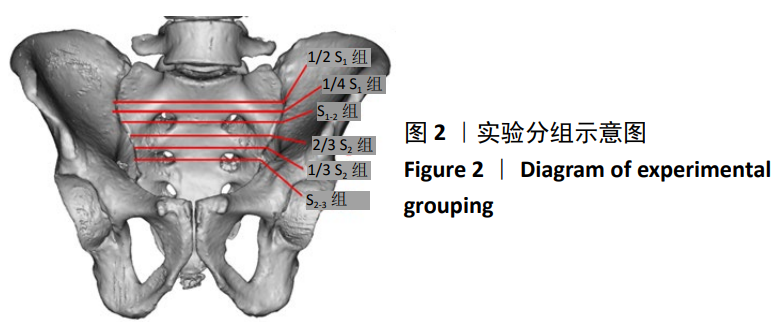
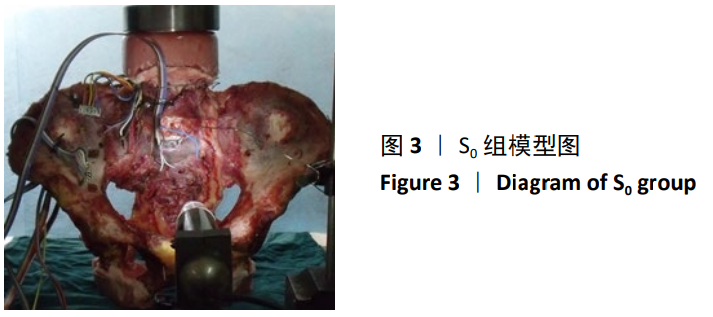
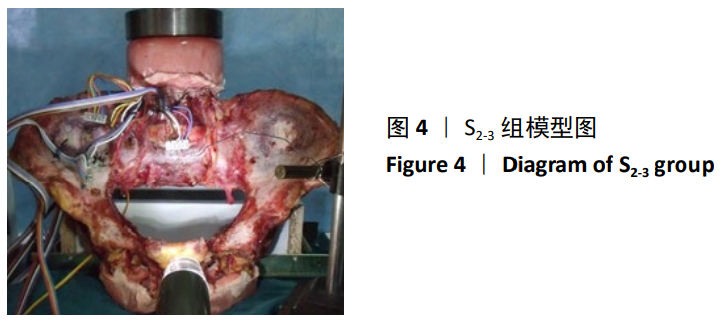
方法:①生物力学实验:选用6具正常成年男性新鲜尸体L5-骨盆标本,应用200 N增量分级加载,以1.4 mm/min速率平稳加载直至1 000 N,逐次测试完整骶骨组以及不同平面骶骨切除组骨盆模型的冯米斯应力变化,比较各组数据间的差异;②临床研究:2012年1月至2019年6月共纳入15例高位骶骨肿瘤单纯切除术病例,其中男6例,女9例,年龄(46.40±14.94)岁。根据术前MRI检查明确肿瘤累及骶骨的范围,确定骶骨切除的范围大小,术后未予重建,记录术后功能与并发症情况。
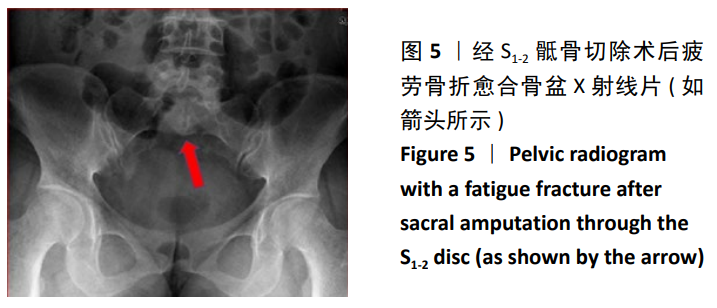
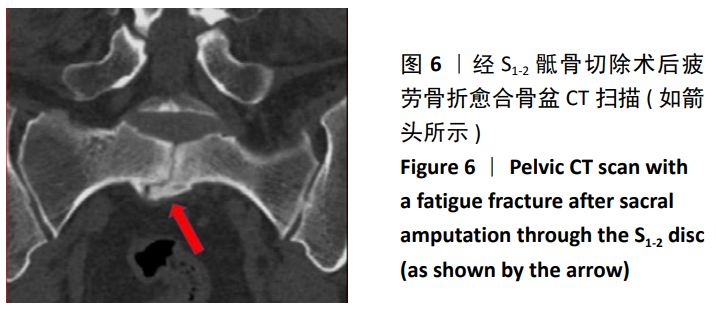
结果与结论:①生物力学实验:随着骶骨切除平面的增高,冯米斯应力在各个测试点均存在不同程度增大,尤以切除平面经过S1下1/4-下1/2时变化明显,与余各组相比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);而S1-2组与2/3 S2组、1/3 S2组相比,A点的冯米斯应力变化差异无显著性意义;②临床试验:15例患者中4例术中保留完整S1椎体(经S1-S2椎间隙切除,如生物力学实验S1-2组切除),3例患者术中如2/3 S2组切除,2例患者术中如1/3 S2组切除,6例患者术中保留完整S1及S2椎体(如S2-3组切除)。患者术后肌肉骨骼肿瘤学会评分为(25.27±3.79)分,所有患者均可行走,9例患者不需要借助支持物即可行走,另有6例患者行走时需要借助助行器,其中1例发生残余骶骨骨折;(3)提示随着骶骨的切除平面增高,残留骶骨的冯米斯应力急剧升高,经S1-S2椎间隙切除骶骨时,骨盆环的稳定性尚可,无需行腰骶髂重建。
https//orcid.org/0000-0002-7637-0935 (姜勇)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: