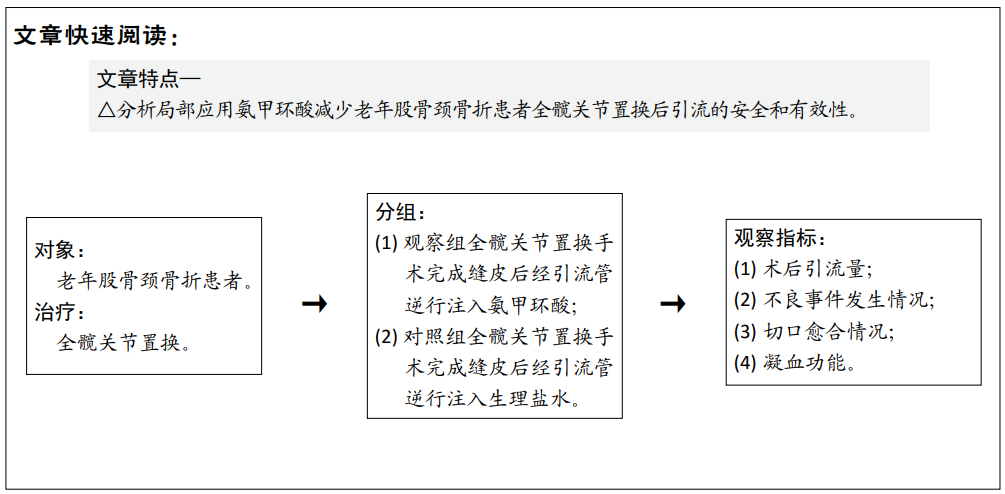
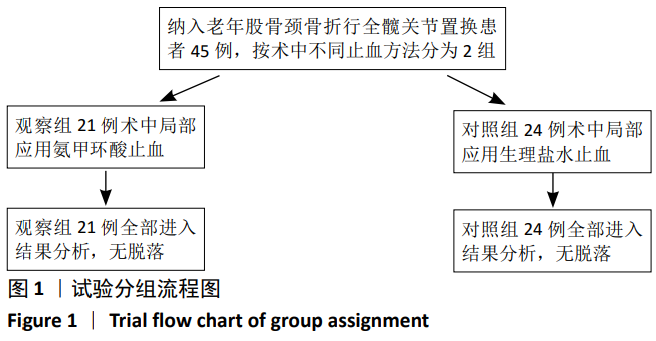
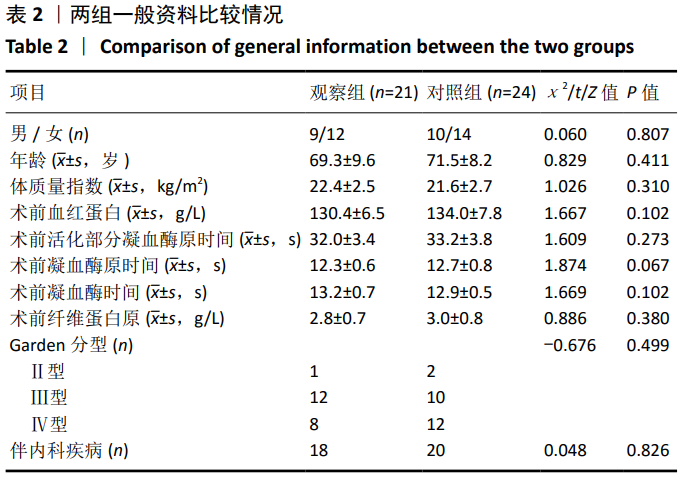
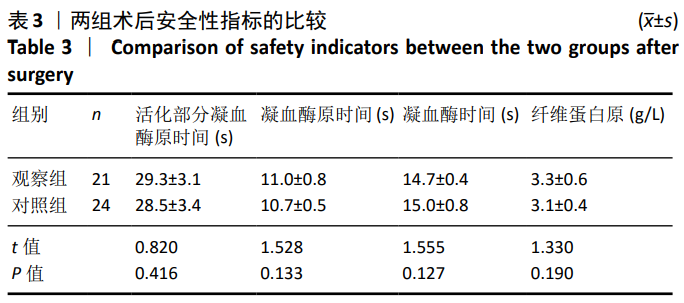
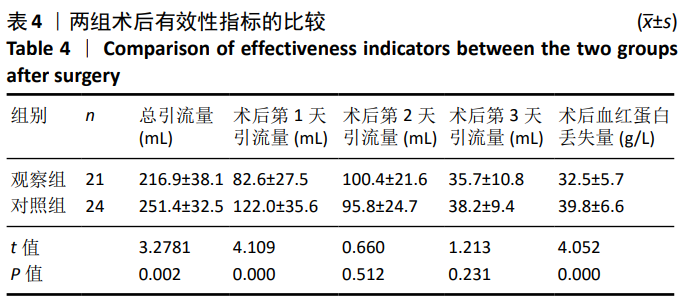
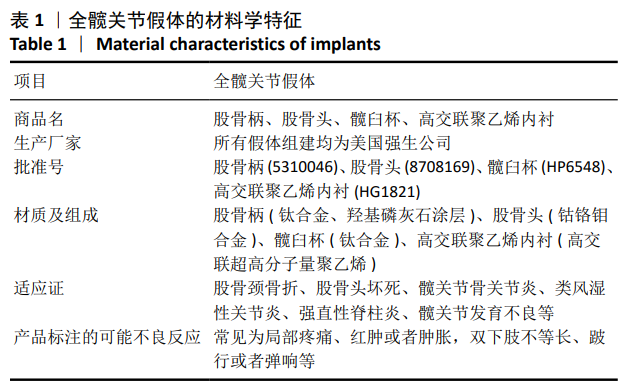
[1] 李宁,刘昊楠,龚晓峰,等.北京某三甲医院股骨颈骨折住院患者现状的流行病学分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2016,48(2): 292-296.
[2] 李强,宋世锋,余斌,等.初次全髋关节置换治疗老年股骨颈骨折的效果及影响因素[J].局解手术学杂志,2018,27(1):68-72.
[3] 危杰.老年股骨颈骨折的治疗要点及注意事项[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(9):826-828.
[4] 金忠宇,曹力.老年股骨颈骨折治疗的相关研究进展[J].医学综述, 2019,25(6):1165-1170,1175.
[5] 王浩洋,康鹏德,裴福兴,等.氨甲环酸减少全髋关节置换术围手术期失血的有效性及安全性研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015, 30(8):649-654.
[6] BLANIÉ A, BELLAMY L, RHAYEM Y, et al. Duration of Postoperative Fibrinolysis after Total Hip or Knee Replacement:A Laboratory Follow-up Study. Thromb Res. 2012;131(1):e6-e11.
[7] DE JONGE T. Pharmacological reduction of bleeding during hip endoprosthetic replacement. Orv Hetil. 2012;153(41):1607-1612.
[8] 朱瑞霞,赵公吟,王亮亮,等.直接前方和后外侧入路人工髋关节置换治疗老年股骨颈骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤杂志,2019, 35(8):730-735.
[9] 胡闯,王兵,王廷江,等.初次全髋关节置换术治疗老年股骨颈骨折的效果及影响因素分析[J].中国综合临床,2017,33(12):1108-1111.
[10] 周宗科,黄泽宇,杨惠林,等.中国骨科手术加速康复围手术期氨甲环酸与抗凝血药应用的专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2019,12(2):81-88.
[11] 朱燕宾,马信龙,韩鸿宾,等.京津冀地区1334例60岁及以上患者股骨颈骨折流行病学特征分析[J].中国临床医生杂志,2015, 43(10):47-49.
[12] 付廷,舒科杰,尹良军.序贯应用氨甲环酸对老年股骨颈骨折全髋关节置换术失血的疗效分析[J].检验医学与临床,2019,16(20): 2982-2984,2988.
[13] BRUCE W,CAMPBELL D,DALY D,et al. Practical recommendations for patient blood management and the reduction of perioperative transfusion in joint replacement surgery. ANZ J Surg, 2012,83(4): 222-229.
[14] 田敏,崔存宝,王东辰,等.老年股骨颈骨折人工髋关节置换67例临床报告[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(14):1325-1327.
[15] 骆国钢,林忠勤,谢海风,等.氨甲环酸不同用药途径对女性股骨颈骨折全髋关节置换术失血的疗效分析[J].中国骨伤,2018,31(12): 1086-1090.
[16] 谢美兆,练伟东,张浩,等.全髋置换局部应用氨甲环酸后输血及成本效益分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2016,22(5):399-402.
[17] 彭浩.氨甲环酸在老年股骨颈骨折全髋关节置换术中的临床应用[J].广州医科大学学报,2019,47(1):114-116.
[18] BENONI G,FREDIN H,KNEBEL R,et al.Blood conservation with tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty:A randomized,double-blind study in 40 primary operations.Acta Orthop Scand. 2001;72(5):442-448.
[19] WEI Z,LIU M.The effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in total hip or knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis of 2720 cases.Transfus Med. 2015;25(3):151-162.
[20] WU XD,CHEN Y,TIAN M,et al.Application of thrombelastography (TEG) for safety evaluation of tranexamic acid in primary total joint arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):214.
[21] 朱前拯,于彩霞,陈星佐,等.氨甲环酸对人工关节置换术治疗老年股骨颈骨折围手术期失血的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018, 20(7):623-626.
[22] ZHANG P, HE J, FANG Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of intravenous tranexamic acid administration in patients undergoing hip fracture surgery for hemostasis. Medicine. 2017;96(21):e6940.
[23] 赵凯华,余锐,刘强,等.骨折患者凝血四项与D-二聚体、FDP检测分析[J].实验与检验医学,2014,32(5):623-625.
[24] 张德盛,刘树平,刘跃洪,等.全髋关节置换术后并发深静脉血栓的危险性分析[J].医学临床研究,2016,33(2):235-237.
[25] 于杰,曾春,蔡道章.骨科大手术围手术期止血及抗凝药物的选择[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2016,10(1):100-104.
[26] 廖柏强.氨甲环酸对老年陈旧性股骨颈骨折伴骨质疏松行髋关节置换术失血的影响[J].中外医学研究,2019,17(3):160-162.
[27] 赵相杰,彭朝华,杨彬.静脉结合关节腔内应用氨甲环酸对全髋关节置换老年病人手术后隐性失血影响的研究[J].实用老年医学, 2018,32(9):835-838.
[28] 张静萍,刘欣伟,韩文锋,等.重组人促红细胞生成素联合氨甲环酸在高龄股骨颈骨折全髋关节置换术围术期血液管理中应用[J].临床军医杂志,2016,44(9):889-891.
[29] 张法尧,赵树森,谭红军.氨甲环酸滞留给药对全髋关节置换术后失血量的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(4):31-34.
[30] 王本海,林松庆,陈金水.单侧THA术后局部应用氨甲环酸与引流管夹闭2h的止血效果分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016, 31(5):554-555.
[31] KOYANO G, JINNO T, KOGA D, et al. Is Closed Suction Drainage Effective in Early Recovery of Hip Joint Function? Comparative Evaluation in One-Stage Bilateral Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;30(1):74-78.
[32] ZHOU KD, WANG HY, WANG Y, et al. Is topical or intravenous tranexamic acid preferred in total hip arthroplasty?A randomized, controlled,noninferiority clinical trial.PLoS One. 2018;13(10): e0204551.
[33] 董锋,严实,禄代锋,等.氨甲环酸对老年股骨颈骨折行全髋关节置换术围手术期失血的疗效分析[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2015, 49(4):331-334.
[34] SINGH J, BALLAL M, MITCHELL P, et al. Effects of Tranexamic Acid on Blood Loss during Total Hip Arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2010;18(3):282-286.
[35] LI J, ZHANG Z, CHEN J. Comparison of efficacy and safety of topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty:A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore).2016;95(36):e4689.
[36] ZHANG P, BAI J, HE J, et al. A systematic review of tranexamic acid usage in patients undergoing femoral fracture surgery.Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:1579-1591.
[37] 华政哲,张敬东,韩文峰,等.氨甲环酸止血对全髋关节置换术围术期失血量影响[J].临床军医杂志,2015,43(11):1115-1117.
[38] YAMASAKI S, MASUHARA K, FUJI T. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss after cementless total hip arthroplasty-prospective randomized study in 40 cases.Int Orthop. 2004;28(2):69-73.
[39] O’BRIEN JG, BATTISTINI B, ZAHARIA F, et al. Effects of tranexamic acid and aprotinin, two antifibrinolytic drugs,on PAF-induced plasma extravasation in unanesthetized rats.Inflammation.2000;24(5):411-429.
[40] WATTS C, HOUDEK M, SEMS S, et al. Tranexamic Acid Safely Reduced Blood Loss in Hemi- and Total Hip Arthroplasty for Acute Femoral Neck Fracture:A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(7): 345-351.
[41] KWAK DK, JANG CY, KIM DH, et al. Topical tranexamic acid in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures treated with hemiarthroplasty:Efficacy and safety?-A case-control study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):228.
[42] 段国庆,张玉革,任春凤.氨甲环酸关节内应用对全髋关节置换术后失血量的影响[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2015,21(5):466-469.
[43] BLANIE A, BELLAMY L, RHAYEM Y, et al. Duration of postoperative fibrinolysis after total hip or knee replacement:a laboratory follow-up study.Thromb Res.2013;131(1):e6-e11.
[44] 郝申申,刘延雄,刘志斌.局部应用氨甲环酸的全髋关节置换:回顾性分析不同时间引流量差异[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(23): 3628-3633.
[45] XU X, LI X, LIU W, et al. Longtime soaking of high concentration tranexamic acidin total hip arthroplasty:A prospective randomized controlled trial in 224 patients.Pak J Med Sci.2015;31(6):1306-1311.
[46] 陆华,孙美煜,顾荣胜,等.局部应用不同剂型氨甲环酸对全髋关节置换术后失血量的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(5): 40-43.
[47] 凡福成,桂斌捷.髋关节置换后氨甲环酸关节腔注射及间断夹管:出血量的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(40):6397-6402.
[48] 赵洪顺,阿尖措,高顺红,等.全髋关节置换局部应用氨甲环酸术中术后失血及白细胞介素6和C-反应蛋白的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(4):493-498.
[49] MCLEAN M, MCCALL K, SMITH I, et al. Tranexamic acid toxicity in human periarticular tissues.Bone Joint Res.2019;8:11-18.
[50] 杨宇翔,肖杰,马翅,等.氨甲环酸在全髋关节置换术中应用研究进展[J].创伤与急危重病医学,2017,5(3):152-156.
|