中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 1008-1013.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2164
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
hsa-miRNA-223-3p调控人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用
耿 瑶1,2,尹志良2,李兴平1,2,肖东琴3,侯伟光1,4
- 1西南医科大学,四川省泸州市 646000;2成飞医院,四川省成都市 610000;3川北医学院第二临床医学院·南充市中心医院组织工程与干细胞研究所,四川省南充市 637000;4航空工业三六三医院,四川省成都市 610000
Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Geng Yao1, 2, Yin Zhiliang2, Li Xingping1, 2, Xiao Dongqin3, Hou Weiguang1, 4
- 1Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Chengfei Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China; 3Research Institute of Tissue Engineering and Stem Cells, Nanchong Central Hospital, the Second Clinical College of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; 4AVIC 363 Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
miRNA:microRNA,又称微小RNA,是一种内源性的小分子RNA,在真核生物细胞中普遍存在,长度为16-29 nt(平均22 nt)。miRNA对基因表达、细胞周期调控乃至发育均有影响。miRNA不编码蛋白,是由其基因转录物经剪切加工形成,成熟的miRNA通过与特定的蛋白质形成复合物而在翻译水平调控基因表达。
Wnt5a:Wnt基因调控的信号传导系统统称为Wnt信号通路,其中Wnt5a主要激活非经典的Wnt/Ca2+信号通路,也可以激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,以实现对细胞分化过程的调控。
背景:研究发现miR-223-3p在骨质疏松患者体内高表达,但其相关机制研究甚少。
目的:探讨hsa-miR-223-3p对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的调节作用。
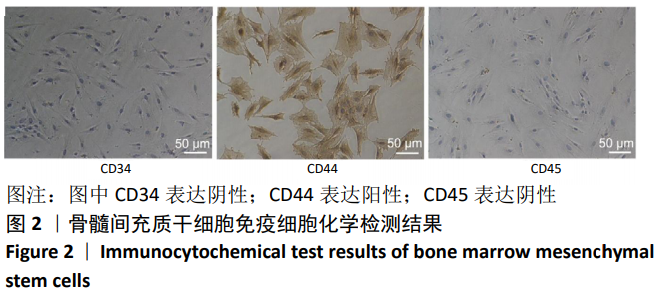
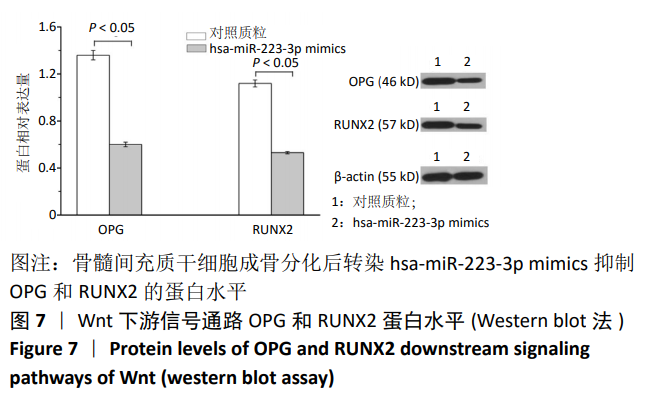
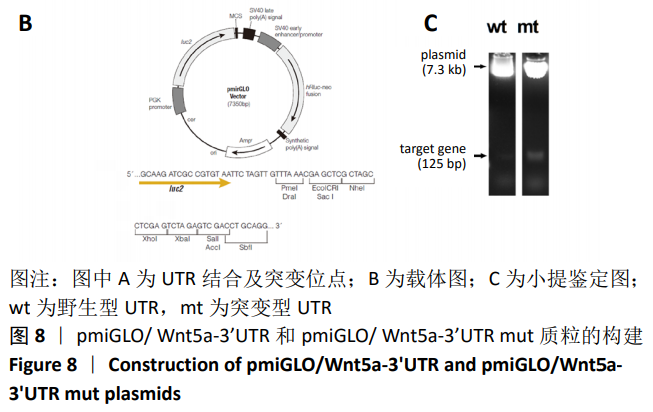
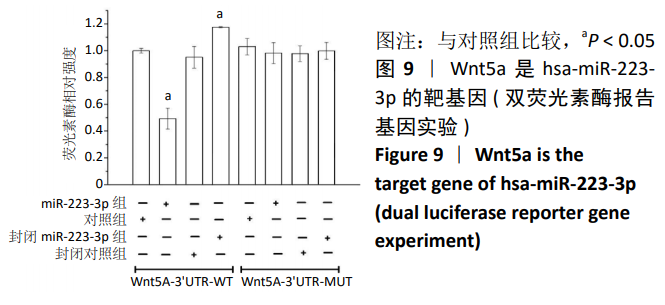
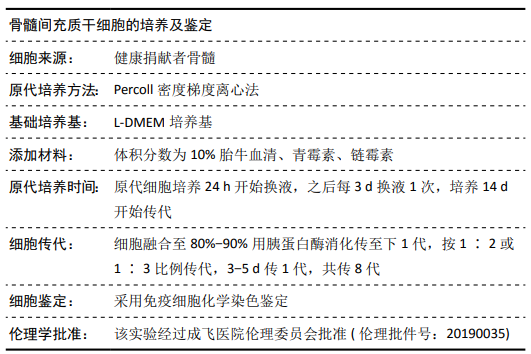
方法:Percoll密度梯度离心法分离、培养骨髓间充质干细胞,诱导其成骨分化,然后过表达hsa-miR-223-3p,RT-qPCR和Western blot方法检测Wnt信号通路标志物Wnt5a及其下游信号分子OPG、RUNX2的mRNA和蛋白水平变化。构建pmirGLO/Wnt5a-3’UTR和pmirGLO/Wnt5a-3’UTR mut质粒,分别与hsa-miR-223-3p mimics/对照质粒共转染至293T细胞,双荧光素酶报告基因系统验证hsa-miR-223-3p与Wnt5a的靶定关系。
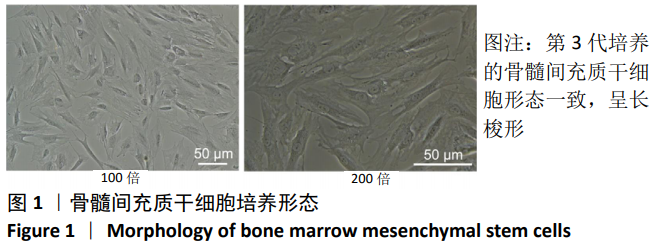
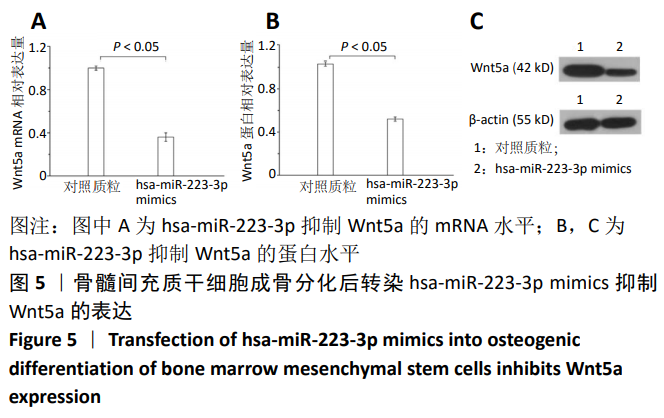
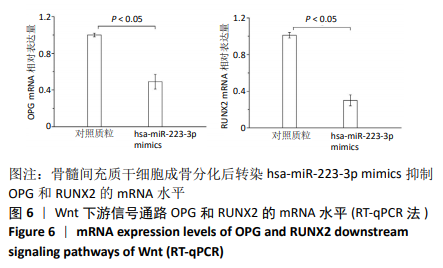
结果与结论:①随着成骨诱导时间的延长,细胞培养液中碱性磷酸酶水平逐渐增加,茜素红染色可见暗红色或红褐色钙盐结节沉积逐渐增加;②过表达hsa-miR-223-3p后,细胞中Wnt5a、OPG、RUNX2的mRNA和蛋白水平降低;③hsa-miR-223-3p直接靶定Wnt5a的3’UTR区,降低Wnt5a的荧光素酶活性;突变掉Wnt5a的结合位点,靶定作用消失。封闭hsa-miR-223-3p后,野生型Wnt5a的荧光素酶活性增加,突变型Wnt5a的荧光素酶活性不变;④结果表明,在骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化过程中,过表达hsa-miR-223-3p可以影响Wnt信号通路标志物Wnt5a及其下游信号分子OPG、RUNX2的表达。hsa-miR-223-3p可直接与Wnt5a结合,Wnt5a作为hsa-miR-223-3p的下游靶基因,受其负向调控。
中图分类号: