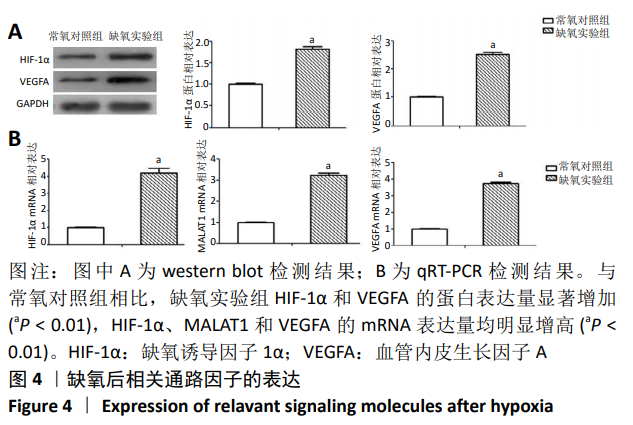
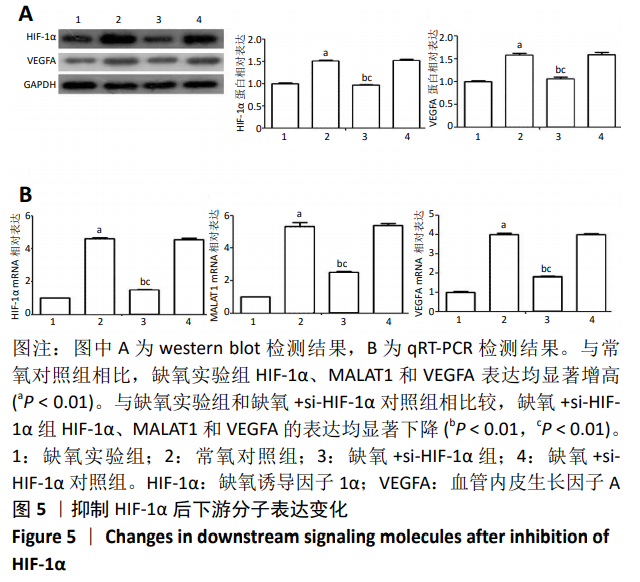
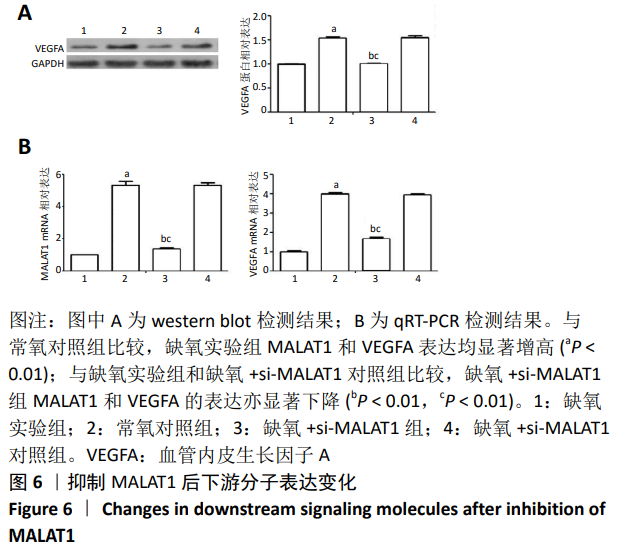
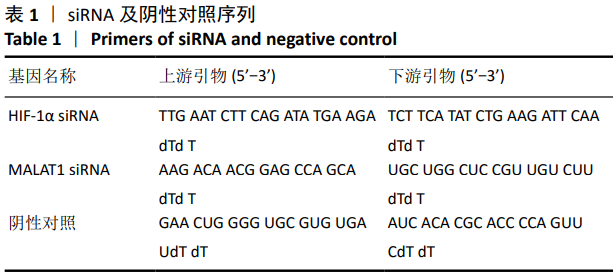
[1] MENG SS, XU XP, CHANG W, et al. LincRNA-p21 promotes mesenchymal stem cell migration capacity and survival through hypoxic preconditioning. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):280.
[2] ZHANG Z, YANG C, SHEN M, et al. Autophagy mediates the beneficial effect of hypoxic preconditioning on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for the therapy of myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):89.
[3] FÁBIÁN Z. The Effects of Hypoxia on the Immune-Modulatory Properties of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2019; 2019:2509606.
[4] LUO Z, WU F, XUE E, et al. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival by inducing HIF-1α in injured neuronal cells derived exosomes culture system. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(2):134.
[5] SHENG L, MAO X, YU Q, et al. Effect of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway on hypoxia-induced proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(1):55-62.
[6] ANTEBI B, RODRIGUEZ LA 2ND, WALKER KP 3RD, et al. Short-term physiological hypoxia potentiates the therapeutic function of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):265.
[7] LAMBERTINI E, PENOLAZZI L, ANGELOZZI M, et al. Hypoxia Preconditioning of Human MSCs: a Direct Evidence of HIF-1α and Collagen Type XV Correlation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(5):2237-2249.
[8] LIN S, ZHU B, HUANG G, et al. Microvesicles derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote U2OS cell growth under hypoxia: the role of PI3K/AKT and HIF-1α. Hum Cell. 2019;32(1):64-74.
[9] CUI P, ZHAO X, LIU J, et al. miR-146a interacting with lncRNA EPB41L4A-AS1 and lncRNA SNHG7 inhibits proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(4):3292-3308.
[10] YUAN Z, BIAN Y, MA X, et al. LncRNA H19 Knockdown in Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppresses Angiogenesis by Associating with EZH2 and Activating Vasohibin-1. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(12):781-790.
[11] 侯婧瑛,汪蕾,龙会宝,等.长链非编码RNA-H19 对缺血缺氧条件下骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生能力的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(13):1969-1975.
[12] LI X, SONG Y, LIU F, et al. Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 Promotes Proliferation, Angiogenesis, and Immunosuppressive Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Inducing VEGF and IDO. J Cell Biochem. 2017; 118(9):2780-2791.
[13] REN L, WEI C, LI K, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 up-regulates VEGF-A and ANGPT2 to promote angiogenesis in brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation via targetting miR-145. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(3): BSR20180226.
[14] BROCK M, SCHUOLER C, LEUENBERGER C, et al. Analysis of hypoxia-induced noncoding RNAs reveals metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 as an important regulator of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017;242(5):487-496.
[15] STONE JK, KIM JH, VUKADIN L, et al. Hypoxia induces cancer cell-specific chromatin interactions and increases MALAT1 expression in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(29):11213-11224.
[16] 侯婧瑛,汪蕾,钟婷婷,等. apelin干预骨髓间充质干细胞在缺血缺氧条件下的生存和血管再生[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(1):6-12.
[17] HOU J, ZHONG T, GUO T, et al. Apelin promotes mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization under hypoxic-ischemic condition in vitro involving the upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor. Exp Mol Pathol. 2017;102(2):203-209.
[18] HOU J, LONG H, ZHOU C, et al. Long noncoding RNA Braveheart promotes cardiogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):4.
[19] HOU J, WANG L, WU Q, et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor A to enhance mesenchymal stem cells survival and angiogenic capacity by inhibiting miR-199a-5p. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):109.
[20] YUN CW, LEE SH. Enhancement of Functionality and Therapeutic Efficacy of Cell-Based Therapy Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Cardiovascular Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):E982.
[21] FAN M, HUANG Y, CHEN Z, et al. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in systolic heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):150.
[22] LIU Y, YANG X, MAUREIRA P, et al. Permanently Hypoxic Cell Culture Yields Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Cells with Higher Therapeutic Potential in the Treatment of Chronic Myocardial Infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(3):1064-1077.
[23] LV B, HUA T, LI F, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 α protects mesenchymal stem cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury via autophagy induction and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2017; 9(5):2492-2499.
[24] PEZZI A, AMORIN B, LAUREANO Á, et al. Effects Of Hypoxia in Long-Term In Vitro Expansion of Human Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(10):3072-3079.
[25] HU Y, CHEN W, WU L, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning improves the survival and neural effects of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells via CXCL12/CXCR4 signalling in a rat model of cerebral infarction. Cell Biochem Funct. 2019;37(7):504-515.
[26] YEO EJ. Hypoxia and aging. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(6):1-15.
[27] LEE JH, YOON YM, LEE SH. Hypoxic Preconditioning Promotes the Bioactivities of Mesenchymal Stem Cells via the HIF-1α-GRP78-Akt Axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(6): E1320.
[28] XUE C, SHEN Y, LI X, et al. Exosomes Derived from Hypoxia-Treated Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhance Angiogenesis Through the PKA Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2018;27(7):456-465.
[29] HAN Y, REN J, BAI Y, et al. Exosomes from hypoxia-treated human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis through VEGF/VEGF-R. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;109:59-68.
[30] ZHANG J, GUAN J, QI X, et al. Dimethyloxaloylglycine Promotes the Angiogenic Activity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from iPSCs via Activation of the PI3K/Akt Pathway for Bone Regeneration. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(6):639-652.
[31] TONG C, HAO H, XIA L, et al. Hypoxia pretreatment of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded in a collagen-chitosan sponge scaffold promotes skin wound healing in diabetic rats with hindlimb ischemia. Wound Repair Regen. 2016;24(1):45-56.
[32] JAÉ N, HEUMÜLLER AW, FOUANI Y, et al. Long non-coding RNAs in vascular biology and disease. Vascul Pharmacol. 2019;114:13-22.
[33] MOREAU PR, ÖRD T, DOWNES NL, et al. Transcriptional Profiling of Hypoxia-Regulated Non-coding RNAs in Human Primary Endothelial Cells. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018;5:159.
[34] LIU H, ZHANG Z, XIONG W, et al. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 mediates hypoxia-induced pro-survival autophagy of endometrial stromal cells in endometriosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(1):439-452.
[35] LI Y, WU Z, YUAN J, et al. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes gastric cancer tumorigenicity and metastasis by regulating vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2017;395:31-44.
[36] SUN Z, OU C, LIU J, et al. YAP1-induced MALAT1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis by sponging miR-126-5p in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2019;38(14):2627-2644.
[37] SALLÉ-LEFORT S, MIARD S, NOLIN MA, et al. Hypoxia upregulates Malat1 expression through a CaMKK/AMPK/HIF-1α axis. Int J Oncol. 2016;49(4): 1731-1736.
[38] PRUSZKO M, MILANO E, FORCATO M, et al. The mutant p53-ID4 complex controls VEGFA isoforms by recruiting lncRNA MALAT1. EMBO Rep. 2017; 18(8):1331-1351.
|