中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 493-498.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2358
• 组织工程骨材料Tissue-engineered bone • 下一篇
载链霉素硫酸钙人工骨椎间孔镜下植入联合经皮置钉治疗腰椎结核
付拴虎1,秦 凯2,卢大汉1,覃海飚1,谷 金1,陈勇喜1,覃浩然1,韦家鼎1,伍 亮1,宋泉生1
- 1广西中医药大学第一附属医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530023;2江西省上饶县人民医院,江西省上饶市 334100
Lumbar spinal tuberculosis implanted with artificial bone with streptomycin sulfate and percutaneous pedicle screw under transforaminal endoscopy
Fu Shuanhu1, Qin Kai2, Lu Dahan1, Qin Haibiao1, Gu Jin1, Chen Yongxi1, Qin Haoran1, Wei Jiading1, Wu Liang1, Song Quansheng1
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2People’s Hospital of Shangrao County, Shangrao 334100, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
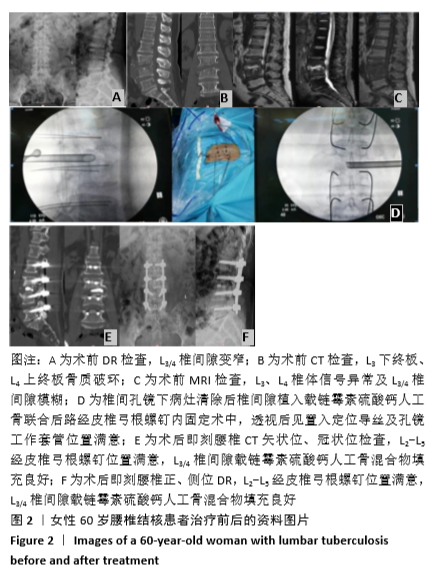
脊柱结核:占结核病的5%-10%,是一种常见的骨关节结核病,在发生的骨关节结核病中占首位,约50%,其中以腰椎发生率最高。结核杆菌侵犯脊柱后,典型的脊柱结核在影像学上可表现为椎间隙变窄、消失,椎体骨质破坏,死骨形成及椎旁脓肿存在,严重者导致后凸畸形、压迫脊髓神经,导致神经功能障碍,甚至截瘫,严重影响患者生活质量及身心健康。
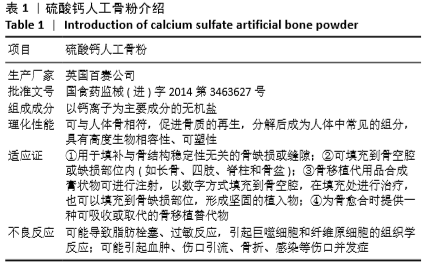
载结核药物硫酸钙人工骨性能:相关动物模型实验证实,载结核药物硫酸钙人工骨可缓慢、持久地释放结核药物,增加局部药物浓度,同时由于硫酸钙人工骨的特殊性,其又可以诱导成骨细胞活跃,修复病灶局部骨缺损,达到骨性融合的目的。
背景:相关骨结核动物模型实验显示,通过硫酸钙人工骨载药可缓慢、持久地释放抗结核药物,增加局部药物浓度,同时其还可修复病灶局部骨缺损,促进骨性融合。
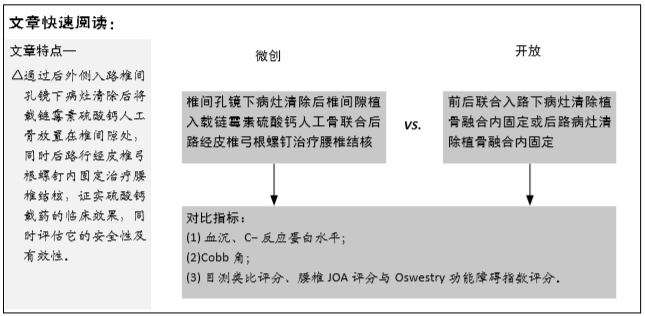
目的:评价椎间孔镜下病灶清除后椎间隙植入载链霉素硫酸钙人工骨联合后路经皮椎弓根螺钉治疗腰椎结核的安全性及有效性。
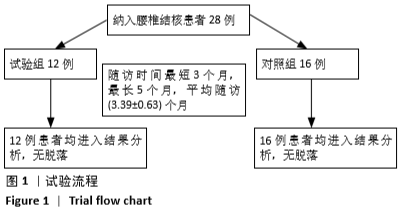
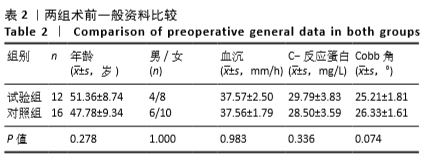
方法:选择2016年7月至2019年6月广西中医药大学第一附属医院收治的28例腰椎结核患者,其中男10例,女18例,年龄36-69岁,试验组12例接受椎间孔镜下病灶清除后椎间隙植入载链霉素硫酸钙人工骨联合后路经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗,对照组16例接受前后联合入路下病灶清除植骨融合内固定或后路病灶清除植骨融合内固定治疗,记录手术时间、术中出血量与住院时间。术后3个月及末次随访时,对比两组血沉、C-反应蛋白水平及Cobb角、目测类比评分、腰椎JOA评分与Oswestry功能障碍指数评分。试验获得广西中医药大学第一附属医院理委员会批准。
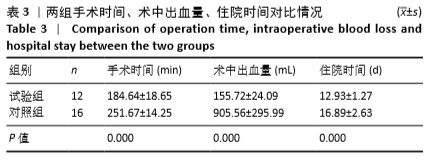
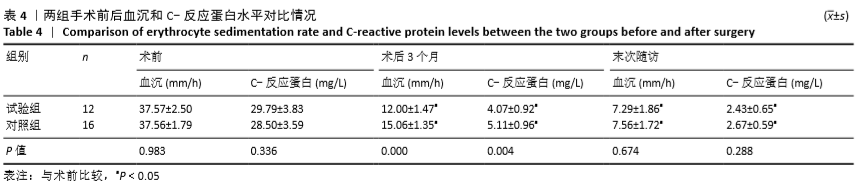
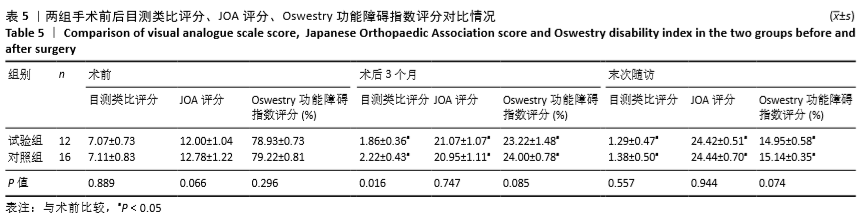
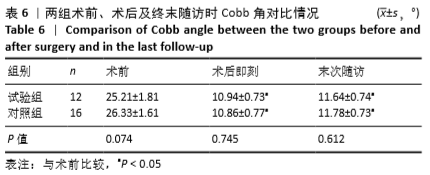
结果与结论:①试验组手术时间、术中出血量与住院时间均少于对照组(P < 0.05);②两组术后3个月及末次随访的血沉、C-反应蛋白水平低于术前(P < 0.05),试验组术后3个月的血沉、C-反应蛋白水平低于对照组(P < 0.05);③两组术后3个月及末次随访的目测类比评分、Oswestry功能障碍指数评分低于术前(P < 0.05),腰椎JOA评分均高于术前(P < 0.05);试验组术后3个月的目测类比评分低于对照组(P < 0.05);④两组术后的Cobb角均有丢失现象,两组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑤结果表明相比传统手术行后路、前后联合入路治疗腰椎结核,后外侧椎间孔镜下植入载链霉素硫酸钙人工骨联合后路经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗腰椎结核同样可以达到满意的临床效果,同时又具有创伤小、恢复快等优势。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0960-9077 (付拴虎)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: