[1] PINTO JM, SCHAIRER JL, PETROVA A. Duration of Hospitalization in Association with Type of Inhalation Therapy Used in the Management of Children with Nonsevere, Acute Bronchiolitis. Pediatr Neonatol. 2016;57(2):140-144.
[2] MEISSNER HC. Viral Bronchiolitis in Children. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(1): 62-72.
[3] 王执勇,李树青,钱秀玲.孟鲁司特治疗呼吸道合胞病毒毛细支气管炎症状及反复喘息疗效研究[J].中国全科医学,2020,23(8): 929-934.
[4] STEIN RT, SHERRILL D, MORGAN WJ, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus in early life and risk of wheeze and allergy by age 13 years. Lancet. 1999; 354(9178):541-545.
[5] HENDERSON J, HILLIARD TN, SHERRIFF A, et al. Hospitalization for RSV bronchiolitis before 12 months of age and subsequent asthma, atopy and wheeze: a longitudinal birth cohort study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2005;16(5):386-392.
[6] 朱其国,袁林,林建成,等.毛细支气管炎患儿血IL-4、IL-10、IL-17的变化及意义[J].中国妇幼健康研究,2020,31(5):649-652.
[7] GRAHAM BS. Immunological goals for respiratory syncytial virus vaccine development. Curr Opin Immunol. 2019;59:57-64.
[8] LIU H, LIANG Z, WANG F, et al. Exosomes from mesenchymal stromal cells reduce murine colonic inflammation via a macrophage-dependent mechanism. JCI Insight. 2019;4(24):e131273.
[9] STONE ML, ZHAO Y, ROBERT SMITH J, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate lung ischemia-reperfusion injury and enhance reconditioning of donor lungs after circulatory death. Respir Res. 2017;18(1):212.
[10] AOKI N, JIN-NO S, NAKAGAWA Y, et al. Identification and characterization of microvesicles secreted by 3T3-L1 adipocytes: redox- and hormone-dependent induction of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8-associated microvesicles. Endocrinology. 2007;148(8):3850-3862.
[11] 张权,张亚奇,饶巍,等.长期传代培养对人脐带间充质干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2019,41(1):42-52.
[12] 李雅慧,张国成,许东亮.雾化吸入干扰素α-1b对呼吸道合胞病毒治疗的实验研究[J].西北国防医学杂志,2010,31(3):203-205.
[13] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[14] SIGURS N, BJARNASON R, SIGURBERGSSON F, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infancy is an important risk factor for asthma and allergy at age 7. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161(5):1501-1507.
[15] BENNETT BL, GAROFALO RP, CRON SG, et al. Immunopathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. J Infect Dis. 2007;195(10): 1532-1540.
[16] 彭程,黎金雨,赵云,等.呼吸道合胞病毒毛细支气管炎患儿中TREM-1/DAP12通路关键信号节点的表达[J].中国感染控制杂志, 2020,19(5):433-439.
[17] PINTO RA, ARREDONDO SM, BONO MR, et al. T helper 1/T helper 2 cytokine imbalance in respiratory syncytial virus infection is associated with increased endogenous plasma cortisol. Pediatrics. 2006; 117(5): e878-886.
[18] 沈朝斌,郁兰,顾燕妮, 等.体内转染黄芪来源miR-396可抑制哮喘小鼠Th2细胞的GATA-3表达[J].中国免疫学杂志,2019,35(24): 3001-3007.
[19] COLLEY T, MERCADO N, KUNORI Y, et al. Defective sirtuin-1 increases IL-4 expression through acetylation of GATA-3 in patients with severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137(5):1595-1597.
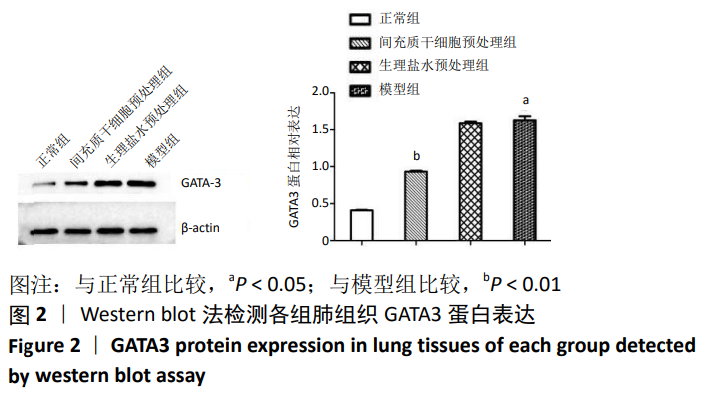
[20] 张雪静,何潇,吴福玲,等.心房钠尿肽对毛细支气管炎小鼠肺组织GATA-3的调控[J].中国免疫学杂志,2018,34(10):1461-1465.
[21] 张恒爱,梅花,刘春枝.间充质干细胞及其外泌体防治支气管肺发育不良研究进展[J].中华新生儿科杂志(中英文),2020,35(3): 232-235.
[22] LI JW, WEI L, HAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosomes alleviate ischemia/reperfusion injury in mouse lung by transporting anti-apoptotic miR-21-5p. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;852:68-76.
[23] LEE JW, FANG X, GUPTA N, et al. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of E. coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in the ex vivo perfused human lung. Version 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(38):16357-16362.
[24] ROYCE SG, MAO W, LIM R, et al. iPSC- and mesenchymoangioblast-derived mesenchymal stem cells provide greater protection against experimental chronic allergic airways disease compared with a clinically used corticosteroid. FASEB J. 2019;33(5):6402-6411.
[25] ARSLAN F, LAI RC, SMEETS MB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301-312.
[26] LEE C, MITSIALIS SA, ASLAM M, et al. Exosomes mediate the cytoprotective action of mesenchymal stromal cells on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2012;126(22):2601-2611.
[27] XU J, WOODS CR, MORA AL, et al. Prevention of endotoxin-induced systemic response by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007;293(1):L131-141.
[28] 金志贤,王清,郭翔,等.间充质干细胞移植肺气肿大鼠肺组织病理改变及炎性因子表达变化[J].山东医药,2015,55(15):20-22.
[29] 汪珺,苏晓三,杨柳,等.骨髓间充质干细胞预防手术后肿瘤肺转移动物模型研究[J].中国癌症杂志,2017,27(2):89-94.
[30] 杨红霞,石清红,翁敏华,等.人羊膜间充质干细胞移植对哮喘小鼠气道杯状细胞增生及黏蛋白5ac表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(25):4050-4055. |