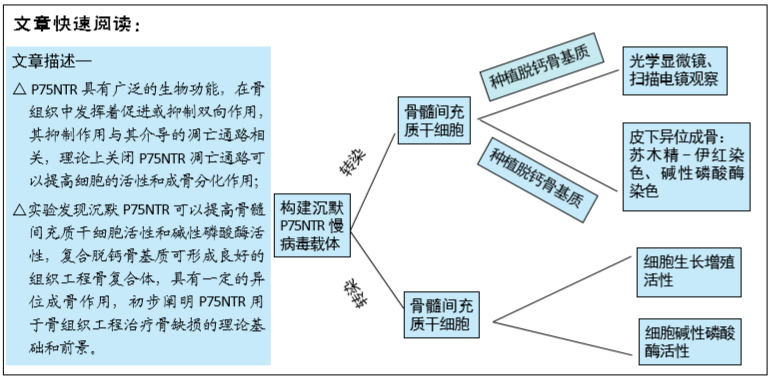
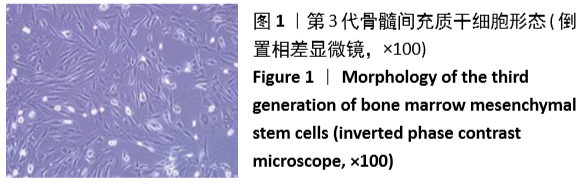
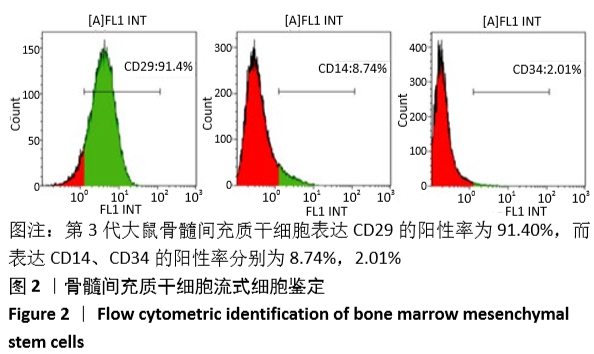
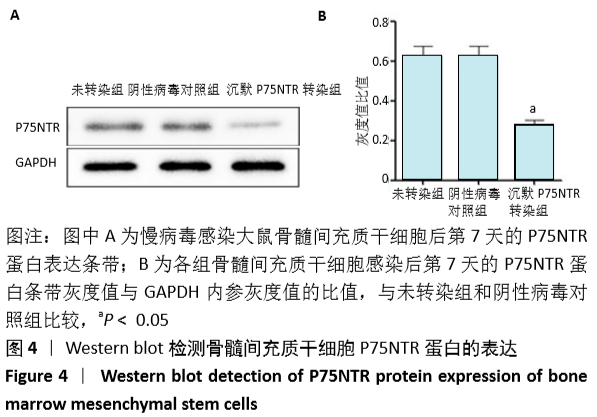
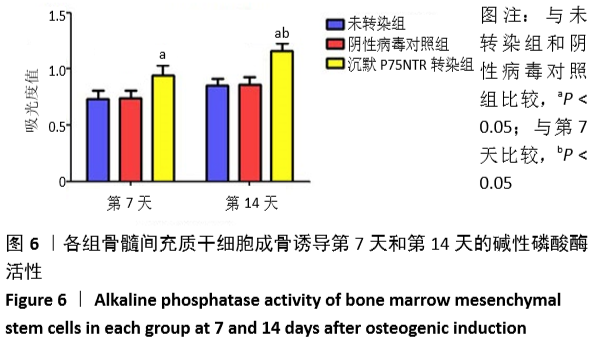
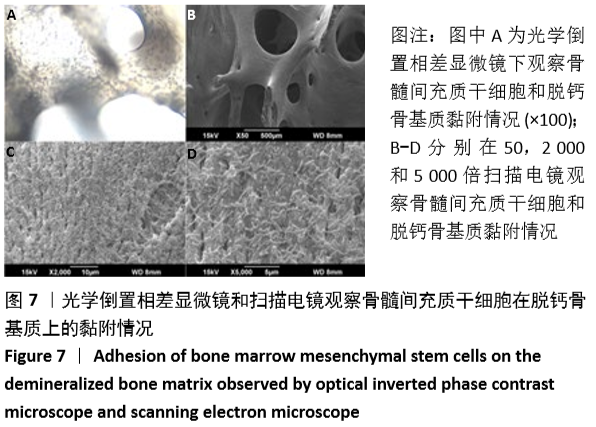
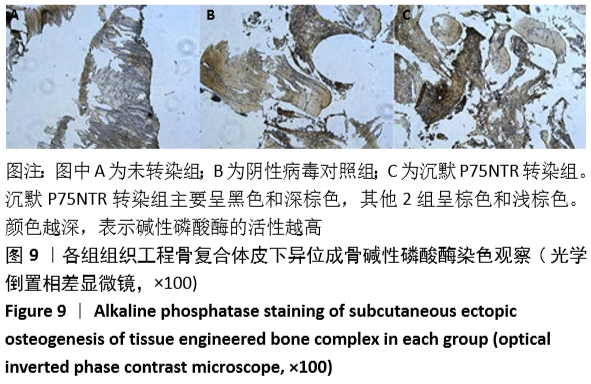
[1] GÓMEZ-BARRENA E, ROSSET P, LOZANO D, et al. Bone fracture healing: cell therapy in delayed unions and nonunions. Bone. 2015;70:93-101.
[2] BLÖCHL A, BLUMENSTEIN L, AHMADIAN MR. Inactivation and activation of Ras by the neurotrophin receptor p75. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20(9): 2321-2335.
[3] COLE HA, OHBA T, NYMAN JS, et al. Fibrin accumulation secondary to loss of plasmin-mediated fibrinolysis drives inflammatory osteoporosis in mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(8):2222-2233.
[4] NYKJAER A, WILLNOW TE. Sortilin: a receptor to regulate neuronal viability and function. Trends Neurosci. 2012;35(4):261-270.
[5] TWISS JL, CHANG JH, SCHANEN NC. Pathophysiological mechanisms for actions of the neurotrophins. Brain Pathol. 2006;16(4):320-332.
[6] ALDER J, FUJIOKA W, GIARRATANA A, et al. Genetic and pharmacological intervention of the p75NTR pathway alters morphological and behavioural recovery following traumatic brain injury in mice. Brain Inj. 2016;30(1):48-65.
[7] SHEN J, CHEN X, LI H, et al. p75 neurotrophin receptor and its novel interaction partner, NIX, are involved in neuronal apoptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;368(1):13-27.
[8] WANG YX, XU K, SU WL, et al. Therapeutic effects of p75 tumor necrosis factor receptor monoclonal antibody on a rat model of traumatic arthritis. J Surg Res. 2014;186(1):234-239.
[9] WEN X, LIU L, DENG M, et al. Characterization of p75(+) ectomesenchymal stem cells from rat embryonic facial process tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;427(1):5-10.
[10] ZHAO M, WEN X, LI G, et al. The capacity and biological characteristic of the p75 neurotrophin receptor-positive ectomesenchymal stem cell in vitro. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;50(2):103-109.
[11] RADA T, REIS RL, GOMES ME. Distinct stem cells subpopulations isolated from human adipose tissue exhibit different chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation potential. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2011;7(1): 64-76.
[12] EDALAT H, HAJEBRAHIMI Z, MOVAHEDIN M, et al. p75NTR suppression in rat bone marrow stromal stem cells significantly reduced their rate of apoptosis during neural differentiation. Neurosci Lett. 2011;498(1): 15-19.
[13] BARCELONA PF, SITARAS N, GALAN A, et al. p75NTR and Its Ligand ProNGF Activate Paracrine Mechanisms Etiological to the Vascular, Inflammatory, and Neurodegenerative Pathologies of Diabetic Retinopathy. J Neurosci. 2016;36(34):8826-8841.
[14] SCHWABE P, SIMON P, KRONBACH Z, et al. A pilot study investigating the histology and growth factor content of human non-union tissue. Int Orthop. 2014;38(12):2623-2629.
[15] RACKWITZ L, REICHERT JC, HAVERSATH M, et al. Cell-based and future therapeutic strategies for femoral head necrosis. Orthopade. 2018; 47(9):770-776.
[16] 张凯,王毅,邢国胜.间充质干细胞的生物学特性及多向分化潜能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(3):539-542.
[17] VILAR M, CHARALAMPOPOULOS I, KENCHAPPA RS, et al. Activation of the p75 neurotrophin receptor through conformational rearrangement of disulphide-linked receptor dimers. Neuron. 2009;62(1):72-83.
[18] TOMELLINI E, LAGADEC C, POLAKOWSKA R, et al. Role of p75 neurotrophin receptor in stem cell biology: more than just a marker. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71(13):2467-2481.
[19] SACHS BD, BAILLIE GS, MCCALL JR, et al. p75 neurotrophin receptor regulates tissue fibrosis through inhibition of plasminogen activation via a PDE4/cAMP/PKA pathway. J Cell Biol. 2007;177(6):1119-1132.
[20] ELSHAER SL, EL-REMESSY AB. Implication of the neurotrophin receptor p75NTR in vascular diseases: beyond the eye. Expert Rev Ophthalmol. 2017;12(2):149-158.
[21] MIKAMI Y, ISHII Y, WATANABE N, et al. CD271/p75(NTR) inhibits the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into osteogenic, adipogenic, chondrogenic, and myogenic lineages. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(5): 901-913.
[22] KARNES JM, DAFFNER SD, WATKINS CM. Multiple roles of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in fracture healing. Bone. 2015;78:87-93.
[23] KO KI, COIMBRA LS, TIAN C, et al. Diabetes reduces mesenchymal stem cells in fracture healing through a TNFα-mediated mechanism. Diabetologia. 2015;58(3):633-642.
[24] 朱伦井,段江涛,黄义杰,等.过表达P75神经生长因子受体负向调控骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(1): 20-26.
[25] 李家勇,王铭,彭称飞,等.P75NTR在兔骨折不愈合局部组织中的表达及意义[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(4):437-440.
[26] ASSIMAKOPOULOU M, KONDYLI M, GATZOUNIS G, et al. Neurotrophin receptors expression and JNK pathway activation in human astrocytomas. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:202.
[27] SUHL KH, PARK JB, PARK EY, et al. Effect of nerve growth factor and its transforming tyrosine kinase protein and low-affinity nerve growth factor receptors on apoptosis of notochordal cells. Int Orthop. 2012; 36(8):1747-1753.
[28] YANG K, WANG Y, JU Y, et al. p75 neurotrophin receptor regulates differential mineralization of rat ectomesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(1):e12290.
[29] LIU Q, LEI L, YU T, et al. Effect of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor on the Neurogenesis and Osteogenesis in Bone Engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(15-16):1283-1292. |