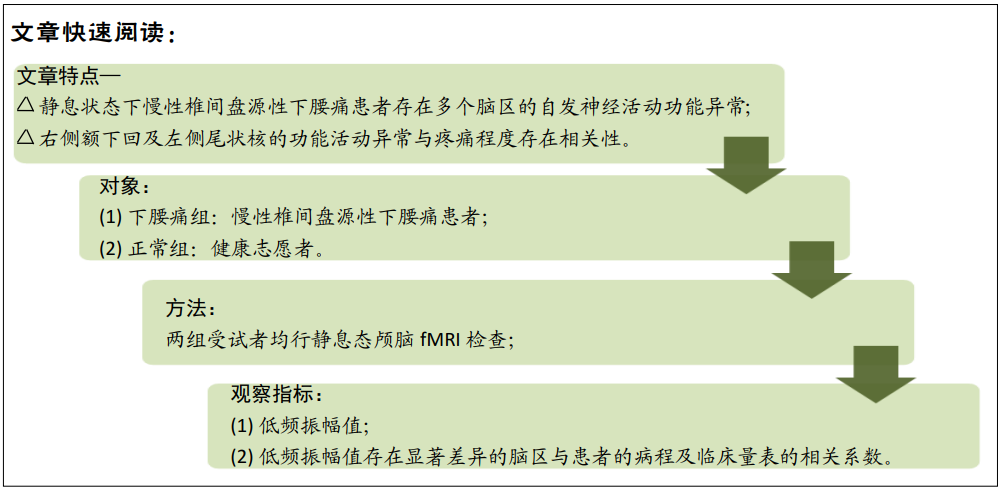
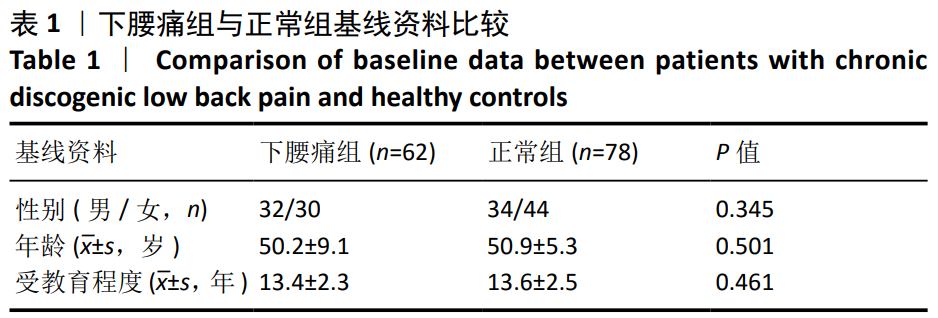
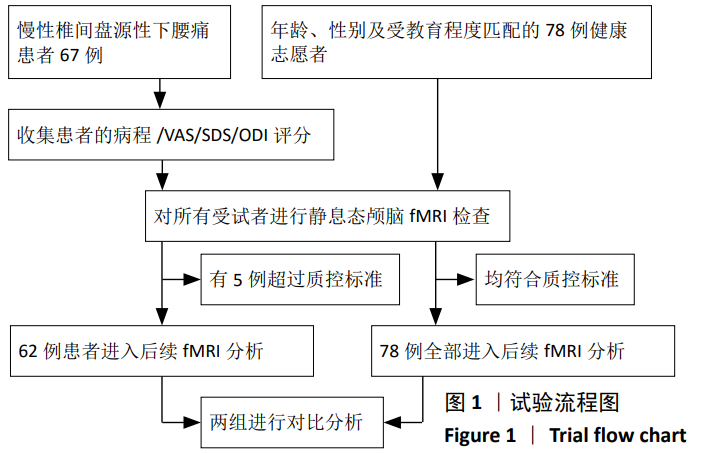
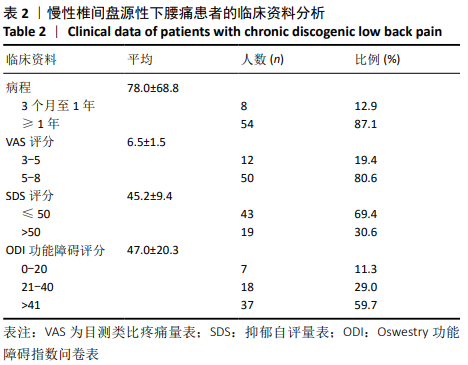
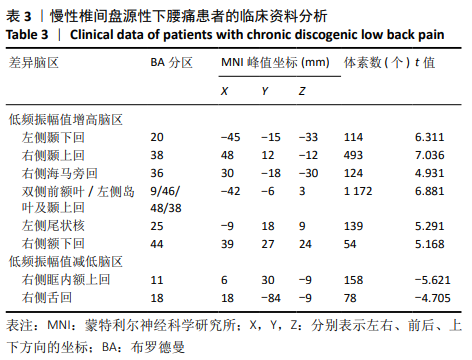
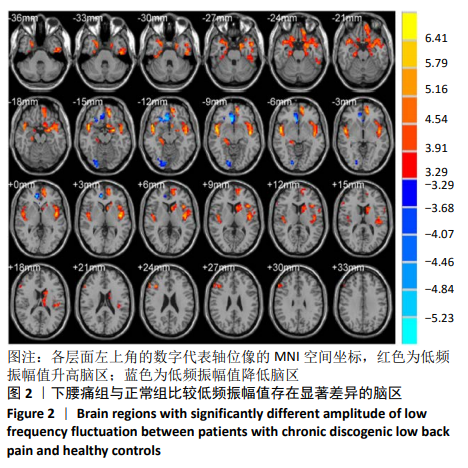
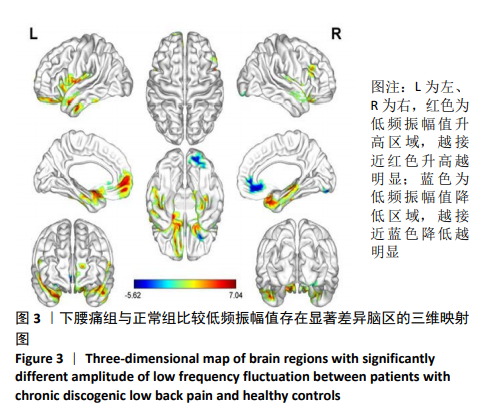
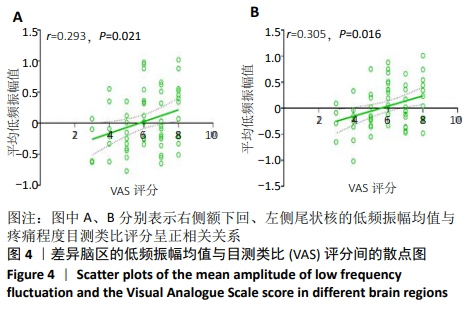
[1] SIMON J, MCAULIFFE M, SHAMIM F, et al. Discogenic low back pain.Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2014;25(2):305-317.
[2] GEURTS JW, WILLEMS PC, KALLEWAARD JW, et al. The Impact of Chronic Discogenic Low Back Pain: Costs and Patients’ Burden. Pain Res Manag. 2018;2018:4696180.
[3] DEPALMA MJ, KETCHUM JM, SAULLO T. What is the source of chronic low back pain and does age play a role?. Pain Med. 2011;12(2):224-233.
[4] 赵洪增,关文华,程敬亮,等.非包含性腰椎间盘突出患者不同介入治疗方法的选择[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3095-3099.
[5] 关文华,赵洪增,韩焱,等.腰椎间盘突出症伴发抑郁情绪与否临床特征的比较[J].中国行为医学科学,2003(5):63-64.
[6] 关文华,赵洪增,韩焱,等.伴发抑郁情绪对经皮腰椎间盘切吸术后疗效的影响(英文)[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(35):8102-8104.
[7] 陈龙梅,王珩.腰椎间盘突出症患者抑郁、焦虑状况及影响因素分析[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2014,20(6):437-440.
[8] SHEN W, TU Y, GOLLUB RL, et al. Visual network alterations in brain functional connectivity in chronic low back pain: A resting state functional connectivity and machine learning study. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;22:101775.
[9] HUANG S, WAKAIZUMI K, WU B, et al. Whole-brain functional network disruption in chronic pain with disk herniation. Pain. 2019;160(12):2829-2840.
[10] 赵彦琳,黄木华,章勇,等.椎间盘突出所致下腰腿痛患者后扣带回功能连接的静息态功能磁共振成像研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2019,38(6): 992-997.
[11] 刘涵静,邓钰,周福庆.慢性腰腿痛患者岛叶功能连接的静息态磁共振成像研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2019,38(11):2015-2020.
[12] ZHOU F, WU L, GUO L, et al. Local connectivity of the resting brain connectome in patients with low back-related leg pain: A multiscale frequency-related Kendall’s coefficient of concordance and coherence-regional homogeneity study. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;21:101661.
[13] 胡兰.椎间盘源性下腰痛患者静息态fMRI局部一致性研究[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2020,18(1):22-25+29.
[14] ZHANG B, JUNG M, TU Y, et al. Identifying brain regions associated with the neuropathology of chronic low back pain: a resting-state amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation study. Br J Anaesth. 2019;123(2):e303-e311.
[15] CHEN X, LU B, YAN CG. Reproducibility of R-fMRI metrics on the impact of different strategies for multiple comparison correction and sample sizes. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018;39(1):300-318.
[16] 李丽,覃媛媛,田甜,等.慢性下腰痛患者静息态功能磁共振成像脑活动差异研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2019,38(5):768-772.
[17] WANG JJ, CHEN X, SAH SK, et al. Amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) and fractional ALFF in migraine patients: a resting-state functional MRI study. Clin Radiol. 2016;71(6):558-564.
[18] 谢伟,李宗芳,赵卫,等.静息态fMRI观察特发性三叉神经痛患者脑内自发性活动[J].中国医学影像技术,2016,32(7):1020-1025.
[19] CHAO-GAN Y, YU-FENG Z. DPARSF: A MATLAB Toolbox for “Pipeline” Data Analysis of Resting-State fMRI. Front Syst Neurosci. 2010;4:13-20.
[20] ASHBURNER J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. Neuroimage. 2007;38(1):95-113.
[21] LI T, ZHANG S, KURATA J. Suppressed descending pain modulatory and enhanced sensorimotor networks in patients with chronic low back pain. J Anesth. 2018;32(6):831-843.
[22] FAIRBANK JC, PYNSENT PB. The Oswestry Disability Index.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(22):2940-2952.
[23] MARTUCCI KT, MACKEY SC. Neuroimaging of Pain: Human Evidence and Clinical Relevance of Central Nervous System Processes and Modulation. Anesthesiology. 2018;128(6):1241-1254.
[24] YANG Q, WANG Z, YANG L, et al. Cortical thickness and functional connectivity abnormality in chronic headache and low back pain patients. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017;38(4):1815-1832.
[25] LIU KC, YANG SK, OU BR,et al. Using Percutaneous Endoscopic Outside-In Technique to Treat Selected Patients with Refractory Discogenic Low Back Pain.Pain Physician.2019;22(2):187-198.
[26] RAYNER L, HOTOPF M, PETKOVA H, et al. Depression in patients with chronic pain attending a specialised pain treatment centre: prevalence and impact on health care costs. Pain. 2016;157(7):1472-1479.
[27] 张珊珊,吴文,刘自平,等.腰背痛对静息状态下岛叶神经功能连接的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2013,35(9):691-695.
[28] RODRIGUEZ-RAECKE R, IHLE K, RITTER C, et al. Neuronal differences between chronic low back pain and depression regarding long-term habituation to pain. Eur J Pain. 2014;18(5):701-711.
[29] ZHOU F, GU L, HONG S, et al. Altered low-frequency oscillation amplitude of resting state-fMRI in patients with discogenic low-back and leg pain. J Pain Res. 2018;11:165-176.
[30] CHEN S, DONG D, JACKSON T, et al. Trait-based food-cravings are encoded by regional homogeneity in the parahippocampal gyrus. Appetite. 2017; 114:155-160.
[31] VACHON-PRESSEAU E, TETREAULT P, PETRE B, et al. Corticolimbic anatomical characteristics predetermine risk for chronic pain. Brain. 2016; 139(Pt 7): 1958-1970.
[32] AYOUB LJ, BARNETT A, LEBOUCHER A, et al. The medial temporal lobe in nociception: a meta-analytic and functional connectivity study. Pain. 2019; 160(6):1245-1260.
[33] 张珊珊,吴文,刘自平,等.腰背痛患者静息态fMRI的脑功能局部一致性研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2013,12(5):506-510.
[34] 毛翠平,杨全新,唐鉴,等.慢性腰背痛患者的大脑灰质异常:基于体素的形态测量学分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2016,36(8):1041-1047.
[35] SCHULTZ W. Reward functions of the basal ganglia. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2016;123(7):679-693.
[36] GUNAYDIN LA, KREITZER AC. Cortico-Basal Ganglia Circuit Function in Psychiatric Disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 2016;78:327-350.
[37] OUCHI K, WATANABE M, TOMIYAMA C, et al. Emotional Effects on Factors Associated with Chronic Low Back Pain. J Pain Res. 2019; 12:3343-3353.
[38] MATSUO Y, KURATA J, SEKIGUCHI M, et al. Attenuation of cortical activity triggering descending pain inhibition in chronic low back pain patients: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Anesth. 2017; 31(4):523-530.
[39] IHARA N, WAKAIZUMI K, NISHIMURA D, et al. Aberrant resting-state functional connectivity of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex to the anterior insula and its association with fear avoidance belief in chronic neck pain patients. Plos One. 2019; 14(8):e0221023.
[40] KONG J, SPAETH RB, WEY HY, et al. S1 is associated with chronic low back pain: a functional and structural MRI study. Mol Pain. 2013; 9:43.
[41] 董帅珂,赵洪增.VBM对腰间盘突出慢性期疼痛患者脑结构的研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2018,16(6):123-126.
[42] HE BJ, SNYDER AZ, VINCENT JL, et al. Breakdown of Functional Connectivity in Frontoparietal Networks Underlies Behavioral Deficits in Spatial Neglect. Neuron. 2007;53(6):905-918.
[43] RAICHLE ME. The brain’s default mode network. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2015; 38:433-447.
[44] TU Y, JUNG M, GOLLUB RL, et al. Abnormal medial prefrontal cortex functional connectivity and its association with clinical symptoms in chronic low back pain. Pain. 2019;160(6):1308-1318.
[45] BECKER S, GANDHI W, POMARES F, et al. Orbitofrontal cortex mediates pain inhibition by monetary reward. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017;12(4): 651-661.
[46] BOCCIA M, NEMMI F, GUARIGLIA C. Neuropsychology of Environmental Navigation in Humans: Review and Meta-Analysis of fMRI Studies in Healthy Participants. Neuropsychology Rev. 2014; 24(2):236-251.
[47] 张珊珊,吴文,王楚怀,等.腰痛静息态功能磁共振比率低频振幅的研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(2):140-145.
[48] BALIKI MN, MANSOUR AR, BARIA AT, et al. Functional reorganization of the default mode network across chronic pain conditions. Plos One.2014; 9(9):e106133. |