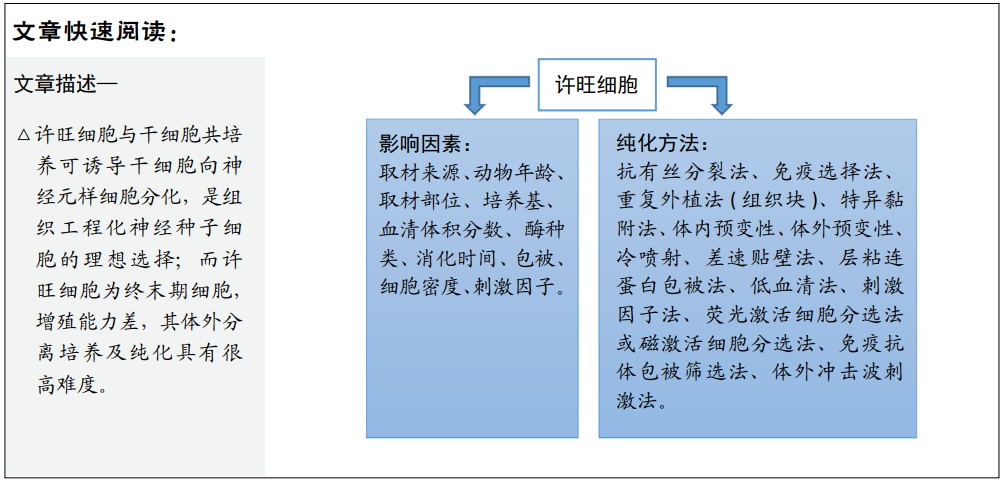
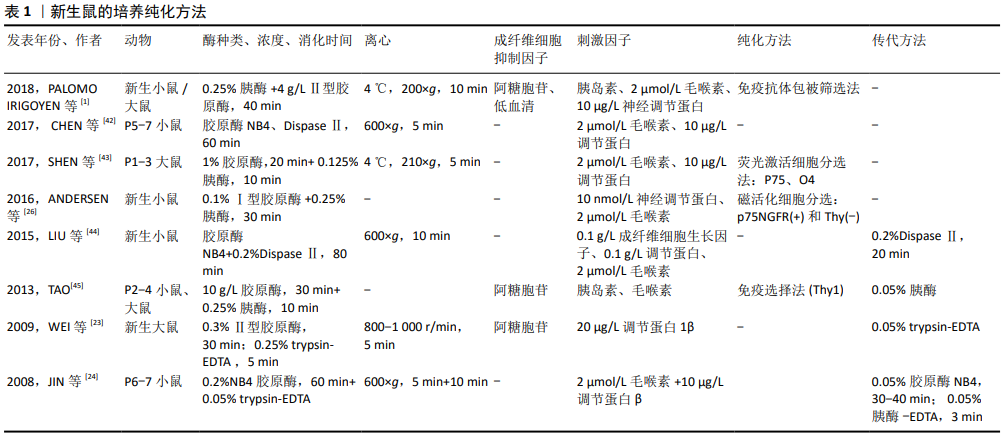
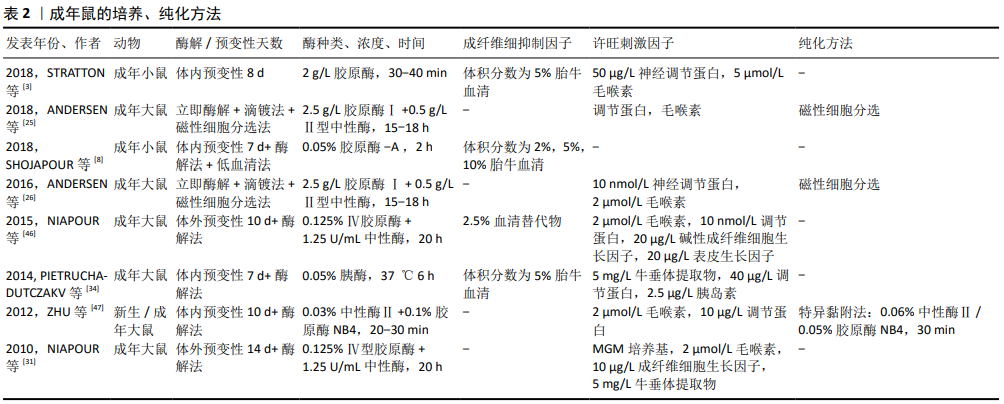
[1] PALOMO IRIGOYEN M, TAMAYO CARO M, PÉREZ ANDRÉS E, et al. Isolation and Purification of Primary Rodent Schwann Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1791:81-93.
[2] SUGA M, HAYASHI Y, FURUE MK. In vitro models of cranial neural crest development toward toxicity tests: frog, mouse, and human. Oral Dis. 2017;23(5):559-565.
[3] STRATTON JA, HOLMES A, ROSIN NL, et al. Macrophages Regulate Schwann Cell Maturation after Nerve Injury. Cell Rep. 2018;24(10):2561-2572.e6.
[4] MIRFEIZI L, STRATTON JA, KUMAR R, et al. Serum-free bioprocessing of adult human and rodent skin-derived Schwann cells: implications for cell therapy in nervous system injury. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(12):3385-3397.
[5] SUH JF, HYUNG S. Primary Motor Neuron Culture to Promote Cellular Viability and Myelination. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1727: 403-411.
[6] GERSEY ZC, BURKS SS, ANDERSON KD, et al. First human experience with autologous Schwann cells to supplement sciatic nerve repair: report of 2 cases with long-term follow-up. Neurosurg Focus. 2017;42(3):E2.
[7] GORDON T, WOOD P, SULAIMAN OAR. Long-Term Denervated Rat Schwann Cells Retain Their Capacity to Proliferate and to Myelinate Axons in vitro. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 ;12:511.
[8] SHOJAPOUR M, MOSAYEBI G, HAJIHOSSEIN R, et al. A Simplified Protocol for the Purification of Schwann Cells and Exosome Isolation from C57BL/6 Mice. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2018;7(1):9-15.
[9] WOOD PM. Separation of functional Schwann cells and neurons from normal peripheral nerve tissue. Brain Res. 1976; 115(3):361-375.
[10] BROCKES JP, FIELDS KL, RAFF MC. Studies on cultured rat Schwann cells. I. Establishment of purified populations from cultures of peripheral nerve. Brain Res. 1979;165(1): 105-118.
[11] ASKANAS V, ENGEL WK, DALAKAS MC, et al. Human schwann cells in tissue culture: histochemical and ultrastructural studies. Arch Neurol. 1980;37(6):329-337.
[12] JIRSOVÁ K, SODAAR P, MANDYS V, et al. Cold jet: a method to obtain pure Schwann cell cultures without the need for cytotoxic, apoptosis-inducing drug treatment. J Neurosci Methods. 1997;78(1-2):133-137.
[13] WU W, JIN YQ, KRETLOW JD, et al. Purification of Schwann cells from adult rats by differential detachment. Biotechnol Lett. 2009;31(11):1703-1708.
[14] CASELLA GT, BUNGE RP, WOOD PM. Improved method for harvesting human Schwann cells from mature peripheral nerve and expansion in vitro. Glia. 1996;17(4): 327-338.
[15] 王世清,范志海,沈忆新.不同部位取材的雪旺细胞培养与纯化研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(2):166-170.
[16] 秦煜,顾立强,吴岚晓,等.感觉性和运动性神经来源许旺细胞神经生长因子的表达[J].中华显微外科杂志,2001,24(4): 278-280.
[17] HERCHER D, REDL H, SCHUH CMAP. Motor and sensory Schwann cell phenotype commitment is diminished by extracorporeal shockwave treatment in vitro. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2020;25(1): 32-43.
[18] TRACHTENBERG JT, THOMPSON WJ. Schwann cell apoptosis at developing neuromuscular junctions is regulated by glial growth factor. Nature. 1996;379(6561): 174-177.
[19] LUTZ AB. Purification of schwann cells from the neonatal and injured adult mouse peripheral nerve. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2014;2014(12):1312-1319.
[20] 汪海滨. 成年小鼠坐骨神经雪旺细胞体外培养的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013.
[21] 周敏, 胡鸣, 何松明, 等.新生大鼠施万细胞体外培养的实验研究[J].中国医药导报,2018,15(13):14-17,181.
[22] TOMKO P, SLOVINSKÁ L, VANICKÝ I. In vitro predegeneration of peripheral nerve; the effect of predegeneration period on rat Schwann cell cultures. Exp Ther Med. 2019; 17(1):596-602.
[23] WEI Y, ZHOU J, ZHENG Z, et al. An improved method for isolating Schwann cells from postnatal rat sciatic nerves. Cell Tissue Res. 2009;337(3):361-369.
[24] JIN YQ, LIU W, HONG TH, et al. Efficient Schwann cell purification by differential cell detachment using multiplex collagenase treatment. J Neurosci Methods. 2008; 170(1):140-148.
[25] ANDERSEN ND, MONJE PV. Isolation, Culture, and Cryopreservation of Adult Rodent Schwann Cells Derived from Immediately Dissociated Teased Fibers. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1739:49-66.
[26] ANDERSEN ND, SRINIVAS S, PIÑERO G, et al. A rapid and versatile method for the isolation, purification and cryogenic storage of Schwann cells from adult rodent nerves. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31781.
[27] NEEDHAM LK, TENNEKOON GI, MCKHANN GM. Selective growth of rat Schwann cells in neuron- and serum-free primary culture. J Neurosci. 1987;7(1):1-9.
[28] KOMIYAMA T, NAKAO Y, TOYAMA Y, et al. A novel technique to isolate adult Schwann cells for an artificial nerve conduit. J Neurosci Methods. 2003;122(2):195-200.
[29] HEDAYATPOUR A, SOBHANI A, BAYATI V, et al. A method for isolation and cultivation of adult Schwann cells for nerve conduit. Arch Iran Med. 2007;10(4):474-480.
[30] 高德坤,孙辉,朱晋,等.乳鼠坐骨神经植块法的雪旺氏细胞培养[J].现代生物医学进展,2018,18(11):2028-2031,2037.
[31] NIAPOUR A, KARAMALI F, KARBALAIE K, et al. Novel method to obtain highly enriched cultures of adult rat Schwann cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2010;32(6):781-786.
[32] KRAUS A, TÄGER J, KOHLER K, et al. Efficacy of various durations of in vitro predegeneration on the cell count and purity of rat Schwann-cell cultures. J Neurotrauma. 2010;27(1):197-203.
[33] HAASTERT-TALINI K. Culture and proliferation of highly purified adult Schwann cells from rat, dog, and man. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;846:189-200.
[34] PIETRUCHA-DUTCZAKV M, MARCOL W, FRANCUZ T, et al. A new protocol for cultivation of predegenerated adult rat Schwann cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2014; 15(3):403-411.
[35] MILLER C, JEFTINIJA S, MALLAPRAGADA S. Micropatterned Schwann cell-seeded biodegradable polymer substrates significantly enhance neurite alignment and outgrowth. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(6):705-715.
[36] SASAGASAKO N, TODA K, HOLLIS M, et al. Myelin gene expression in immortalized Schwann cells: relationship to cell density and proliferation. J Neurochem. 1996;66(4):1432-1439.
[37] WANG H, WU J, ZHANG X, et al. Study of synergistic role of allogenic skin-derived precursor differentiated Schwann cells and heregulin-1β in nerve regeneration with an acellular nerve allograft. Neurochem Int. 2016;97:146-153.
[38] FUENTEALBA L, SCHWORER C, SCHROERING A, et al. Heregulin and forskolin-induced cyclin D3 expression in Schwann cells: role of a CCAAT promoter element and CCAAT enhancer binding protein. Glia. 2004; 45(3): 238-248.
[39] SOWA Y, KISHIDA T, TOMITA K, et al. Involvement of PDGF-BB and IGF-1 in Activation of Human Schwann Cells by Platelet-Rich Plasma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(6):1025e-1036e.
[40] 胡华麟,杨小四,杨元元,等.高糖及高糖加胰岛素对雪旺细胞培养的影响[J].包头医学院学报,2019,35(5):82-83.
[41] KOMIYAMA A, SUZUKI K. Age-related changes in attachment and proliferation of mouse Schwann cells in vitro. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1991;62(1):7-16.
[42] CHEN L, JIN Y, YANG X, et al. Fat tissue, a potential Schwann cell reservoir: isolation and identification of adipose-derived Schwann cells. Am J Transl Res. 2017; 9(5): 2579-2594.
[43] SHEN M, TANG W, CAO Z, et al. Isolation of rat Schwann cells based on cell sorting. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(2):1747-1752.
[44] LIU Z, JIN YQ, CHEN L, et al. Specific marker expression and cell state of Schwann cells during culture in vitro. PLoS One. 2015; 10(4):e0123278.
[45] TAO Y. Isolation and culture of Schwann cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1018:93-104.
[46] NIAPOUR N, MOHAMMADI-GHALEHBIN B, GOLMOHAMMADI MG, et al. Efficacy of optimized in vitro predegeneration period on the cell count and purity of canine Schwann cell cultures. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(3):307-311.
[47] ZHU J, QIN J, SHEN Z, et al. Dispase rapidly and effectively purifies Schwann cells from newborn mice and adult rats. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(4):256-260.
[48] ANAND U, OTTO WR, BOUNTRA C, et al. Cytosine arabinoside affects the heat and capsaicin receptor TRPV1 localisation and sensitivity in human sensory neurons. J Neurooncol. 2008;89(1):1-7.
[49] VROEMEN M, WEIDNER N. Purification of Schwann cells by selection of p75 low affinity nerve growth factor receptor expressing cells from adult peripheral nerve. J Neurosci Methods. 2003;124(2):135-143.
[50] SCHUH CM, HAUSNER T, REDL HR. A therapeutic shock propels Schwann cells to proliferate in peripheral nerve injury. Brain Circ. 2016;2(3):138-140.
[51] MITTERMAYR R, HARTINGER J, ANTONIC V, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) minimizes ischemic tissue necrosis irrespective of application time and promotes tissue revascularization by stimulating angiogenesis. Ann Surg. 2011;253(5):1024-1032.
[52] HAUSNER T, PAJER K, HALAT G, et al. Improved rate of peripheral nerve regeneration induced by extracorporeal shock wave treatment in the rat. Exp Neurol. 2012;236(2):363-370.
[53] SCHUH CM, HERCHER D, STAINER M, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave treatment: A novel tool to improve Schwann cell isolation and culture. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(6): 760-770.
[54] WEIHS AM, FUCHS C, TEUSCHL AH, et al. Shock wave treatment enhances cell proliferation and improves wound healing by ATP release-coupled extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(39):27090-27104.
[55] HAYNES LW, RUSHTON JA, PERRINS MF, et al. Diploid and hyperdiploid rat Schwann cell strains displaying negative autoregulation of growth in vitro and myelin sheath-formation in vivo. J Neurosci Methods. 1994;52(2):119-127.
[56] BROOKS AE, ATHAUDA G, BUNGE MB, et al. Culture and Expansion of Rodent and Porcine Schwann Cells for Preclinical Animal Studies. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1739: 111-126.
[57] WU Z, LI Q, XIE S, et al. In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility evaluation of a 3D bioprinted gelatin-sodium alginate/rat Schwann-cell scaffold. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;109:110530.
[58] 张振辉,王庆德,梅伟,等.新型组织工程化神经导管修复大鼠周围神经缺损[J].中华显微外科杂志,2018,41(6):563-567.
[59] STRAUCH B, RODRIGUEZ DM, DIAZ J, et al. Autologous Schwann cells drive regeneration through a 6-cm autogenous venous nerve conduit. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2001;17(8):589-595.
[60] CHEN W, WEI ZR, WU BH, et al. Effects of combined transplantation of rat Schwann cells and fibroblasts on nerve regeneration of denervated perforator flaps in rats and the mechanism. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2019;35(2):134-142.
[61] SAHEB-AL-ZAMANI M, YAN Y, FARBER SJ, et al. Limited regeneration in long acellular nerve allografts is associated with increased Schwann cell senescence. Exp Neurol. 2013; 247:165-177.
[62] LEVI AD, BURKS SS, ANDERSON KD, et al. The Use of Autologous Schwann Cells to Supplement Sciatic Nerve Repair With a Large Gap: First in Human Experience. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(7):1395-1403.
|