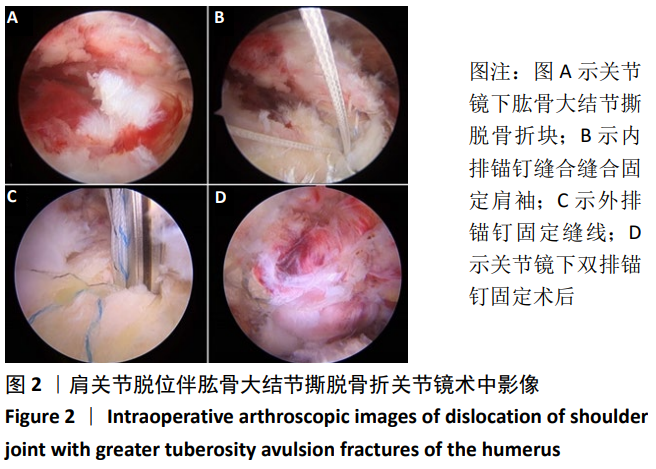
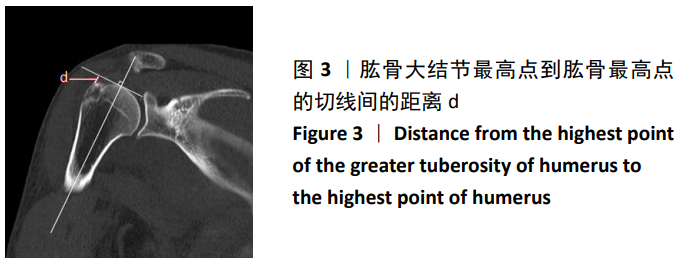
[1] KESMEZACAR H. The evaluation and treatment of acute anterior shoulder dislocation. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2005; 39 Suppl 1: 40-47.
[2] DUSSING F, PLACHEL F, GROSSAUER T, et al. Anterior shoulder dislocation and concomitant fracture of the greater tuberosity: Clinical and radiological results. Obere Extrem.2018;13(3): 211-217.
[3] GODIN JA, KATTHAGEN JC, FRITZ EM, et al. Arthroscopic Treatment of Greater Tuberosity Avulsion Fractures. Arthrosc Tech. 2017; 6(3): e777-e783.
[4] MUTCH J, LAFLAMME GY, HAGEMEISTER N, et al. A new morphological classification for greater tuberosity fractures of the proximal humerus: validation and clinical implication. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(5):646-651.
[5] MATTYASOVSZKY SG, BURKHART KJ, AHLERS C, et al. Isolated fractures of the greater tuberosity of the proximal humerus: a long-term retrospective study of 30 patients. Acta Orthop. 2011; 82(6): 714-720.
[6] ROULEAU DM, MUTCH J. Surgical treatment of displaced greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016; 24(1): 46-56.
[7] WHITE EA, SKALSKI MR, PATEL DB, et al. Isolated greater tuberosity fractures of the proximal humerus: anatomy, injury patterns, multimodality imaging, and approach to management. Emerg Radiol. 2018; 25(3): 235-246.
[8] LEVY DM, ERICKSON BJ, HARRIS JD, et al. Management of isolated greater tuberosity fractures: a systematic review. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2017; 46(6): E445-E453.
[9] BOGDAN Y, GAUSDEN EB, ZBEDA R, et al. An alternative technique for greater tuberosity fractures: use of the mesh plate. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017; 137(8):1067-1070.
[10] WHITE EA, SKALSKI MR, PATEL DB, et al. Isolated greater tuberosity fractures of the proximal humerus: anatomy, injury patterns, multimodality imaging, and approach to management. Emerg Radiol. 2018;25(3):235-246.
[11] MUHM M, AREND S, WINKLER H. Associated injuries with greater tuberosity fractures: Mechanism of injury, diagnostics, treatment. Der Unfallchirurg. 2017; 120(10):854-864.
[12] LONGO UG, CORBETT S. Missed fractures of the greater tuberosity. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):313.
[13] MUTCH J, LAFLAMME GY, HAGEMEISTER N, et al. A new morphological classification for greater tuberosity fractures of the proximal humerus: validation and clinical implications. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(5):646-651.
[14] BRAIS G, MÉNARD J, MUTCH J, et al. Transosseous braided-tape and double-row fixations are better than tension band for avulsion-type greater tuberosity fractures. Injury. 2015;46(6):1007-1012.
[15] MORASH K, RAVIPATI APT. Arthroscopic, nonrigid fixation of a displaced glenoid fracture after anterior shoulder dislocation. Arthrosc Tech. 2020;9(2): e233-e237.
[16] MONTGOMERY C, O’BRIAIN DE, HURLEY ET, et al. Video Analysis of Shoulder Dislocations in Rugby: Insights Into the Dislocating Mechanisms. Am J Sports Med. 2019; 47(14): 3469-3475.
[17] 梁达强,丘志河,柳海峰,等.肩关节前向脱位及合并损伤的手术治疗进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2019,33(6):768-773.
[18] HÉBERT-DAVIES J, MUTCH J, ROULEAU D. Delayed migration of greater tuberosity fractures associated with anterior shoulder dislocation. J Orthop Trauma.2015; 29(10): e396-400.
[19] SHAW L, HONG CK, KUAN FC, et al. The incidence of occult and missed surgical neck fractures in patients with isolated greater tuberosity fracture of the proximal humerus. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019; 20(1):482.
[20] CHENG MF, HUNG SH, SU YP, et al. Displaced isolated greater tuberosity fractures of elder adults treated with plate osteosynthesis. J Chin Med Assoc. 2019;82(4):318-321.
[21] JI JH, JEONG JJ, KIM YY, et al. Clinical and radiologic outcomes of arthroscopic suture bridge repair for the greater tuberosity fractures of the proximal humerus. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017; 137(1): 9-17.
[22] JANSSEN SJ, HERMANUSSEN HH, GUITTON TG, et al. Greater tuberosity fractures: does fracture assessment and treatment recommendation vary based on imaging modality? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(5): 1257-1265.
[23] 张德刚,孙建云,李萌,等.钩状钢板与空心螺钉治疗劈裂型肱骨大结节骨折的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(6):495-499.
[24] 刘刚,张磊,汪国友,等.全关节镜下双排缝合锚钉修复肱骨大结节MutchⅠ型骨折的临床分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(19): 3005-3010.
[25] 王光勇,杜俊生,钟兵.钢板和空心螺钉置入修复劈裂型肱骨大结节骨折:肩关节功能比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(40): 6482-6487.
[26] GAUDELLI C, MNARD J, MUTCH J, et al. Locking plate fixation provides superior fixation of humerus split type greater tuberosity fractures than tension bands and double row suture bridges. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2014;29(9):1003-1008.
[27] LIN CL, YEH ML, SU FC, et al. Different suture anchor fixation techniques affect contact properties in humeral greater tuberosity fracture: a biomechanical study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):26.
[28] GUO J, LIU Y, JIN L, et al. Size of greater tuberosity fragment: a risk of iatrogenic injury during shoulder dislocation reduction. Int Orthop.2019;43(5):1215-1222.
[29] HU C, ZHOU K, PAN F, et al. Application of pre-contoured anatomic locking plate for treatment of humerus split type greater tuberosity fractures: A prospective review of 68 cases with an average follow-up of 25 years. Injury. 2018;49(6):1108-1112.
[30] YOON TH, CHOI CH, CHOI YR, et al. Clinical outcomes of minimally invasive open reduction and internal fixation by screw and washer for displaced greater tuberosity fracture of the humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(6):e173-e177. |