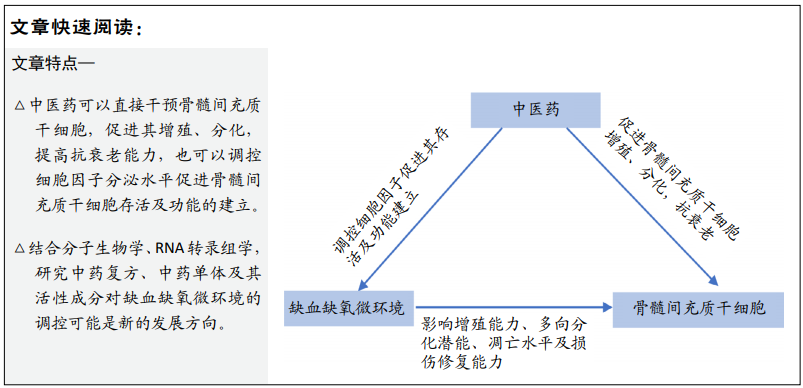
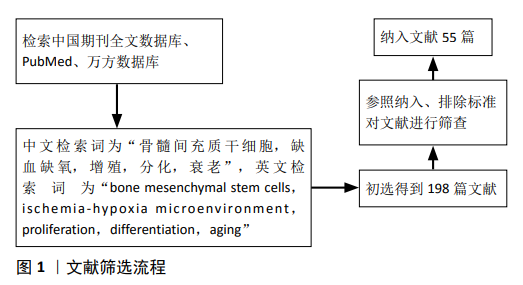
[1] HAN YS, YUN SP, LEE JH, et al. C-Met-Activated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Rescue Ischemic Damage via Interaction with Cellular Prion Protein. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(5):1835-1848.
[2] LEE C, HU J, RALLS S, et al. The molecular profiles of neural stem cell niche in the adult subventricular zone. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50501.
[3] 张宝霞, 张金生. 基于干细胞衰老理论探讨化旧生新法抗衰防衰的细胞学特性[J]. 新中医, 2019,51(8):317-320.
[4] SONG M, MOHAMAD O, GU X, et al. Restoration of intracortical and thalamocortical circuits after transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into the ischemic brain of mice. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(11):2001-2015.
[5] WEI L, FRASER JL, LU ZY, et al. Transplantation of hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhances angiogenesis and neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2012; 46(3): 635-645.
[6] MENDLER MR, MENDLER I, HASSAN MA, et al. Predictive Value of Thompson-Score for Long-Term Neurological and Cognitive Outcome in Term Newborns with Perinatal Asphyxia and Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Undergoing Controlled Hypothermia Treatment. Neonatology. 2018;114(4):341-347.
[7] 龚佼, 刘铭. 人诱导性多能干细胞移植治疗新生小鼠缺氧缺血性脑病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(33):5322-5327.
[8] KIM DH, KIM DW, JUNG BH, et al. Ginsenoside Rb2 suppresses the glutamate-mediated oxidative stress and neuronal cell death in HT22 cells. J Ginseng Res. 2019;43(2):326-334.
[9] PELL VR, SPIROSKI AM, MULVEY J, et al. Ischemic preconditioning protects against cardiac ischemia reperfusion injury without affecting succinate accumulation or oxidation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;123: 88-91.
[10] YANG Z, WU QQ, XIAO Y, et al. Aucubin Protects against Myocardial Infarction-Induced Cardiac Remodeling via nNOS/NO-Regulated Oxidative Stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:4327901.
[11] ZHANG Q, ZHAO Y, XU Y, et al. Sodium ferulate and n-butylidenephthalate combined with bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) improve the therapeutic effects of angiogenesis and neurogenesis after rat focal cerebral ischemia. J Transl Med. 2016;14(1):223.
[12] TOMA C, PITTENGER MF, CAHILL KS, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to a cardiomyocyte phenotype in the adult murine heart. Circulation. 2002;105(1):93-98.
[13] GAO F, CHIU SM, MOTAN DA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and immunomodulation: current status and future prospects. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(1):e2062.
[14] MIURA Y. Basics and clinical application of human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2015;56(10):2195-2204.
[15] LIONAKI E, MARKAKI M, TAVERNARAKIS N. Autophagy and ageing: insights from invertebrate model organisms. Ageing Res Rev. 2013; 12(1):413-428.
[16] 周龙,何帆,王磊.间充质干细胞早衰的原因及预防[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(29):4721-4728.
[17] 林瑶,谷真真,潘宇,等.干细胞衰老与衰老微环境调控的研究进展[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2018,18(15):2997-3000,2991.
[18] 孟宪会, 戚宇华, Doulathunnisa J, 等. 间充质干细胞衰老中核内miRNA表达谱特征与功能分析[J]. 东南大学学报(医学版), 2019, 38(2):214-223.
[19] LEE JY, YU KR, KIM HS, et al. BMI1 inhibits senescence and enhances the immunomodulatory properties of human mesenchymal stem cells via the direct suppression of MKP-1/DUSP1. Aging (Albany NY). 2016;8(8):1670-1689.
[20] CHOI HR, CHO KA, KANG HT, et al. Restoration of senescent human diploid fibroblasts by modulation of the extracellular matrix. Aging Cell. 2011;10(1):148-157.
[21] 张阳阳,张金生. 基于衰老相关因子探讨活血化瘀法调控干细胞衰老的有效性[J].中国中医药现代远程教育, 2015,13(14):7-8.
[22] 崔国宁,刘喜平,董俊刚,等.微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞自噬水平的影响研究进展[J]. 转化医学杂志, 2018,7(6):338-340,349.
[23] 曹茜,刘秀南.干细胞衰老机制的研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘, 2018,18(92):38-39.
[24] HU C, ZHAO L, WU D, et al. Modulating autophagy in mesenchymal stem cells effectively protects against hypoxia- or ischemia-induced injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):120.
[25] XIAO C, WANG K, XU Y, et al. Transplanted Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Autophagic Flux in Infarcted Hearts via the Exosomal Transfer of miR-125b. Circ Res. 2018;123(5):564-578.
[26] 胡朋言,王伟,梁雪,等.细胞自噬与相关中医辨证体系的研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2018,36(9): 2217-2219.
[27] SUN P, LIU L, PAN Y, et al. Intracranial Atherosclerosis Burden and Stroke Recurrence for Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis (sICAS). Aging Dis. 2018;9(6):1096-1102.
[28] 王媛,秦合伟,刘建东.血管软化丸治疗脑梗死对血栓相关因子和自噬的影响[J].实用中医药杂志,2019,35(1): 3-5.
[29] HE Q, LIU Q, CHEN Y, et al. Long-Zhi Decoction Medicated Serum Promotes Angiogenesis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Based on Autophagy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018; 2018:6857398.
[30] 周胜强. 补阳还五汤调控Cav1/mTOR/ULK1通路介导的自噬抗脑缺血损伤机制研究[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2017
[31] DONG F, PATNAIK S, DUAN ZH, et al. A Novel Role for CAMKK1 in the Regulation of the Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(9):1759-1766.
[32] PENG X, JI C, TAN L, et al. Long non-coding RNA TNRC6C-AS1 promotes methylation of STK4 to inhibit thyroid carcinoma cell apoptosis and autophagy via Hippo signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(1):304-316.
[33] PANT T, DHANASEKARAN A, BAI X, et al. Genome-wide differential expression profiling of lncRNAs and mRNAs associated with early diabetic cardiomyopathy. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15345.
[34] FEI L, ZHANG J, NIU H, et al. Effects of Rosuvastatin and MiR-126 on Myocardial Injury Induced by Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats: Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGF-A). Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:2324-2334.
[35] HUANG F, ZHU X, HU XQ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells modified with miR-126 release angiogenic factors and activate Notch ligand Delta-like-4, enhancing ischemic angiogenesis and cell survival. Int J Mol Med. 2013;31(2):484-492.
[36] COSTA V, RAIMONDI L, CONIGLIARO A, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1Α may regulate the commitment of mesenchymal stromal cells toward angio-osteogenesis by mirna-675-5P. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(12): 1412-1425.
[37] SHI XF, WANG H, XIAO FJ, et al. MiRNA-486 regulates angiogenic activity and survival of mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia through modulating Akt signal. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 470(3):670-677.
[38] ONG SG, LEE WH, HUANG M, et al. Cross talk of combined gene and cell therapy in ischemic heart disease: role of exosomal microRNA transfer. Circulation. 2014;130(11 Suppl 1):S60-69.
[39] XIN H, LI Y, LIU Z, et al. MiR-133b promotes neural plasticity and functional recovery after treatment of stroke with multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in rats via transfer of exosome-enriched extracellular particles. Stem Cells. 2013;31(12):2737-2746.
[40] WANG Y, PAN X, FAN Y, et al. Dysregulated expression of microRNAs and mRNAs in myocardial infarction. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(11): 2291-2304.
[41] 郭杨,马勇,成吉华,等.益肾通络复方含药血清对兔骨髓间充质干细胞体外增殖和成骨分化的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志, 2015,21(5):508-510.
[42] 张黎声,韩小晶,罗志荣,等.淫羊藿苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞迁移作用的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志, 2017,24(2):44-48.
[43] 银楠楠,卢昌均,顿玲露.通窍活血汤诱导骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及分化机制[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(20):118-119.
[44] 倪广晓,韩晓勇,周宏斌,等.隐丹参酮体外诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞分化的实验研究[J].河北中医药学报, 2018,33(6): 47-51.
[45] ZHAO Y, LI Y, TONG L, et al. Analysis of microRNA Expression Profiles Induced by Yiqifumai Injection in Rats with Chronic Heart Failure. Front Physiol. 2018;9:48.
[46] ZHANG Y, ZHANG L, ZHANG Y, et al. YiQiFuMai Powder Injection Attenuates Coronary Artery Ligation-Induced Heart Failure Through Improving Mitochondrial Function via Regulating ROS Generation and CaMKII Signaling Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:381.
[47] PANG LZ, JU AC, ZHENG XJ, et al. YiQiFuMai Powder Injection attenuates coronary artery ligation-induced myocardial remodeling and heart failure through modulating MAPKs signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;202:67-77.
[48] 赵慧杰.加味丹参饮含药血清对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及分泌bFGF、VEGF的影响[J].亚太传统医药, 2019,15(8):41-43.
[49] 张金生,张宝霞,朱慧芳,等. 干细胞、微环境与活血化瘀[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(23):3484-3490.
[50] 张宝霞,张金生,张阳阳,等.三七总皂苷、红景天苷、黄芪有效组分对心肌梗死大鼠模型骨髓间充质干细胞动员作用研究[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2016,22(8):137-142.
[51] 张金生,张宝霞,朱慧芳,等.机体衰老、干细胞衰老与补肾化瘀生新[J].中医研究,2015,28(12): 1-3.
[52] 杜楠楠,汪引芳,张鹏,等.中药单体诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌细胞分化的研究新进展[J].中国医药导报,2019,16(23):30-33.
[53] 张金生,张宝霞,朱慧芳,等.三七总皂苷对归巢到脑梗死边缘区CD105+骨髓间充质干细胞增殖分化的实验研究[J].北京中医药大学学报, 2014,37(11):777-780,785.
[54] 陈宏,张娟,王云宝, 等.补肾活血化浊中药促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖与分化研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报, 2019,21(7): 105-108.
[55] NAH SY, KIM DH, RHIM H. Ginsenosides: are any of them candidates for drugs acting on the central nervous system? CNS Drug Rev. 2007; 13(4):381-404. |