中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 1387-1392.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.4013
• 脊柱植入物Spinal implants • 上一篇 下一篇
微创经椎间孔椎间融合治疗单节段腰椎管狭窄症对腰椎-骨盆平衡的改善作用
姚汝斌,王仕永,杨开舜
- 大理大学第一附属医院脊柱外科,云南省大理市 671000
Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis improves lumbar-pelvic balance
Yao Rubin, Wang Shiyong, Yang Kaishun
- Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dali University, Dali 671000, Yunnan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
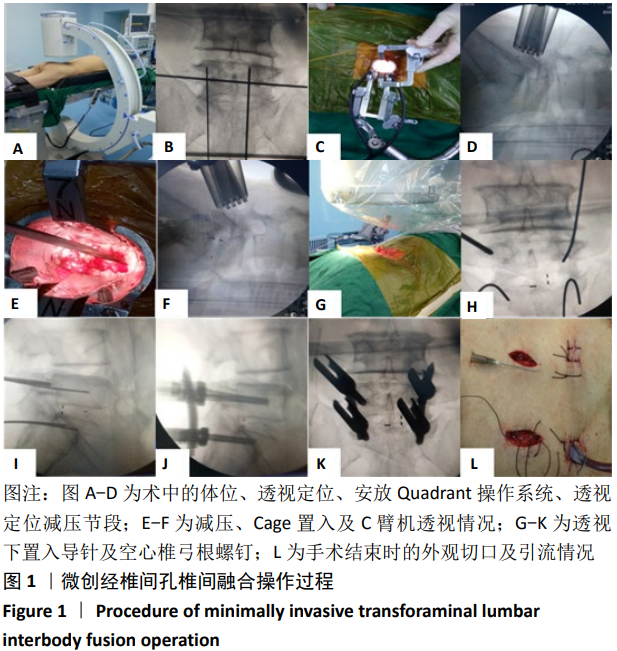
微创经椎间孔椎间融合:于2002年Foley等首次报道,该技术不破坏多裂肌在棘突的起点部位,通过解剖明确的神经血管和肌肉间隙,限制外科操作通道的宽度来减少软组织损伤。
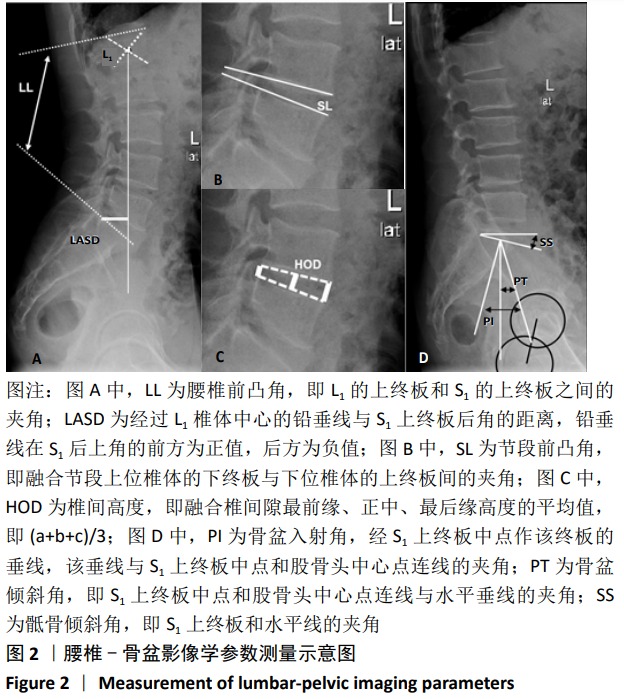
腰椎-骨盆参数:骨盆形态对整个脊柱序列有决定性作用,也是脊柱尤其是腰椎生理曲度重建的重要参考指标,目前被广泛使用的腰椎-骨盆矢状位参数有骨盆入射角、骨盆倾斜角、骶骨倾斜角、腰椎前凸角、腰椎节段前凸、L1中垂线与S1后上角的距离等。
背景:越来越多的研究认为腰椎-骨盆参数与腰椎融合术后的临床效果以及邻近节段退变密切相关,但微创经椎间孔椎间融合对腰椎-骨盆参数的影响并不明确。
目的:评价微创经椎间孔椎间融合对单节段腰椎管狭窄症患者腰椎-骨盆影像学参数的影响。
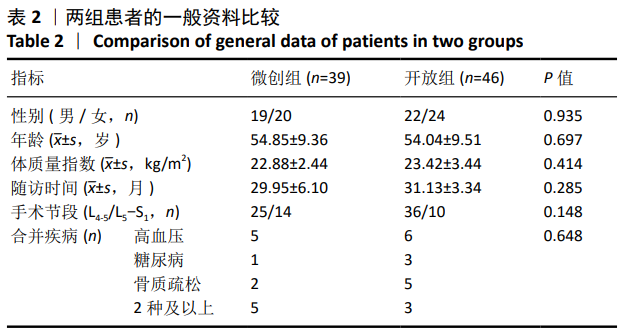
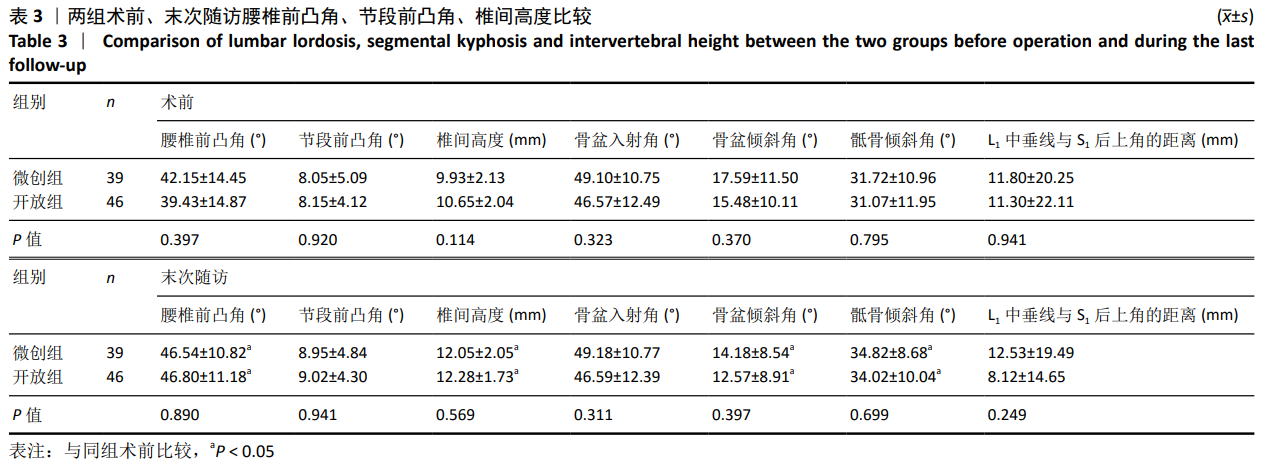
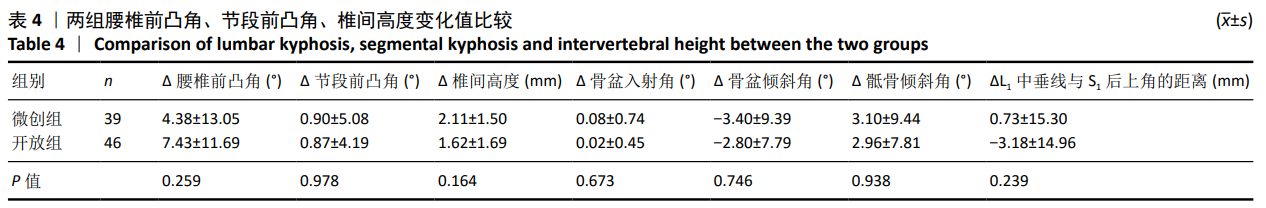
方法:回顾性分析2015年1月至2017年1月于大理大学第一附属医院就诊,采用经椎间孔椎间融合治疗的85例单节段腰椎管狭窄症患者的临床资料,其中行微创经椎间孔椎间融合手术39例(微创组),行开放经椎间孔椎间融合手术46例(开放组)。在包含双侧股骨头的站立腰椎侧位X射线片上,测量所有患者术前及末次随访时的腰椎前凸角、节段前凸角、椎间高度、L1中垂线与S1后上角的距离、骨盆入射角、骨盆倾斜角、骶骨倾斜角,并计算骨盆入射角与腰椎前凸角的差值及腰椎前凸角与骨盆入射角的比值。
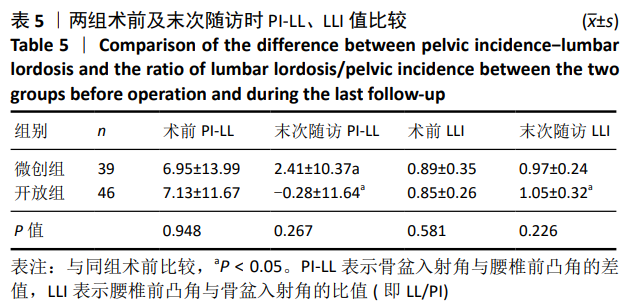
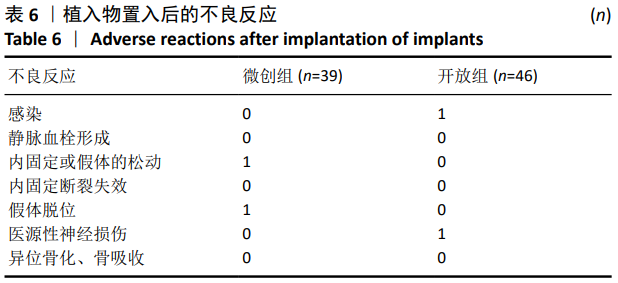
结果与结论:①末次随访时,两组的腰椎前凸角、椎间高度、骶骨倾斜角均较术前增大,而骨盆倾斜角较术前减小,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);两组末次随访时的腰椎前凸角、节段前凸角、椎间高度、骨盆入射角、骨盆倾斜角、骶骨倾斜角、L1中垂线与S1后上角的距离相比,差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②末次随访时,两组的腰椎前凸角、节段前凸角、椎间高度、骨盆入射角、骨盆倾斜角、骶骨倾斜角、L1中垂线与S1后上角的距离与术前对应参数的差值相比,差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③两组的骨盆入射角与腰椎前凸角差值在末次随访时均较术前明显减小,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);两组的腰椎前凸角与骨盆入射角比值在末次随访时均较术前增大,其中开放组变化显著(P < 0.05);但骨盆入射角与腰椎前凸角差值及腰椎前凸角与骨盆入射角比值两组间比较,差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④提示对于单节段腰椎椎管狭窄症,与开放经椎间孔椎间融合相比,微创经椎间孔椎间融合在恢复腰椎生理前凸、椎间高度、改善腰椎-骨盆平衡方面拥有同等的效果。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6481-6816 (姚汝斌)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: