中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 996-1001.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2162
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
泡状棘球绦虫原头蚴抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向成纤维细胞的分化
梁学奇1,郭黎姣2,陈贺捷2,武 杰2,孙雅琪2,邢稚坤2,邹海亮2,陈雪玲2,吴向未1
- 1石河子大学医学院第一附属医院普外科,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832008;2石河子大学医学院免疫学教研室,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832008
Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts
Liang Xueqi1, Guo Lijiao2, Chen Hejie2, Wu Jie2, Sun Yaqi2, Xing Zhikun2, Zou Hailiang2, Chen Xueling2, Wu Xiangwei1
- 1Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Immunology, School of Medicine, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
浸润性:泡状棘球蚴病生物学特征类似于肿瘤样病变,其具有浸润性生长和转移的生物学特性,导致其病情严重,并难以治疗。
外囊壁:在感染细粒棘球蚴病后,虫体在生长过程中挤压肝脏,形成占位性病变,肝包虫囊肿膨胀性生长过程中形成内层纤维囊壁;肝静脉系统受挤压和囊周Glisson系统不断纤维化,形成另一层纤维囊壁(外囊壁),外囊壁的形成可以有效控制细粒棘球蚴的营养摄取,局部限制病灶的生长及转移,从而感染细粒棘球蚴的宿主可以避免像泡状棘球蚴病因浸润性生长及转移导致的病情恶化。虫体与寄生的人体形成了动态平衡。
背景:肝泡状棘球蚴病生物学特征类似于肿瘤样病变,其具有浸润性生长和转移的生物学特性,增加了手术的难度。外囊壁的纤维化可以抑制泡状棘球蚴的生长,使疾病处于静止期。有关间充质干细胞在泡状棘球蚴病外囊壁纤维化过程中的作用尚不明确。
目的:探讨泡状棘球绦虫原头蚴对骨髓间充质干细胞向成纤维细胞分化的影响。
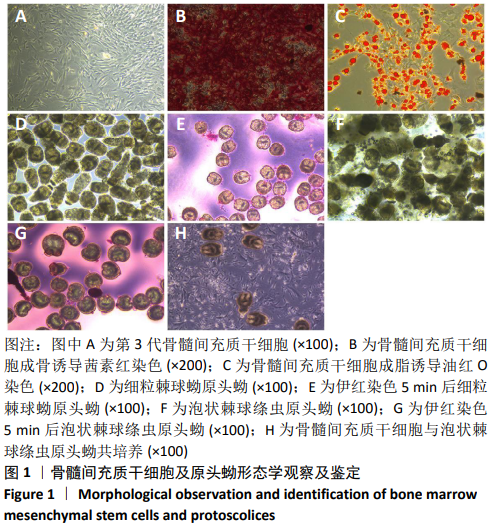
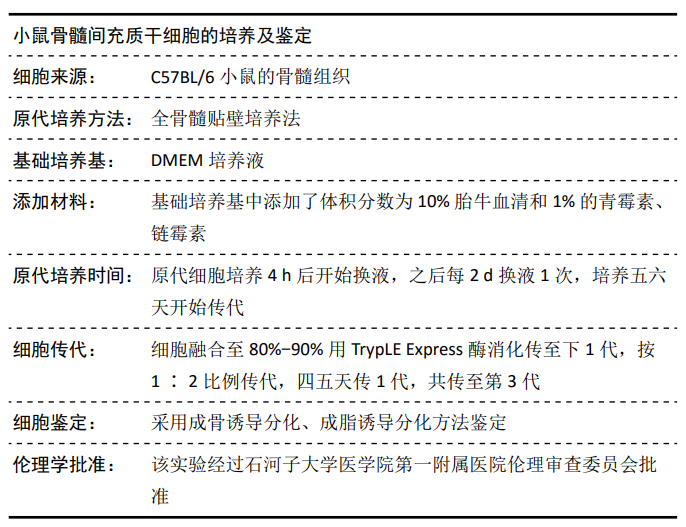
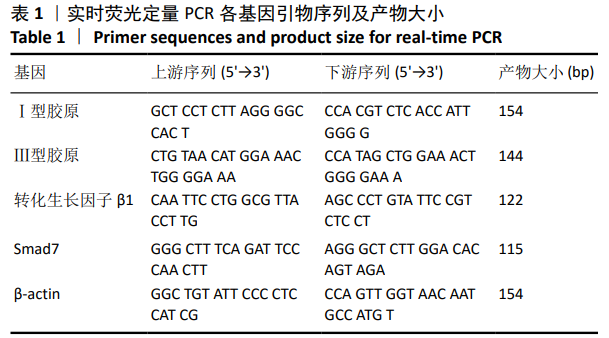
方法:取4周龄C57BL/6小鼠股骨骨髓,利用贴壁培养法分离培养骨髓间充质干细胞;从感染泡状棘球蚴的沙鼠体内提取泡状棘球绦虫原头蚴,从感染细粒棘球蚴病的羊肝中提取细粒棘球绦虫原头蚴。实验分为3组,泡状棘球蚴组:第3代骨髓间充质干细胞和泡状棘球绦虫原头蚴共培养;细粒棘球蚴组:第3代骨髓间充质干细胞和细粒棘球绦虫原头蚴共培养;单纯对照组为第3代骨髓间充质干细胞单独培养。在培养1,3,5,7 d,采用实时荧光定量PCR检测Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原、转化生长因子β1和Smad7基因表达,Western blot检测Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原、Smad7和磷酸化Smad2/3蛋白表达,ELISA检测培养上清中Ⅰ型胶原和Ⅲ型胶原水平。
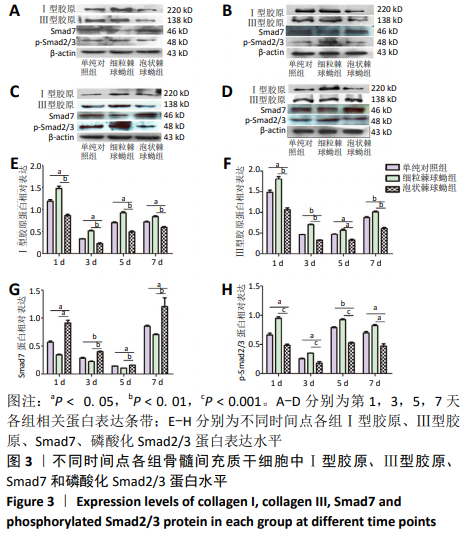
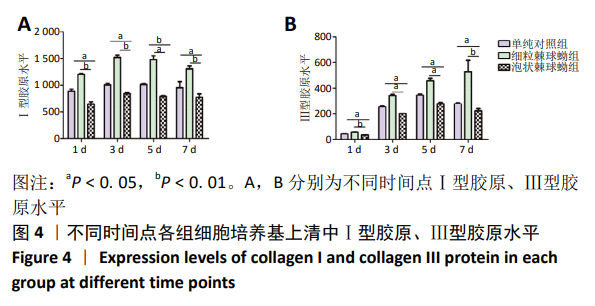
结果与结论:①实时荧光定量PCR检测显示,泡状棘球蚴组骨髓间充质干细胞中Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原、转化生长因子β1 mRNA相对表达量显著低于单纯对照组和细粒棘球蚴组(P < 0.05);Smad7 mRNA相对表达量显著高于单纯对照组和细粒棘球蚴组(P < 0.05);②Western blot检测显示,泡状棘球蚴组Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原和磷酸化Smad2/3蛋白相对表达量均显著低于单纯对照组和细粒棘球蚴组(P < 0.05),Smad7蛋白相对表达量显著高于单纯对照组和细粒棘球蚴组(P < 0.05);③ELISA检测显示,泡状棘球蚴组上清中Ⅰ型胶原和Ⅲ型胶原水平均显著低于单纯对照组和细粒棘球蚴组(P < 0.05);④结果表明,泡状棘球蚴原头蚴可能通过TGF-β/smad信号通路,诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分泌Smad7,抑制Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原和转化生长因子β1分泌,从而抑制了骨髓间充质干细胞的纤维化。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3897-6629(吴向未)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: