中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 1088-1095.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2113
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展
万 然,史 旭,刘京松,王岩松
- 哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院骨科,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150001
-
收稿日期:2019-12-26修回日期:2020-01-04接受日期:2020-02-19出版日期:2021-03-08发布日期:2020-12-09 -
通讯作者:王岩松,医学博士,主任医师,哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院骨科,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150001 -
作者简介:万然,男,1994年生,江西省人,汉族,哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院在读硕士,主要从事脊髓损伤方面研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(81871781)
Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome
Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong
- Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2019-12-26Revised:2020-01-04Accepted:2020-02-19Online:2021-03-08Published:2020-12-09 -
Contact:Wang Yansong, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Wan Ran, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81871781
摘要:
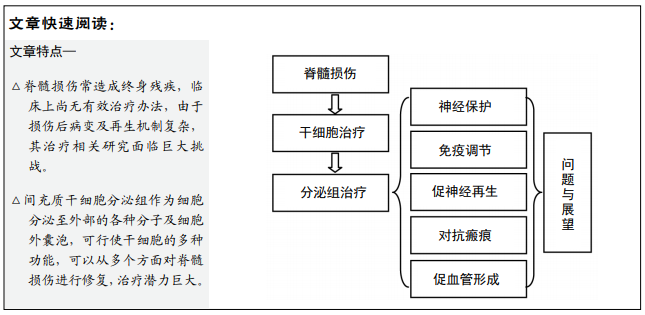
文题释义:
脊髓损伤:创伤等各种原因导致脊髓结构破坏、神经传导通路中断,由于中枢神经系统固有再生能力有限且损伤局部环境不利于再生,常导致永久性的神经功能缺陷。其病变与再生机制复杂,治疗需要从神经保护、解放神经再生潜力、对抗周围再生抑制环境等多方面进行。
间充质干细胞分泌组:是间充质干细胞分泌至细胞外空间的各种分子或细胞外囊泡,主要由间充质干细胞培养基去除杂质后获得,通过各种可溶性分子(如生长因子、趋化因子)及外泌体介导了间充质干细胞的大部分治疗作用,并且能避免细胞移植的各种弊端。
背景:由于中枢神经系统的固有再生能力有限,脊髓损伤常导致患者出现永久性的感觉、运动及自主神经功能障碍,严重影响其生活质量,目前临床上尚无有效改善神经功能恢复的方法。现研究认为间充质干细胞分泌组由于介导了细胞移植的主要治疗作用且避免了细胞排异等问题,因此将成为治疗脊髓损伤的有力工具。
目的:总结间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展,并分析目前面临的问题及其未来发展方向。
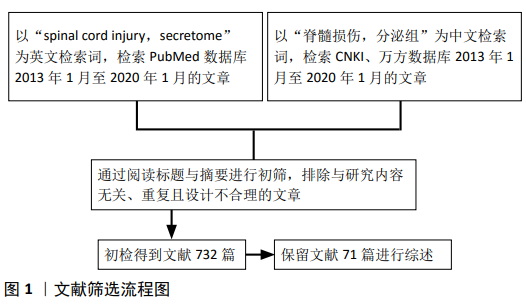
方法:以“spinal cord injury,secretome”为关键词检索PubMed数据库,以“脊髓损伤,分泌组”为关键词检索CNKI、万方数据库,检索时限为2013年1月至2020年1月,排除与文章研究目的无关及重复性文章,纳入符合标准的71篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:间充质干细胞分泌组中富含各种生长因子、神经营养因子等可溶性分子及细胞外囊泡,在减少细胞凋亡、调节免疫应答、抑制瘢痕形成、促进神经再生及血管形成方面都起到了显著作用。大量的研究表明,间充质干细胞分泌组可以促进脊髓损伤后的神经再生及功能恢复,且避免了细胞移植的种种弊端,未来将成为治疗脊髓损伤的可靠方法。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5879-1728(万然)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095.
Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095.
目前临床上对于急性脊髓损伤的治疗方法仅限于手术减压和大剂量甲基强的松龙冲击治疗[4,8],手术治疗的目的是重建脊柱稳定性和脊髓减压,限制继发性损伤,这是脊髓损伤紧急治疗的重要基石;甲基强的松龙是脊髓损伤治疗的标准药物,主要通过抑制创伤后的脂质过氧化来保护神经功
能[9],尽管存在类固醇相关的不良反应,但是目前临床上暂无替代药物。此外,临床医生会通过避免全身低血压和维持平均动脉压来保证脊髓灌注;后期的康复治疗尽可能地恢复功能、减少并发症,以提高患者长期生活质量[1,8]。
2.2 间充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤 随着组织工程学的发展,干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的方法已被大量研究所使用,其中不同来源的间充质干细胞(mesenchymal stem cells,MSCs)因为具有易于分离、相对易于保存和回避了大量伦理问题的优点尤其受到关注[14]。间充质干细胞是多能成体干细胞,最初由骨髓中分离得到,具有分化成中胚层甚至其他谱系的能力,目前通常从骨髓、脂肪、脐带、胎盘、乳牙、外周血等组织样本中获取。大量实验表明间充质干细胞对受损脊髓的神经再生与功能恢复具有明显促进作用[15-16],其治疗脊髓损伤的潜在机制包括向神经元、胶质细胞的分化及细胞的旁分泌作用,其分化、替代作用目前尚存争议。通过旁分泌作用,间充质干细胞可以调节各种细胞的增殖与分化,并在宿主微环境发挥免疫调节、神经保护、神经营养、促血管形成等功
能[14,17],因此间充质干细胞能减少继发性损伤造成的神经元丢失,并进一步促进神经再生。MUKHAMEDSHINA等[18]使用骨髓、脂肪、牙髓来源的间充质干细胞治疗大鼠及猪脊髓损伤,发现3种细胞在不同模型中均能减少空腔形成,恢复部分躯体感觉通路。成建平等[19]将骨髓间充质干细胞注入大鼠脊髓实质,减少了损伤后的神经元凋亡,降低了启动炎症反应的肿瘤坏死因子α的表达水平,大鼠后肢功能明显恢复。
2.3 无细胞治疗的衍生 早期的研究主要将间充质干细胞的治疗效果归因于其多向分化能力,然而最近的研究表明移植后细胞不能长时间存活(通常小于1周),且全身注射情况下移植到受损部位的细胞数量稀少,其中大量研究发现单独使用细胞分泌到外界的成分甚至可以产生与细胞移植相当的治疗效果[20-22],因此越来越多的学者认为干细胞移植后分化起到的作用较小,其治疗效果可能来源于分泌到细胞外的分子,这些分子在细胞过程的调节中起到了关键作用。
用无细胞治疗方法代替细胞治疗的理论基础是发现间充质干细胞旁分泌作用介导了细胞移植的主要治疗效果[23],无细胞治疗是通过收集细胞分泌出的各种物质,即使用细胞分泌组进行治疗的方式。此外,使用细胞分泌组进行无细胞治疗可以避免移植细胞的诸多弊端,具有以下优势:①避免了活细胞移植存在的的安全隐患,如免疫排斥反应、栓子形成、致瘤性、心律失常、钙化骨化和疾病传播[10],到目前为止尚未有报道提出细胞分泌组出现安全问题;②细胞分泌组可以像传统药物一样标准化其剂量和效能[23];③冻存甚至冻干不会减少细胞分泌组效能,而细胞冻存需要配合有潜在毒性的冷冻保存剂,且要求苛刻[11];④避免了细胞收集过程,省去了培养、扩增细胞所需的大量时间、花费,细胞分泌组更加经济实用,有利于商品化[24];⑤大规模生产时,可以通过实验条件和细胞系的选择来提供适当的生物活性因子[21];⑥战场医疗、急性疾病等紧急情况下,细胞分泌组是可以即刻使用的[25];⑦移植干细胞寿命短,且细胞衰老会导致遗传不稳定[13];⑧目前活细胞移植仍存在伦理问题[22]。越来越多的证据表明,细胞分泌组具有明确的治疗效果,因此近年来,无细胞治疗作为细胞治疗的替代方法而备受瞩目。
2.4 间充质干细胞分泌组
2.4.1 间充质干细胞分泌组的定义及成分 间充质干细胞分泌组或称条件培养基,被定义为间充质干细胞分泌至细胞外空间的各种分子和细胞外囊泡(EVs),这些分子包括可溶性蛋白(如生长因子、趋化因子、抗体、酶、黏附分子、受体、激素、抗菌肽等)、游离核酸、脂质[11,26-27],这些蛋白大都积极参与调节细胞黏附、增殖、迁移、分化、免疫应答、细胞防御、细胞存活、信息传递等多种细胞进程,从而起到免疫调节、抗凋亡、抗纤维化、促进组织再生等功能[21];细胞外囊泡为脂质双分子层结构,被认为是细胞内重要的通讯介质,常携带大量上述蛋白质、DNA、RNA等[20,28],参与调节靶细胞的多种信号通路。细胞外囊泡根据其大小和来源可分为凋亡小体(500-2 000 nm)、微泡(150-600 nm)和外泌体(40-
150 nm)[20-21],凋亡小体是细胞凋亡过程中从细胞内分裂出的最大的细胞外囊泡,含组蛋白和DNA片段;微泡由质膜出芽产生,富含神经鞘磷脂和神经酰胺;外泌体由多泡体内部萌出,多泡体与质膜融合后向外释放外泌体,外泌体含一系列进化保守蛋白如四聚体蛋白、热休克蛋白[20,22]。
目前已有一部分研究使用蛋白组学的方法对间充质干细胞分泌组的具体成分进行了分析,发现其中富含的各种生长因子、趋化因子、神经营养因子等等,与脊髓损伤后的神经保护及神经再生过程密切相关。SCHIRA等[29]通过质谱分析和生物信息学方法从人脐带间充质干细胞分泌组鉴定出
1 156种具有代表性的蛋白,其中不乏参与细胞黏附、细胞迁移、血管形成、细胞骨架建立和细胞外基质组建等生物学过程的蛋白:455种蛋白参与细胞通讯;426种参与发育;307种参与细胞分化;170种参与细胞增殖;53种参与细胞生长,其中有31种重要的促神经生长因子如MANF、神经元衍生神经营养因子(NDNF)、色素上皮衍生因子(PEDF)、SPARC等等;44种与血管发育相关的蛋白如基质金属蛋白酶(MMP-2)、血管形成素2、金属蛋白酶14 (MMP-14)。MATSUBARA等[30]使用细胞因子抗体阵列分析检测了人牙髓间充质干细胞分泌组,发现了79种蛋白质,其中28种参与了神经再生过程,单核细胞趋化蛋白1(MCP-1)、唾液酸结合性免疫球蛋白样凝集素9 (ED-Siglec-9)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)参与到了神经修复过程中M2型巨噬细胞的极化。
2.4.2 间充质干细胞外泌体 作为间充质干细胞分泌组的重要组成部分,近年来其外泌体(exosome)也成为了治疗脊髓损伤相关研究的热点。利用外泌体的理化特性,通过超速离心、过滤、免疫亲和分离、聚合物沉淀等方法可以从细胞分泌组分离出其中的外泌体[31]。外泌体内包含各种可溶性蛋白、核酸、脂质[32],可以通过细胞膜融合、受体配体相互作用或是内吞作用,向靶细胞传递信息分子,从而起到细胞间交流的作用[33]。外泌体的产生、装配与摄取过程详见图2。相较于间充质干细胞,其外泌体不仅能通过血脑屏障,还会选择性地富集多种RNA。EIRIN等[34]发现相较于间充质干细胞,至少4种miRNA和255种mRNA在外泌体中被富集,而且与血管生成、组织再生相关的基因优先表达,因此外泌体对脊髓损伤会产生较强的生物学效力。间充质干细胞外泌体中的RNAs(mRNA、miRNA、lncRNA)等信号分子由靶细胞摄取并影响细胞的基因表达,从而外泌体能参与到细胞周期、细胞免疫应答、细胞黏附与迁移等细胞过程的调控,在大量脊髓损伤相关研究中显示出其减少神经元凋亡、促进轴突生长、促进血管再生的多重作用[32]。周燕等[35]对脊髓损伤大鼠静脉注射骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体,结果抑制了炎性细胞的活化,减少了神经元的凋亡,大鼠后肢运动功能明显改善。HUANG等[36]发现间充质干细胞外泌体可向脊髓损伤部位转移,并通过其负载的miRNA-126起到促进神经再生、血管形成的作用。
2.4.3 间充质干细胞分泌组的获取与应用策略 目前脊髓损伤治疗相关的研究中,细胞分泌组通常直接来源于未受刺激的间充质干细胞产生的上清液,待细胞稳定后,通过离心及0.22 μm滤器过滤去除上清液中的细胞碎片即可获得细胞分泌组[11]。由于血清当中本身存在大量的可溶性分子及囊泡,因此收集细胞分泌组前通常将间充质干细胞进行无血清培
养[38]。由于不同的培养条件会明显影响细胞分泌组的成分,当需要突出细胞分泌组某方面的作用时,各学者相应地探索不同的培养条件,这些培养方法包括3D培养、蛋白预处理、基因工程修饰、药物预处理、物理预处理[16]。如缺氧条件下间充质干细胞分泌组血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)水平更高[39],有利于脊髓损伤处血管形成;TNFγ等炎症因子刺激间充质干细胞可使分泌组中前列腺素E2(PGE-2)、白细胞介素10等抗炎成分增加[40],在脊髓继发性损伤中起到更强的炎症抑制作用。
细胞分泌组应用于脊髓损伤模型时,各研究通常有不同的应用策略。在衡量细胞分泌组剂量时会应用不同的标准,通常包括细胞分泌组的蛋白浓度[41]、冻干后细胞分泌组干重或是分泌组来源的细胞数量[42-43],因此剂量难以统一;脊髓损伤动物实验中,细胞分泌组的给药途径通常为蛛网膜下腔注射[44]、静脉注射或是腹腔注 射[45-46];给药次数也分为一次性给药或多次给药[45,47],虽然各实验结果均表明了细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的有效性,但是不同的实验间难以相互比较给药策略的优劣。此外,部分学者会通过各种方法分离出细胞分泌组中的外泌体进行实验,不同的分离方式亦有些许区别,如超速离心法得到的外泌体大小均匀却易于损伤其结构,过滤法省时省力却降低提取纯度[31]。大量研究表明,细胞分泌组与其内含的外泌体对脊髓损伤都具有良好治疗效果,细胞分泌组具有易于收集、细胞因子含量高的优点,其外泌体则具有成分更加精确、易于标准化的优点,但是尚无研究直接比较二者疗效,因此二者优劣有待深究[11]。目前尚缺乏实验研究对比细胞分泌组不同的收集与应用策略对脊髓损伤疗效的影响,这也是间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤研究需要解决的问题之一,此策略的优化与标准化对未来细胞分泌组的推广至关重要。
2.4.4 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗的研究现状 如同间充质干细胞治疗,其细胞分泌组由于具备抗炎、抗氧化、抗凋亡、抗纤维化等各种功能,现已被应用于呼吸、泌尿生殖、循环、骨关节、神经、皮肤等各系统疾病模型的研究,表1详细列举了分泌组在不同疾病模型中的应用及其效果。
除了蛋白成分,细胞分泌组中的细胞外囊泡由于保留了细胞的归巢能力,可以被细胞内吞及穿过血脑屏障,其脂质层更是可以防止药物降解,因此在药物输送的研究中具有很大的潜力[26],比如利用其向肿瘤细胞的归巢能力,可以考虑向肿瘤递送特定的药物[11]。此外细胞外囊泡中的其他成分可能也起到了不同的生理作用,如 miRNAs(miRNA30参与肾脏保护、miRNA22参与心肌恢复)、lncRNA(YRNA1参与肝细胞保护)、脂质成分(PGE-2参与脑损伤修复)[11,27]。
尽管大量动物实验已经证明了间充质干细胞分泌组治疗的安全性及有效性,但目前相关的早期临床试验仍较少,其治疗初具成效:脂肪间充质干细胞分泌组可以促进激光换肤术后皮肤的愈合,增加脱发患者毛发数量;骨髓间充质干细胞分泌组可以增加上颌窦底提升术后骨体积;骨髓间充质干细胞分泌组在多发性硬化的研究中显示出治疗潜力[11,20]。
2.5 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤 CRILGER最早在体外证明了骨髓间充质干细胞可以通过分泌脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)和β-神经生长因子(β-NGF)来促进神经元的存活和轴突再生[13],至今大量体内或体外实验都已经证明了细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的安全性及有效性。部分研究对比了间充质干细胞及其分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的效果,结果细胞分泌组起到了与细胞移植相同的疗效,而细胞治疗未起到明显的替代作用[29,45,48]。间充质干细胞分泌组的可溶性成分及外泌体具有神经保护、免疫调节、减少瘢痕形成、促进神经再生及血管形成的多重功能。比如在骨髓间充质干细胞的分泌组中可以找到与轴突生长和神经存活相关的胰岛素样生长因子1(IGF-1)、肝细胞生长因子(HGF)、血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子β(TGF-β),改善损伤局部环境,减少瘢痕形成的干细胞因子(SCF)、基质细胞衍生因子(SDF-1α)、MCP-1和血管内皮生长因子[13];间充质干细胞外泌体内miRNA-21、miRNA-146a、miRNA181参与炎症反应抑制[49]。
脊髓损伤的病变及再生机制错综复杂,针对其中单一的靶点难以达到整体上满意的治疗效果[4]。间充质干细胞分泌组中包含了神经营养因子、生长因子、趋化因子等各种可溶性分子,其外泌体则作为细胞间的信使参与细胞进程调控,使得细胞分泌组从神经保护、免疫调节、对抗瘢痕、促进神经再生及血管形成5个方面发挥作用,各种分子调节的细胞进程相互协同,进而可以形成一个支持神经再生和功能恢复的网络。因此分泌组治疗脊髓损伤潜力巨大。
2.5.1 间充质干细胞分泌组的神经保护作用 脊髓继发性损伤阶段,细胞凋亡、脂质过氧化损伤、细胞毒作用等病理因素会介导神经元的进一步死亡,其中细胞凋亡是导致神经元丢失的主要原因。Bcl-2家族和Caspase家族介导细胞的凋亡过程,其中抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2和促凋亡蛋白Bax可以作为细胞凋亡反应的标志物,Bcl-2/Bax异二聚体可避免细胞凋亡[32]。
间充质干细胞分泌组通过增加组织抗凋亡蛋白的表达或内含的凋亡抑制蛋白,改善局部微环境,减少神经元丢失。LI等[50]发现注射骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体后,大鼠脊髓损伤处Bcl-2蛋白表达水平升高,而Bax、cleaved Caspase-3、cleaved Caspase-9表达水平明显下降,神经元丢失减少。胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白6(IGFBP6)是一种生长因子,可以增加胰岛素样生长因子1受体介导的Akt磷酸化,降低线粒体内促凋亡相关蛋白Bax表达[16]。JEON等[51]证明在双氧水诱导的神经元损伤模型中,间充质干细胞分泌组通过IGFBP6降低了促凋亡蛋白Bax的表达,起到了保护原代皮质神经元的作用。
除了减少细胞凋亡,间充质干细胞分泌组改变了损伤微环境,从而能够减少过氧化、细胞毒性作用等损伤,起到神经保护作用。YENG等[52]使用脐带间充质干细胞分泌组静脉注射的方法改善了脊髓损伤大鼠的下肢运动功能,此研究中细胞分泌组明显降低了脊髓内活性氧(一氧化氮、2,3-二羟苯甲酸)、酶促氧化剂及脂质过氧化产物(丙二醛)的水平,通过减少氧化损伤起到神经保护作用。NADPH氧化酶4同工酶(NOX)是细胞内活性氧(ROS)的重要来源,脊髓损伤后氧化应激反应导致活性氧堆积,造成蛋白质、DNA损伤,引起细胞死亡[53]。赵林林[54]通过慢病毒使骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体内过表达miRNA-25,并将其注入脊髓损伤大鼠蛛网膜下腔,结果显著减低了大鼠脊髓组织内NOX4的表达水平,活性氧减少,有效降低了氧化应激引起的细胞死亡。
2.5.2 间充质干细胞分泌组的免疫调节作用 间充质干细胞分泌组可以影响各种免疫细胞的增殖和活化,研究证明细胞分泌组在先天性免疫和适应性免疫中都有调节作用。炎症不仅参与了继发性损伤的组织破坏也与坏死组织清除、再生反应密切相关,细胞分泌组很好地调节了炎症反应,起到了协调与平衡的作用[20]。早期细胞分泌组通过选择性地动员各种免疫细胞,起到清除凋亡细胞和髓鞘碎片的作用。NEIRINCKX等[55]发现骨髓间充质干细胞分泌组含各种集落刺激因子、白细胞介素、趋化因子,包括粒细胞集落刺激因子(G-CSF)、白细胞介素6、CCL5、CXCL12,对巨噬细胞具有高度趋化作用,这些因子会在体内选择性招募、活化巨噬细胞,调节脊髓损伤的早期炎症事件、有效清除损伤处的坏死组织,并对后期的轴突再生起到有利作用,最终引起脊髓损伤大鼠出现早期的功能恢复。
除了早期动员炎症细胞,细胞分泌组可以在持续炎性反应引起组织损伤的阶段,调节促炎与抗炎因子的水平,并抑制各种炎性细胞的增殖、活化,起到炎症抑制作用,从而减轻炎性反应在继发性损伤过程中造成的组织破坏[13]。间充质干细胞分泌组可以参与抗原识别、T细胞增殖活化、T细胞效应阶段的调控,从免疫反应的3个主要阶段介导炎症的抑制[56],其主要的炎性抑制因子包括转化生长因子β、白细胞介素1受体拮抗体(IL-1Ra)、白细胞介素37、IL12P70、睫状神经营养因子(CNTF)、人神经营养因子3(NT-3)、白细胞介素10、白细胞介素13等[56-57]。转化生长因子β2可以减少CD4+辅助T细胞和CD8+细胞毒性T细胞的增殖[16],白细胞介素1受体拮抗体与白细胞介素1受体结合,竞争性抑制白细胞介素1的促炎作用,减少白细胞浸润[20]。白细胞介素37是参与间充质干细胞免疫调节作用的关键分子,通过细胞内转移机制进入细胞核,阻止促炎的细胞因子如白细胞介素1α、肿瘤坏死因子、CXCL2的转录[10]。GIACOPPO等[41]发现静脉注射牙源性间充质干细胞分泌组后,丰富的白细胞介素37使小鼠脊髓内白细胞介素1α、肿瘤坏死因子表达减少,此外白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β等抗炎细胞因子表达明显增加,白细胞浸润减少,病变区域的炎性反应减轻,小鼠出现明显的功能恢复。CHUDICKOVA等[44]通过蛛网膜下腔注射脐带间充质干细胞分泌组,显著增加了脊髓损伤大鼠血清中白细胞介素10、IL12p70等抗炎因子的水平,降低了白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6等促炎因子水平,改善了功能评分。此外,KANG等[58]使用过表达miRNA-21的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体治疗脊髓损伤大鼠,结果miRNA-21可下调PTEN,抑制核因子κB的活化,从而控制炎症反应,促进损伤修复。
巨噬细胞在脊髓损伤过程中由于表型不同,起到了积极或是消极的作用,通常M1型表现为促炎型,会杀伤周围细胞并阻止细胞增殖,其持续存在导致了阻碍神经再生的慢性炎症;M2型则起到抑制炎症损伤及促进组织修复的作用,对受损脊髓有益[59]。间充质干细胞分泌组可以通过参与调节巨噬细胞的表型,减轻其促炎作用,甚至逆转为炎症抑制、促进再生的状态。LANKFORD等[45]对脊髓损伤大鼠进行骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体的静脉注射,发现这些外泌体被损伤处的M2型巨噬细胞吞噬,并阻止M2型巨噬细胞转化为M1型促炎状态,大鼠功能明显恢复。SHIMOJIMA等[60]发现注射人乳牙间充质干细胞分泌组可以减轻神经炎症,改善脊髓功能,其主要成分唾液酸结合Ig样凝集素9 (ED-Siglec-9)可促进巨噬细胞由M1型向M2型转化,抑制巨噬细胞释放促炎因子并减少促炎性细胞Th1/Th17的增殖。
2.5.3 间充质干细胞分泌组促进神经再生的作用 尽管中枢神经系统再生的机制十分复杂,但是既往大量研究已经证明了细胞分泌组通过一系列神经营养因子、生长因子等成分,有效地介导了神经再生,并切实地改善了脊髓功能的恢复。这些因子主要包括脑源性神经营养因子、神经生长因子、血管内皮生长因子、肝细胞生长因子、胶质细胞源性神经营养因子(GDNF)、人神经营养因子3、干细胞因子、碱性成纤维生长因子(bFGF)等等[13],虽然其中有很多因子诱导神经再生的机制尚不明了,但可以肯定的是,各种因子协同作用,构成了促进中枢神经系统再生的坚实网络[29]。脑源性神经营养因子是神经元分化的关键因子,与趋化因子CXCL-1协同作用会使脊髓组织中ERK1/2磷酸化水平升高,并通过ERK1/2通路的激活介导神经的再生功能[61]。神经生长因子是神经元发育、成熟及轴突生长的关键调控因子[62]。肝细胞生长因子可以促进运动神经元神经突生长,刺激小胶质细胞及许旺细胞增殖[11]。胶质细胞源性神经营养因子可以促进感觉及运动神经元的生长,刺激轴突的保留与再生[27]。OLIVEIRA等[63]
检测到脂肪间充质干细胞分泌组含脑源性神经营养因子、胶质细胞源性神经营养因子、神经生长因子,可以有效刺激大鼠脊髓损伤后感觉及运动神经元的生长,促进轴突再生。KANEKIYO等[48]检测到骨髓间充质干细胞分泌组丰富的胰岛素样生长因子1、转化生长因子β1和肝细胞生长因子,有效促进了脊髓损伤大鼠神经元生长与功能恢复。此外,YU等[64]
通过尾静脉注射骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体治疗大鼠脊髓损伤,该研究中外泌体内miRNA-29b明显提高了反映轴突生长的神经丝蛋白200(NF200)的表达水平,大鼠功能评分明显改善。
间充质干细胞分泌组不仅能直接刺激轴突生长,各种研究表明其中还存在各种分子通过参与细胞外基质构建、诱导胶质细胞迁移等过程间接地促进神经再生。层粘连蛋白能够参与构建细胞外基质支持神经突的黏附与生长,基质细胞衍生因子1(SDF-1)可诱导少突胶质前体细胞的迁移与分化[13]。SCHIRA等[29]发现人脐带间充质干细胞分泌组当中富含层粘连蛋白及基质细胞衍生因子1,可促进原代皮质神经元的生长,此外集落刺激因子(CSF)、神经纤毛蛋白1、血小板衍化生长因子(PDGF)等参与到了星形胶质细胞、成纤维细胞的迁移过程。STEWART等[65]发现骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的基质细胞衍生因子1通过结合趋化因子偶联受体4(CXCR4)和趋化因子偶联受体7(CXCR7)促进胶质细胞迁移,明显改善了大鼠脊髓损伤区域轴突密度。
2.5.4 间充质干细胞分泌组对抗瘢痕的作用 胶质瘢痕内含CSPGs等各种轴突再生抑制因子,脊髓损伤后胶质瘢痕形成的物理化学屏障长期存在会明显地阻碍轴突再生及功能恢复。多项研究证明了间充质干细胞分泌组可以减少瘢痕形成从而改善脊髓损伤的预后。斑马鱼的脊髓损伤修复模型中,一种微小RNA miRNA-133被多能间充质干细胞外泌体运载至星形胶质细胞,下调了结缔组织生长因子表达,从而起到了减少瘢痕形成的作用[66]。LIU等[67]的研究也发现骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体使大鼠脊髓损伤处的胶质瘢痕减少了75%。
除了减少胶质瘢痕的形成,分泌组还可以有效地拮抗瘢痕中各种轴突再生抑制因子如CSPGs、Nogo-A的作用,从而促进轴突再生。CSPGs、NogoA、髓磷脂相关糖蛋白主要来源于星形胶质细胞和髓鞘碎片,这些抑制物与轴突顶端的生长锥接触后激活Rho蛋白,导致生长锥塌陷、回缩,轴突生长停止[68]。各种神经营养蛋白包括粒细胞集落刺激因子、成纤维生长因子、基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)等,可以起到降解神经抑制分子的作用,尤其是基质金属蛋白酶可以有效降解神经蛋白聚糖等神经抑制因子[20]。WRIGHT等[69]发现骨髓间充质干细胞分泌组中的神经营养蛋白基质金属蛋白酶8可以减轻Nogo-A及神经蛋白聚糖对神经元黏附及延伸的抑制作用,从而刺激神经突生长。REN等[70]使用高表达miRNA-133b的脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体治疗脊髓损伤大鼠,结果明显降低了RhoA蛋白的水平,解除了其轴突生长抑制作用,大鼠出现明显的神经再生及功能恢复。
2.5.5 间充质干细胞分泌组促进血管形成的作用 血管形成是新的脉管系统从现存的血管中产生的过程,由于脊髓损伤破坏了脊髓原本的的血液供应,明显加重组织损伤,因而缺血成为继发性损伤的一大特征[4-5],脊髓微血管网络的重建会明显促进神经功能的恢复。促进血管形成对组织愈合和功能恢复十分重要,多项研究证明间充质干细胞分泌组对血管形成起到了关键性的作用[20]。间充质干细胞分泌组参与到了血管形成的多个关键步骤,包括诱导内皮细胞增殖与迁移、促进管腔形成、防止内皮细胞凋亡[10]。血管内皮生长因子是间充质干细胞分泌组促血管形成的关键因子,血管内皮生长因子通过与血管内皮生长因子受体2(VEGFR2)结合,抑制Caspase9的活性,从而起到促进血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移和存活的作用,抑制血管内皮生长因子会使血管结构不稳定[16]。GOMES等[71]使用脂肪间充质干细胞分泌组治疗大鼠脊髓损伤,其富含的血管内皮生长因子使新生血管密集、结构成熟,有效改善了大鼠神经功能。此外,SCHIRA等[29]发现人脐带间充质干细胞分泌组内血管生成素2、基质金属蛋白酶2、基质金属蛋白酶14、基质金属蛋白酶19和纺锤蛋白4等共同促进了脊髓损伤后血管的构建过程。HUANG等[36]发现骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体能将miRNA-126运载至大鼠脊髓损伤部位,通过减少血管生成负性调控因子SPRED1及PIK3R2的表达起到促进血管内皮细胞迁移及血管形成的作用。
2.6 问题与展望 虽然之前的研究已经证明了间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的有效性,但是将细胞分泌组真正投入临床使用之前还需要克服以下诸多问题:①细胞分泌组纯化的问题[23],获取细胞分泌组之前培养细胞会用到各种商品化的培养基,因此额外的培养基成分可能会被同时收集;②细胞分泌组成分选择的问题[11],虽然使用其中的特定成分会使治疗过程更加精确,但是特定组分与细胞分泌组整体应用的对比效果还有待验证,且多数学者认为细胞分泌组起效需要各种因子协同作用,直接使用细胞分泌组整体避免了成分的筛选也更加经济;③细胞分泌组是含多种分子的混合物,其临床标准化较为困难[28];④生产过程还需符合药品生产质量管理规范才能达到商业化生产水平[21];⑤目前其来源细胞培养时通常以胎牛血清提供营养,这就存在人畜共患病的风险;⑥细胞分泌组的具体使用方案有待进一步优化,如给药频率、最佳剂量等等。
将来需要发展出可靠的分离手段以纯化细胞分泌组;优化并统一细胞培养、细胞系选择、分泌组收集及应用的策略;找到简单、可靠的方法对产品特征进行标准化;使用经济、安全的纯化学培养基或血清替代物来取代胎牛血清。此外,采用各种方法如缺氧、血清剥夺和炎症激动预处理间充质干细胞来刺激其功能,或是采用3D培养方式模拟细胞外基质环境,可显著增加分泌组的含量和治疗效果[20,22-23],在未来的研究中也大有前景。

| [1] GUO S, PERETS N, BETZER O, et al. Intranasal Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Loaded with Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog siRNA Repairs Complete Spinal Cord Injury. ACS Nano.2019;13(9):10015-10028. [2] BRADBURY EJ, BURNSIDE ER. Moving beyond the glial scar for spinal cord repair. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3879. [3] COURTINE G, SOFRONIEW MV. Spinal cord repair: advances in biology and technology. Nat Med. 2019;25(6):898-908. [4] HUTSON TH, DI GIOVANNI S. The translational landscape in spinal cord injury: focus on neuroplasticity and regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019; 15(12):732-745. [5] KOBAYAKAWA K, OHKAWA Y, YOSHIZAKI S, et al. Macrophage centripetal migration drives spontaneous healing process after spinal cord injury. Sci Adv. 2019;5(5):5086. [6] HUTSON TH, KATHE C, PALMISANO I, et al. Cbp-dependent histone acetylation mediates axon regeneration induced by environmental enrichment in rodent spinal cord injury models. Sci Transl Med. 2019; 11: 487. [7] CHEN D, ZENG W, FU Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with minocycline improve spinal cord injury in a rat model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(10):11957-11969. [8] AHUJA CS, WILSON JR, NORI S, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17018. [9] ONG W, PINESE C, CHEW SY. Scaffold-mediated sequential drug gene delivery to promote nerve regeneration and remyelination following traumatic nerve injuries. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;149-150: 19-48. [10] VIZOSO FJ, EIRO N, CID S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9):pii:E1852. [11] BOGATCHEVA NV, COLEMAN ME. Conditioned Medium of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: A New Class of Therapeutics. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019; 84(11):1375-1389. [12] SOO KIM, TAE MIN KIM. Generation of mesenchymal stem-like cells for producing extracellular vesicles. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11(5): 270-280. [13] TEIXEIRA FG, CARVALHO MM, SOUSA N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells secretome: a new paradigm for central nervous system regeneration. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(20):3871-3882. [14] COFANO F, BOIDO M, MONTICELLI M, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Spinal Cord Injury: Current Options, Limitations, and Future of Cell Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11). pii: E2698. [15] Ramalho BDS, Almeida FM, Sales CM, et al.Injection of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by intravenous or intraperitoneal routes is a viable alternative to spinal cord injury treatment in mice.Neural Regen Res. 2018; 13(6):1046-1053. [16] L PK, KANDOI S, MISRA R, et al. The mesenchymal stem cell secretome: A new paradigm towards cell-free therapeutic mode in regenerative medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:1-9. [17] MOU S, ZHOU M, LI Y, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for the Improvement of Angiogenesis and Fat-Grafting Application. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(4):869-880. [18] MUKHAMEDSHINA Y, SHULMAN I, OGURCOV S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Contusion: A Comparative Study on Small and Large Animal Models. Biomolecules. 2019;9(12). pii: E811. [19] 成建平,李华,李雄杰.骨髓间充质干细胞移植联用山胡椒叶提取物可改善脊髓损伤区域的炎症反应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(13): 1975-1981 [20] HARRELL CR, FELLABAUM C, JOVICIC N, et al. Molecular Mechanisms Responsible for Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome. Cells. 2019;8(5). pii: E467. [21] MIZUKAMI A, THOMÉ CH, FERREIRA GA, et al. Proteomic Identification and Time-Course Monitoring of Secreted Proteins During Expansion of Human Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal in Stirred-Tank Bioreactor. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:154 [22] LIU A, ZHANG X, HE H, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived secretome and vesicles for lung injury and disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019:1-16 [23] HONG HE, KIM OH, KWAK BJ, et al. Antioxidant action of hypoxic conditioned media from adipose-derived stem cells in the hepatic injury of expressing higher reactive oxygen species. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019;97(4):159-167 [24] KOSOL W, KUMAR S, MARRERO-BERRÍOS I, et al. Medium conditioned by human mesenchymal stromal cells reverses low serum and hypoxia-induced inhibition of wound closure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020; 522(2):335-341. [25] BONOVA P, JACHOVA J, NEMETHOVA M, et al. Rapid remote conditioning mediates modulation of blood cell paracrine activity and leads to the production of a secretome with neuroprotective features. J Neurochem. 2019 Oct 10. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14889. [26] BARI E, PERTEGHELLA S, CATENACCI L, et al. Freeze-dried and GMP-compliant pharmaceuticals containing exosomes for acellular mesenchymal stromal cell immunomodulant therapy. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2019;14(6): 753-765 [27] MAN RC, SULAIMAN N, IDRUS R, et al. Insights into the Effects of the Dental Stem Cell Secretome on Nerve Regeneration: Towards Cell-Free Treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:4596150 [28] RIBEIRO TO, SILVEIRA BM, MEIRA MC, et al. Investigating the potential of the secretome of mesenchymal stem cells derived from sickle cell disease patients. PLoS One. 2019;14(10):e0222093 [29] SCHIRA J, FALKENBERG H, HENDRICKS M, et al. Characterization of Regenerative Phenotype of Unrestricted Somatic Stem Cells (USSC) from Human Umbilical Cord Blood (hUCB) by Functional Secretome Analysis. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015;14(10):2630-2643 [30] MATSUBARA K, MATSUSHITA Y, SAKAI K, et al. Secreted ectodomain of sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin-9 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 promote recovery after rat spinal cord injury by altering macrophage polarity. J Neurosci. 2015;35(6):2452-2464 [31] 朱佳敏,刘玉梅,张自强,等.干细胞源外泌体修复神经损伤的研究现状[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2019,35(13):1413-1416 [32] 史冬玲,何冰倩,戴灵豪.外泌体治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2018,38(06):849-852 [33] 叶涌,陈晓庆,浩洁,等.间充质干细胞外泌体治疗脊髓损伤研究进[J]. 交通医学, 2019,33(5):425-428+432 [34] EIRIN A, ZHU XY, PURANIK AS, et al. Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of the molecular cargo of extracellular vesicles derived from porcine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2017; 12(3):e0174303 [35] 周燕,王琳,裴双,等.骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体可减少脊髓损伤后A1型星形胶质细胞的活化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(21):3294-3301 [36] HUANG JH, XU Y, YIN XM, et al. Exosomes Derived from miR-126-modified MSCs Promote Angiogenesis and Neurogenesis and Attenuate Apoptosis after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Neuroscience. 2020;424:133-145 [37] REZAIE J, RAHBARGHAZI R, PEZESHKI M, et al. Cardioprotective role of extracellular vesicles: A highlight on exosome beneficial effects in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):21732-21745 [38] 周文树.间充质干细胞外泌体的纯化及对脊髓损伤修复的初步探讨[D]. 昆明:昆明理工大学, 2018. [39] HAN Y, REN J, BAI Y, et al. Exosomes from hypoxia-treated human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis through VEGF/VEGF-R. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;109:59-68 [40] HARTING MT, SRIVASTAVA AK, ZHAORIGETU S, et al. Inflammation- Stimulated Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Inflammation. Stem Cells. 2018;36(1):79-90 [41] GIACOPPO S, THANGAVELU SR, DIOMEDE F, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of hypoxia-preconditioned human periodontal ligament cell secretome in an experimental model of multiple sclerosis: a key role of IL-37. FASEB J. 2017; 31(12):5592-5608 [42] LIANG M, LIU W, PENG Z, et al. The therapeutic effect of secretome from human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in age-related osteoporosis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1357-1366 [43] SAGARADZE G, BASALOVA N, KIRPATOVSKY V, et al. A magic kick for regeneration: role of mesenchymal stromal cell secretome in spermatogonial stem cell niche recovery. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019; 10(1): 342 [44] CHUDICKOVA M, VACKOVA I, MACHOVA URDZIKOVA L, et al. The Effect of Wharton Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Conditioned Media in the Treatment of a Rat Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20. pii: E4516. [45] LANKFORD KL, ARROYO EJ, NAZIMEK K, et al. Intravenously delivered mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes target M2-type macrophages in the injured spinal cord. PLoS One. 2018;13(1): e0190358. [46] DENG K, LIN DL, HANZLICEK B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and their secretome partially restore nerve and urethral function in a dual muscle and nerve injury stress urinary incontinence model. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015;308(2):F92-F100. [47] CIZKOVA D, CUBINKOVA V, SMOLEK T, et al. Localized Intrathecal Delivery of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Conditioned Media Improves Functional Recovery in A Rat Model of Contusive Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19:870. [48] KANEKIYO K, WAKABAYASHI T, NAKANO N, et al. Effects of Intrathecal Injection of the Conditioned Medium from Bone Marrow Stromal Cells on Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(3):521-532. [49] 王琳. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体对大鼠脊髓损伤后运动功能恢复和星形胶质细胞活化的影响[D].郑州:郑州大学, 2018. [50] LI C, JIAO G, WU W, et al. Exosomes from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Neuronal Apoptosis and Promote Motor Function Recovery via the Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(11): 1373-1383 [51] JEON HJ, PARK J, SHIN JH, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 released from human mesenchymal stem cells confers neuronal protection through IGF-1R-mediated signaling. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):1860-1868 [52] YENG CH, CHEN PJ, CHANG HK, et al. Attenuating spinal cord injury by conditioned medium from human umbilical cord blood-derived CD34⁺ cells in rats. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;55(1):85-93. [53] CASTALDO M, ZOLLO C, ESPOSITO G, et al. NOX2-Dependent Reactive Oxygen Species Regulate Formyl-Peptide Receptor 1-Mediated TrkA Transactivation in SH-SY5Y Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:2051235. [54] 赵林林.过表达miR-25的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体对脊髓短暂缺血的保护作用[D].沈阳:中国医科大学, 2019. [55] NEIRINCKX V, AGIRMAN G, COSTE C, et al. Adult bone marrow mesenchymal and neural crest stem cells are chemoattractive and accelerate motor recovery in a mouse model of spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6: 211. [56] BERMUDEZ MA, SENDON-LAGO J, SEOANE S, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of conditioned medium from human uterine cervical stem cells in uveitis. Exp Eye Res. 2016;149:84-92. [57] ZAGOURA DS, ROUBELAKIS MG, BITSIKA V, et al. Therapeutic potential of a distinct population of human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells and their secreted molecules in mice with acute hepatic failure. Gut. 2012; 61(6):894-906. [58] KANG J, LI Z, ZHI Z, et al. MiR-21 derived from the exosomes of MSCs regulates the death and differentiation of neurons in patients with spinal cord injury. Gene Ther. 2019;26(12):491-503. [59] MILICH LM, RYAN CB, LEE JK. The origin, fate, and contribution of macrophages to spinal cord injury pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2019; 137(5):785-797. [60] SHIMOJIMA C, TAKEUCHI H, JIN S, et al. Conditioned Medium from the Stem Cells of Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2016; 196(10):4164-4171 [61] HAIDER T, HÖFTBERGER R, RÜGER B, et al. The secretome of apoptotic human peripheral blood mononuclear cells attenuates secondary damage following spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol. 2015;267:230-242. [62] 宋旆文.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基对神经干细胞凋亡及分化的影响[D].合肥:安徽医科大学, 2014. [63] OLIVEIRA E, ASSUNÇÃO-SILVA RC, ZIV-POLAT O, et al. Influence of Different ECM-Like Hydrogels on Neurite Outgrowth Induced by Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:6319129. [64] YU T, ZHAO C, HOU S, et al. Exosomes secreted from miRNA-29b-modified mesenchymal stem cells repaired spinal cord injury in rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019;52(12):e8735. [65] STEWART AN, KENDZIORSKI G, DEAK ZM, et al. Co-transplantation of mesenchymal and neural stem cells and overexpressing stromal-derived factor-1 for treating spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2017;1672:91-105. [66] GIMONA M, PACHLER K, LANER-PLAMBERGER S, et al. Manufacturing of Human Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Clinical Use. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(6). pii: E1190. [67] LIU W, WANG Y, GONG F, et al. Exosomes Derived from Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury by Suppressing the Activation of A1 Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocytes. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(3):469-484. [68] 李栋. miR-133b修饰的MSCs来源外泌体对大鼠脊髓损伤后神经功能恢复的作用及机制研究[D]. 苏州:苏州大学, 2017. [69] WRIGHT KT, UCHIDA K, BARA JJ, et al. Spinal motor neurite outgrowth over glial scar inhibitors is enhanced by coculture with bone marrow stromal cells. Spine J. 2014;14(8):1722-33 [70] REN ZW, ZHOU JG, XIONG ZK, et al. Effect of exosomes derived from MiR-133b-modified ADSCs on the recovery of neurological function after SCI. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(1):52-60. [71] GOMES ED, MENDES SS, ASSUNÇÃO-SILVA RC, et al. Co-Transplantation of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Cells and Olfactory Ensheathing Cells for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. Stem Cells. 2018;36(5):696-708. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 闵友江, 姚海华, 孙 洁, 周 璇, 余 航, 孙前谱, 洪恩四. 磁共振评价“三通针法”对脊髓损伤患者脑功能的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | 张 超, 吕 欣. 髋臼骨折固定后的异位骨化:危险因素、预防及其治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | 周继辉, 李新志, 周 游, 黄 卫, 陈文瑶. 髌骨骨折修复内植物选择的多重问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | 王德斌, 毕郑刚. 尺骨鹰嘴骨折-脱位解剖力学、损伤特点、固定修复及3D技术应用的相关问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [6] | 蒋红英, 朱 亮, 余 曦, 黄 靖, 向小娜, 兰正燕, 何红晨. 富血小板血浆干预脊髓损伤患者压力性损伤的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [7] | 姬志祥, 蓝常贡. 尿酸盐转运蛋白在痛风中的多态性和治疗相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [8] | 袁 美, 张新新, 郭祎莎, 毕 霞. 循环microRNA在血管性认知障碍诊断中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [9] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [10] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [11] | 赵 敏, 冯柳祥, 陈 垚, 顾 霞, 王平义, 李一梅, 李文华. 低氧环境下外泌体可作为疾病的标志物[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [12] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [13] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [14] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [15] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
因此长期的残疾会给患者及家属带来严重的心理和经济负担。尽管多年来脊髓损伤相关实验研究取得了很大的进展,但仍未发现治疗脊髓损伤的可靠手段[2],因此寻找脊髓损伤的有效治疗方法已迫在眉睫。
组织工程学研究试图通过细胞移植的方法来促进脊髓的再生[9],其中间充质干细胞由于其免疫调节、促进组织再生等功能备受瞩目。然而大量研究发现细胞治疗的效果主要源于其旁分泌作用,甚至其中部分研究证明单独使用细胞分泌到外界的成分(细胞分泌组)可以产生与细胞移植相当的效果[10-12]。由于细胞治疗还存在免疫排斥反应、储存困难等诸多问题[10],因此应用间充质干细胞分泌组(mesenchymal stem cell secretome)进行无细胞治疗的方法,可以完美地代替细胞治疗,在未来成为治疗脊髓损伤的利器。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
injury,secretome”为英文检索词,“脊髓损伤、分泌组”为中文检索词,排除与综述不相关及重复的文章,共选入71篇文献。
1.2 筛选方法
1.2.1 文献入选标准 ①与间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤相关的研究;②权威杂志在同领域内近期发表的文章;③具有原创性、文章论点可靠。
1.2.2 文献的排除标准 ①重复性研究;②设计不合理的研究;③与主题内容无关的文章。
1.3 文献质量评估方法 初检得到文献732篇,通过阅读标题与摘要进行初筛,排除与研究内容无关、重复且设计不合理的文章,根据纳入标准进一步筛选后,共保留文献71篇,包括英文文献60篇,中文文献11篇。文献筛选流程见图1。
近年来间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究已经取得了很大的进步,虽然分泌组仍存在分离纯化、临床标准化等诸多方面的问题,但随着组织工程学的快速发展,相应问题逐步解决,使用间充质干细胞分泌组进行无细胞治疗将会成为脊髓损伤治疗的方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程

文题释义:
脊髓损伤:创伤等各种原因导致脊髓结构破坏、神经传导通路中断,由于中枢神经系统固有再生能力有限且损伤局部环境不利于再生,常导致永久性的神经功能缺陷。其病变与再生机制复杂,治疗需要从神经保护、解放神经再生潜力、对抗周围再生抑制环境等多方面进行。
间充质干细胞分泌组:是间充质干细胞分泌至细胞外空间的各种分子或细胞外囊泡,主要由间充质干细胞培养基去除杂质后获得,通过各种可溶性分子(如生长因子、趋化因子)及外泌体介导了间充质干细胞的大部分治疗作用,并且能避免细胞移植的各种弊端。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
早期的研究主要将间充质干细胞的治疗效果归因于其多向分化能力,然而最近的研究表明移植后细胞不能长时间存活(通常小于1周),且全身注射情况下移植到受损部位的细胞数量稀少,其中大量研究发现单独使用细胞分泌到外界的成分甚至可以产生与细胞移植相当的治疗效果,因此越来越多的学者认为干细胞移植后分化起到的作用较小,其治疗效果可能来源于分泌到细胞外的分子,这些分子在细胞过程的调节中起到了关键作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||