中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (22): 3479-3486.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3160
• 组织工程血管材料 tissue-engineered vascular materials • 上一篇 下一篇
构建预血管化细胞膜片及血管形成相关因子的表达
莫剑玲1,2,何少茹2,1,冯博文1,2,简敏桥2,张晓晖2,刘财盛2,梁一晶2,刘玉梅2,陈 亮2,周海榆2,刘艳辉2
- 1南方医科大学第二临床医学院,广东省广州市 510515;2 广东省人民医院(广东省医学科学院),广东省广州市 510080
Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors
Mo Jianling1, 2, He Shaoru2, 1, Feng Bowen1, 2, Jian Minqiao2, Zhang Xiaohui2, Liu Caisheng2, Liang Yijing2, Liu Yumei2, Chen Liang2, #br# Zhou Haiyu2, Liu Yanhui2#br#
- 1The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
细胞膜片技术:细胞膜片技术由日本学者OKANO等发明,该项技术具备许多优势,它不仅可以免去因使用胰蛋白酶消化给细胞带来伤害过程,保留了细胞外基质等结构,而且在维持细胞良好功能及提高细胞利用率中具有绝对优势。
组织工程:是应用细胞学和工程学的原理,研究开发用于修复或改善缺损组织、器官结构和功能的生物替代物的一门科学。组织工程技术是通过人体的基本单位——细胞,借助临时的三维支架和正常的生长方式建造出自然健康的自体组织,它的出现为组织缺损修复描绘了美好的前景。
背景:组织工程组织血管化问题难以解决,成为制约其临床应用的关键。
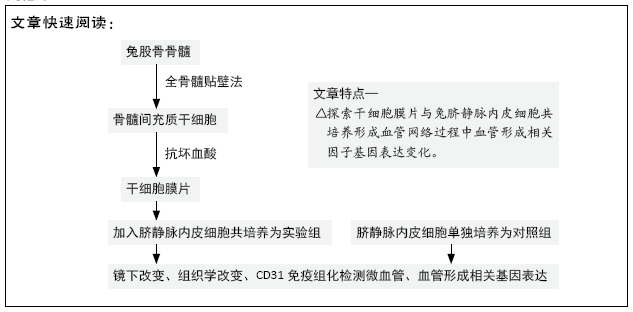
目的:探讨兔脐静脉内皮细胞与干细胞膜片共培养形成预血管化细胞膜片的可行性,分析其血管形成相关因子基因表达。
方法:采用全骨髓贴壁法体外分离培养兔骨髓间充质干细胞,经抗坏血酸作用形成干细胞膜片。实验组将干细胞膜片与兔脐静脉内皮细胞共培养以形成预血管化细胞膜片,以单独培养的兔脐静脉内皮细胞为对照,培养3,7,14 d时,光镜、苏木精-伊红染色观察细胞形态与组织学改变,RT-PCR检测血管形成相关因子mRNA表达,免疫组化染色观察血管化网络结构。
结果与结论:①光镜显示,实验组培养3 d后细胞发生迁移、重排,7 d后可见脐静脉内皮细胞之间发生“联系”,形成网状结构,14 d网状结构更加明显见;对照组细胞密度不断增加,形成细胞团,未见细胞发生重排、迁移形成网状结构;②苏木精-伊红染色显示,实验组培养3 d细胞排列不均匀,7 d时细胞呈条索状排列,14 d时细胞呈网状结构;对照组细胞呈铺路石样堆积且密度不断增大,无条索状、网状结构形成;③RT-PCR检测显示,实验组培养7 d的血管内皮生长因子mRNA表达高于对照组(P < 0.05),培养14 d的碱性成纤维细胞生长因子mRNA表达高于对照组(P < 0.05),培养7,14 d的血管生成素1 mRNA表达高于对照组(P < 0.05),培养3,7,14 d的血管生成素2 mRNA表达高于对照组(P < 0.05);④CD31免疫组化染色显示,实验组形成血管网状结构,对照组无网状结构形成;⑤结果表明,兔脐静脉内皮细胞与干细胞膜片共培养可以成功构建预血管化细胞膜片,显著表达血管形成相关基因。
中图分类号: