[1] AKITA S. Wound Repair and Regeneration: Mechanisms, Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6328.
[2] LAY K, KUME T, FUCHS E. FOXC1 maintains the hair follicle stem cell niche and governs stem cell quiescence to preserve long-term tissue-regenerating potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016; 113(11): E1506-E1515.
[3] FAN XL, ZHANG Y, LI X, et al. Mechanisms underlying the protective effects of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020:1-24.
[4] AZEVEDO MM, LISBOA C, COBRADO L, et al. Hard-to-heal wounds, biofilm and wound healing: an intricate interrelationship. Br J Nurs. 2020;29(5):S6-S13.
[5] LI S, MOHAMEDI AH, SENKOWSKY J, et al. Imaging in Chronic Wound Diagnostics. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020; 9(5):245-263.
[6] LIU J, HU F, TANG J, et al. Homemade-device-induced negative pressure promotes wound healing more efficiently than VSD-induced positive pressure by regulating inflammation, proliferation and remodeling. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39(4): 879-888.
[7] KARALASHVILI L, MARDALEISHVILI K, UHRYN M, et al. Current condition and challenges in treatment of non-healing wound after radiation therapy (Review). Georgian Med News. 2018; (280-281): 23-28.
[8] CAMERNIK K, ZUPAN J. Complete assessment of multilineage differentiation potential of human skeletal muscle-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2019; 2045: 131-144.
[9] LAURITANO D, PALMIERI A, CANDOTTO V, et al. Regenerative dentistry and stem cells: a multilineage differentiation as a safe and useful alternative way of harvesting and selection adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Drug Targets. 2018; 19(16): 1991-1997.
[10] LI Z, HU X, ZHONG JF. Mesenchymal stem cells: characteristics, function, and application. Stem Cells Int. 2019; 2019: 8106818.
[11] BALAJI S, KESWANI SG, CROMBLEHOLME TM. The role of mesenchymal stem cells in the regenerative wound healing phenotype. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2012; 1(4): 159-165.
[12] SI Z, WANG X, SUN C, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells: Sources, potency, and implications for regenerative therapies. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019; 114: 108765.
[13] VARGHESE J, GRIFFIN M, MOSAHEBI A, et al. Systematic review of patient factors affecting adipose stem cell viability and function: implications for regenerative therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017; 8(1): 45.
[14] DOS SANTOS JF, BORÇARI NR, DA SILVA ARAÚJO M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into keratinocytes and express epidermal kallikreins: Towards an in vitro model of human epidermis. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(8):13141-13155.
[15] MAHMOOD R, MEHMOOD A, CHOUDHERY MS, et al. Human neonatal stem cell-derived skin substitute improves healing of severe burn wounds in a rat model. Cell Biol Int. 2019; 43(2): 147-157.
[16] 刘博宇,蒲磊,张应杰,等.干细胞治疗皮肤缺损:是未来研究的重点[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(25):4082-4088.
[17] ENCISO N, AVEDILLO L, FERMIN ML, et al. Regenerative potential of allogeneic adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal cells in canine cutaneous wounds. Acta Vet Scand. 2020; 62(1):13.
[18] BULATI M, MICELI V, GALLO A, et al. The immunomodulatory properties of the human amnion-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells are induced by inf-gamma produced by activated lymphomonocytes and are mediated by cell-to-cell contact and soluble factors. Front Immunol. 2020;11:54.
[19] NEMETH K, LEELAHAVANICHKUL A, YUEN PS, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med. 2009;15(1):42-49.
[20] EL-SAYED M, EL-FEKY MA, EL-AMIR MI, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of mesenchymal stem cells: Cell origin and cell quality variations. Mol Biol Rep. 2019; 46(1):1157-1165.
[21] JIANG D, SINGH K, MUSCHHAMMER J, et al. MSCs rescue impaired wound healing in a murine LAD1 model by adaptive responses to low TGF-β1 levels. EMBO Rep. 2020;21(4):e49115.
[22] MYUNG H, JANG H, MYUNG JK, et al. Platelet-rich plasma improves the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing their secretion of angiogenic factors in a combined radiation and wound injury model. Exp Dermatol. 2020; 29(2): 158-167.
[23] DALIRFARDOUEI R, JAMIALAHMADI K, JAFARIAN AH, et al. Promising effects of exosomes isolated from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing process in diabetic mouse model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019; 13(4): 555-568.
[24] 张恩国,陈尚雅,杨叶,等.干细胞源外泌体应用于再生医学的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(5): 801-806.
[25] HUO J, SUN S, GENG Z, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promoted cutaneous wound healing by regulating keratinocyte migration via beta2-adrenergic receptor signaling. Mol Pharm. 2018; 15(7): 2513-2527.
[26] HOSSEINZADEH S, SOLEIMANI M, VOSSOUGHI M, et al. Study of epithelial differentiation and protein expression of keratinocyte-mesenchyme stem cell co-cultivation on electrospun nylon/B. vulgaris extract composite scaffold. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017; 75: 653-662.
[27] DONG L, HAO H, LIU J, et al. A conditioned medium of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing wnt7a promotes wound repair and regeneration of hair follicles in mice. Stem Cells Int. 2017; 2017: 3738071.
[28] MURPHY KC, WHITEHEAD J, FALAHEE PC, et al. Multifactorial experimental design to optimize the anti-inflammatory and proangiogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cell spheroids. Stem Cells. 2017; 35(6): 1493-1504.
[29] CLARK AY, MARTIN KE, GARCIA JR, et al. Integrin-specific hydrogels modulate transplanted human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell survival, engraftment, and reparative activities. Nat Commun. 2020; 11(1): 114.
[30] ZENG B, LIU L, WANG S, et al. ILK regulates MSCs survival and angiogenesis partially through AKT and mTOR signaling pathways. Acta Histochem. 2017; 119(4): 400-406.
[31] MAO Q, LIANG XL, WU YF, et al. ILK promotes survival and self-renewal of hypoxic MSCs via the activation of lncTCF7-Wnt pathway induced by IL-6/STAT3 signaling. Gene Ther. 2019; 26(5): 165-176.
[32] LI X, HE L, YUE Q, et al. MiR-9-5p promotes MSC migration by activating beta-catenin signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017; 313(1): C80-C93.
[33] COPLAND IB, LORD-DUFOUR S, CUERQUIS J, et al. Improved autograft survival of mesenchymal stromal cells by plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 inhibition. Stem Cells. 2009;27(2):467-477.
[34] LI Y, ZHANG Y, LIU X, et al. Lutein inhibits proliferation, invasion and migration of hypoxic breast cancer cells via downregulation of HES1. Int J Oncol. 2018; 52(6): 2119-2129.
[35] LV B, HUA T, LI F, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha protects mesenchymal stem cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury via autophagy induction and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2017; 9(5): 2492-2499.
[36] ZHAO L, LIU X, ZHANG Y, et al. Enhanced cell survival and paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor promote cardioprotection in myocardial infarction. Exp Cell Res. 2016; 344(1): 30-39.
[37] DONG J, ZHANG Z, HUANG H, et al. miR-10a rejuvenates aged human mesenchymal stem cells and improves heart function after myocardial infarction through KLF4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018; 9(1): 151.
[38] HOU J, WANG L, WU Q, et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor A to enhance mesenchymal stem cells survival and angiogenic capacity by inhibiting miR-199a-5p. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018; 9(1): 109.
[39] ZHANG H, WANG Y, LV Q, et al. MicroRNA-21 overexpression promotes the neuroprotective efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Neurol. 2018; 9: 931.
[40] XIANG Q, HONG D, LIAO Y, et al. Overexpression of Gremlin1 in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Hindlimb Ischemia in Mice by Enhancing Cell Survival. J Cell Physiol. 2017; 232(5): 996-1007.
[41] HE H, ZHAO ZH, HAN FS, et al. Overexpression of protein kinase C varepsilon improves retention and survival of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in rat acute myocardial infarction. Cell Death Dis. 2016; 7: e2056.
[42] AHN SM, KIM YR, SHIN YI, et al. Therapeutic Potential of a Combination of Electroacupuncture and TrkB-Expressing Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Ischemic Stroke. Mol Neurobiol. 2019; 56(1): 157-173.
[43] ALVES VBF, DE SOUSA BC, FONSECA MTC, et al. A single administration of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) induces durable and sustained long-term regulation of inflammatory response in experimental colitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2019;196(2): 139-154.
[44] NI X, OU C, GUO J, et al. Lentiviral vector-mediated co-overexpression of VEGF and Bcl-2 improves mesenchymal stem cell survival and enhances paracrine effects in vitro. Int J Mol Med. 2017; 40(2): 418-426.
[45] LIU Y, ZHANG X, CHEN J, et al. Inhibition of mircoRNA-34a Enhances Survival of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Under Oxidative Stress. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:264-271.
[46] HAN SM, HAN SH, COH YR, et al. Enhanced proliferation and differentiation of Oct4- and Sox2-overexpressing human adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Mol Med. 2014; 46: e101.
[47] LI Q, HAN SM, SONG WJ, et al. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Oct4/Sox2-overexpressing Human Adipose Tissue-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. In Vivo. 2017; 31(3): 349-356.
[48] JUNG YH, LEE HJ, KIM JS, et al. EphB2 signaling-mediated Sirt3 expression reduces MSC senescence by maintaining mitochondrial ROS homeostasis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017; 110: 368-380.
[49] MUHAR AM, PUTRA A, WARLI SM, et al. Hypoxia-mesenchymal stem cells inhibit intra-peritoneal adhesions formation by upregulation of the IL-10 expression. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019; 7(23): 3937-3943.
[50] JIANG CM, LIU J, ZHAO JY, et al. Effects of hypoxia on the immunomodulatory properties of human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Dent Res. 2015; 94(1): 69-77.
[51] De FARIA CA, ZANETTE DL, SILVA WA, et al. PAI-1 inhibition by simvastatin as a positive adjuvant in cell therapy. Mol Biol Rep. 2019; 46(1): 1511-1517.
[52] TSAI SF, TARNG DC. Anemia in patients of diabetic kidney disease. J Chin Med Assoc. 2019; 82(10): 752-755.
[53] AUZMENDI J, PUCHULU MB, RODRÍGUEZ JCG, et al. EPO and EPO-Receptor System as Potential Actionable Mechanism for the Protection of Brain and Heart in Refractory Epilepsy and SUDEP. Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(12):1356-1364.
[54] LU H, WU X, WANG Z, et al. Erythropoietin-activated mesenchymal stem cells promote healing ulcers by improving microenvironment. J Surg Res. 2016; 205(2): 464-473.
[55] BAI X, XI J, BI Y, et al. TNF-alpha promotes survival and migration of MSCs under oxidative stress via NF-kappaB pathway to attenuate intimal hyperplasia in vein grafts. J Cell Mol Med. 2017; 21(9): 2077-2091.
[56] LU N, LI X, TAN R, et al. HIF-1alpha/Beclin1-Mediated Autophagy Is Involved in Neuroprotection Induced by Hypoxic Preconditioning. J Mol Neurosci. 2018; 66(2): 238-250.
[57] KIM DS, KO YJ, LEE MW, et al. Effect of low oxygen tension on the biological characteristics of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016; 21(6): 1089-1099.
[58] LEE JH, YOON YM, LEE SH. Hypoxic Preconditioning Promotes the Bioactivities of Mesenchymal Stem Cells via the HIF-1α-GRP78-Akt Axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(6):1320.
[59] HEO JS, KIM HO, SONG SY, et al. Poly-L-lysine Prevents Senescence and Augments Growth in Culturing Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ex Vivo. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016: 8196078.
[60] SANAP A, CHANDRACANSHI B, SHAH T, et al. Herbal pre-conditioning induces proliferation and delays senescence in Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017; 93: 772-778.
[61] KHAN M, AKHTAR S, MOHSIN S, et al. Growth factor preconditioning increases the function of diabetes-impaired mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(1):67-75.
[62] KHAN M, ALI F, MOHSIN S, et al. Preconditioning diabetic mesenchymal stem cells with myogenic medium increases their ability to repair diabetic heart. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(3):58.
[63] 宋奕辰,胡亮,周露,等.血管紧张素II预处理提高骨髓间充质干细胞抗凋亡能力[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 34(9): 1157-1162.
[64] 杨靖,柴家科,刘玲英,等.血管紧张素-II (Ang-II)处理后的人脐带MSCs上清液对HUVEC凋亡和增殖的影响[J].现代生物医学进展, 2016, 16(10): 1816-1820. |

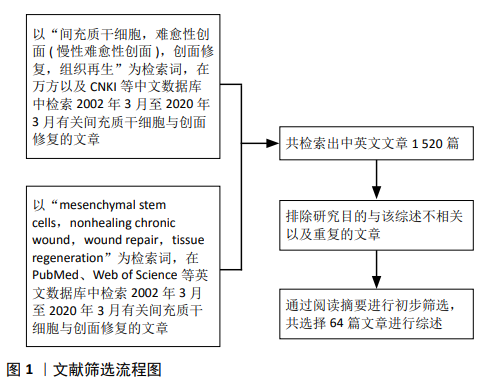
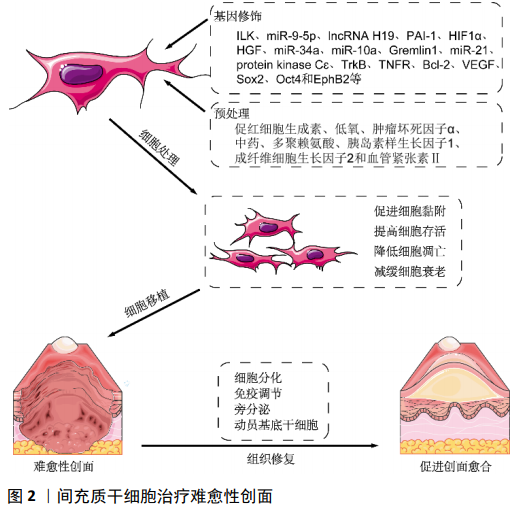 目前,间充质干细胞同种异体移植治疗皮肤烧伤的临床Ⅰ期试验正在进行(NCT02104713),并显现出良好的效果。因此,在保证间充质干细胞质量的前提下,应用间充质干细胞移植治疗难愈性创面,遏制难愈性创面患者病情进展,值得尝试。但需要进一步实验研究去探索将更多的基因修饰和/或预处理技术结合起来,使间充质干细胞具备更强的抵抗创面微环境的能力、以及向靶细胞分化能力和旁分泌效应,增强其修复效果。
目前,间充质干细胞同种异体移植治疗皮肤烧伤的临床Ⅰ期试验正在进行(NCT02104713),并显现出良好的效果。因此,在保证间充质干细胞质量的前提下,应用间充质干细胞移植治疗难愈性创面,遏制难愈性创面患者病情进展,值得尝试。但需要进一步实验研究去探索将更多的基因修饰和/或预处理技术结合起来,使间充质干细胞具备更强的抵抗创面微环境的能力、以及向靶细胞分化能力和旁分泌效应,增强其修复效果。