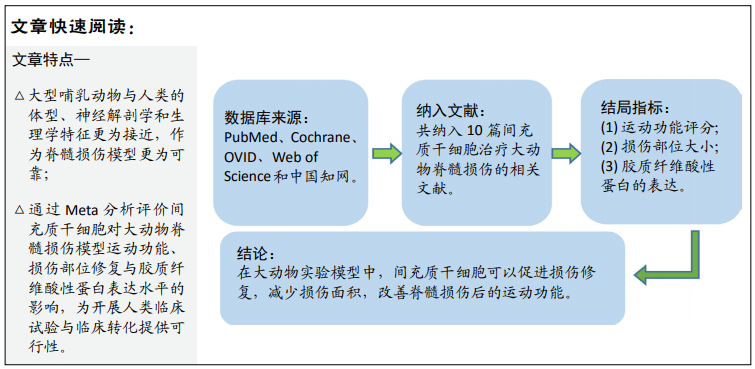
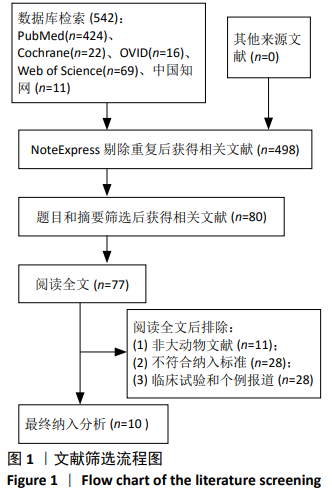
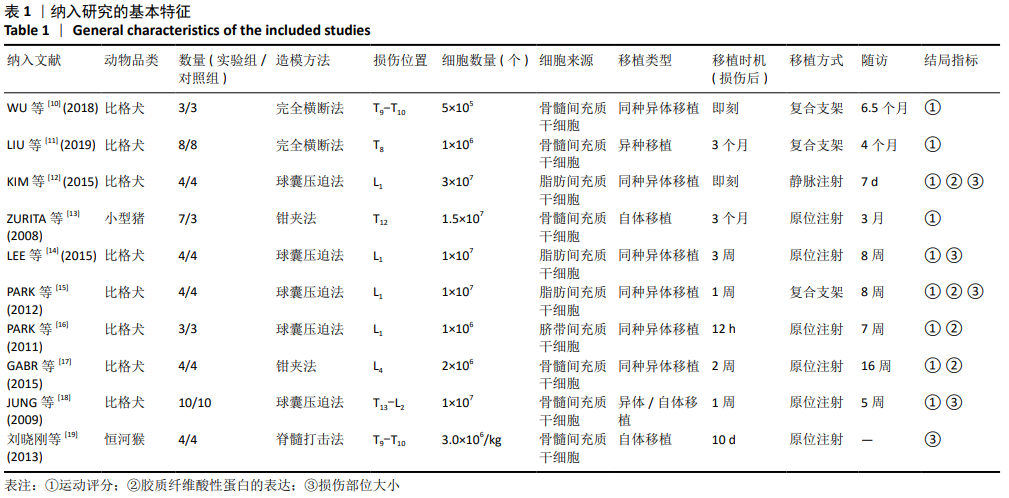
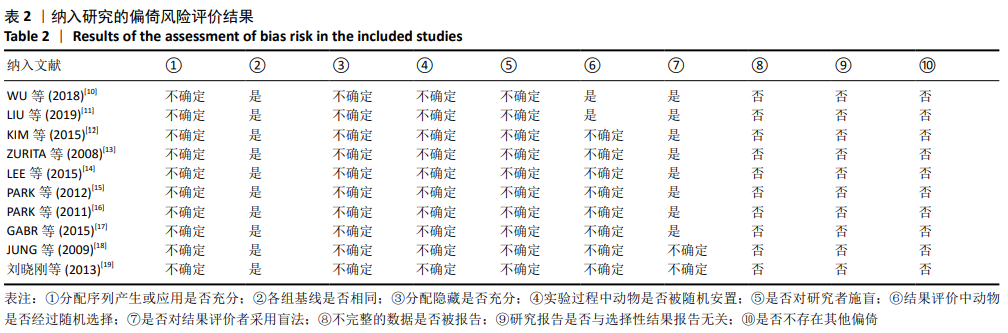
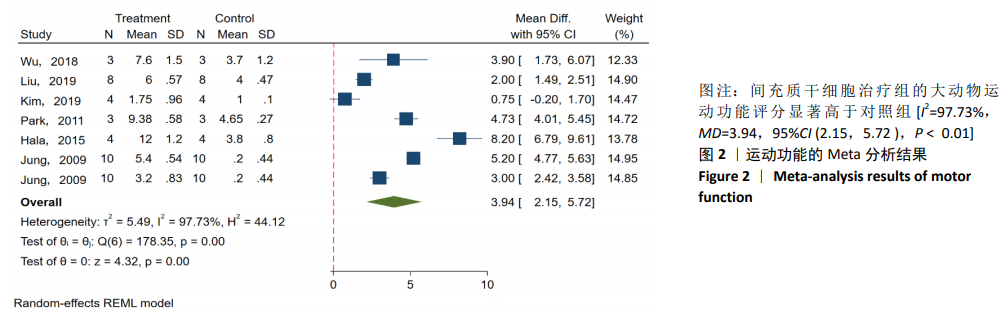
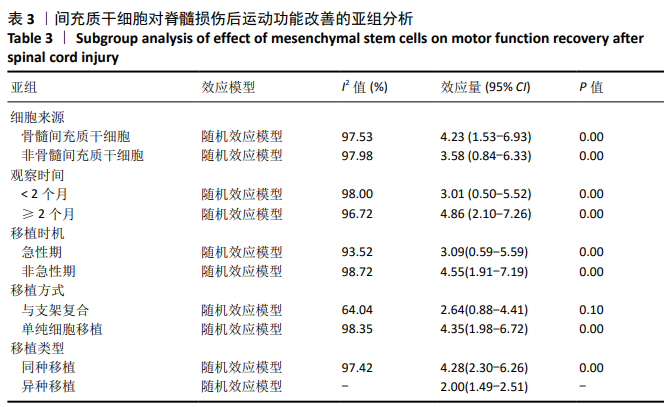
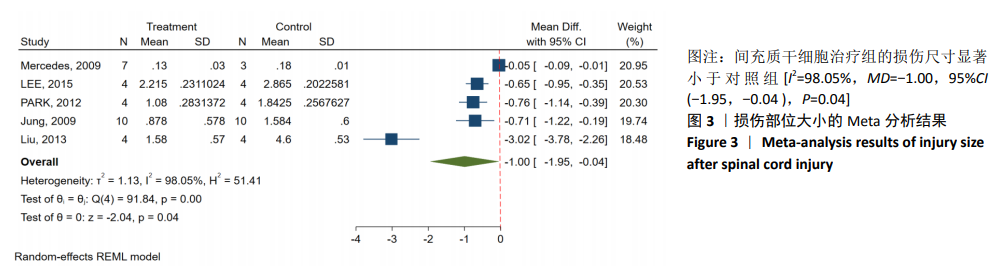
[1] BADHIWALA JH, WILSON JR, FEHLINGS MG. Global burden of traumatic brain and spinal cord injury. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1): 24-25.
[2] GBD 2016 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY AND SPINAL CORD INJURY COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1):56-87.
[3] 刘克勋,霍洪军,赵岩,等. 间充质干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的进展及发展趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(21): 3410-3416.
[4] NITZSCHE F, MÜLLER C, LUKOMSKA B, et al. Concise Review: MSC Adhesion Cascade-Insights into Homing and Transendothelial Migration. Stem Cells. 2017;35(6): 1446-1460.
[5] MUKHAMEDSHINA YO, AKHMETZYANOVA ER, KOSTENNIKOV AA, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Application Combined With Fibrin Matrix Promotes Structural and Functional Recovery Following Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:343.
[6] COFANO F, BOIDO M, MONTICELLI M, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Spinal Cord Injury: Current Options, Limitations, and Future of Cell Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):2698.
[7] KWON BK, STREIJGER F, HILL CE, et al. Large animal and primate models of spinal cord injury for the testing of novel therapies. Exp Neurol. 2015;269:154-168.
[8] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282.
[9] HOOIJMANS CR, ROVERS MM, DE VRIES RB, et al. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:43.
[10] WU GH, SHI HJ, CHE MT, et al. Recovery of paralyzed limb motor function in canine with complete spinal cord injury following implantation of MSC-derived neural network tissue. Biomaterials. 2018;181: 15-34.
[11] LIU D, LI X, XIAO Z, et al. Different functional bio-scaffolds share similar neurological mechanism to promote locomotor recovery of canines with complete spinal cord injury. Biomaterials. 2019;214:119230.
[12] KIM Y, JO SH, KIM WH, et al. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of intravenously injected adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in dogs with acute spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:229.
[13] ZURITA M, VAQUERO J, BONILLA C, et al. Functional recovery of chronic paraplegic pigs after autologous transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells. Transplantation. 2008;86(6):845-853.
[14] LEE SH, KIM Y, RHEW D, et al. Effect of the combination of mesenchymal stromal cells and chondroitinase ABC on chronic spinal cord injury. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(10): 1374-1383.
[15] PARK SS, LEE YJ, LEE SH, et al. Functional recovery after spinal cord injury in dogs treated with a combination of Matrigel and neural-induced adipose-derived mesenchymal Stem cells. Cytotherapy. 2012;14(5):584-597.
[16] PARK SS, BYEON YE, RYU HH, et al. Comparison of canine umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation times: involvement of astrogliosis, inflammation, intracellular actin cytoskeleton pathways, and neurotrophin-3. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(11-12):1867-1880.
[17] GABR H, EL-KHEIR WA, FARGHALI HA, et al. Intrathecal Transplantation of Autologous Adherent Bone Marrow Cells Induces Functional Neurological Recovery in a Canine Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(9):1813-1827.
[18] JUNG DI, HA J, KANG BT, et al. A comparison of autologous and allogenic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in canine spinal cord injury. J Neurol Sci. 2009;285(1-2):67-77.
[19] 刘晓刚,邓宇斌,蔡辉,等. 控释胶质细胞源性神经营养因子与骨髓间充质干细胞源神经元样细胞移植可减少脊髓损伤后空洞形成[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(1):68-73.
[20] BASSO DM, FISHER LC, ANDERSON AJ, et al. Basso Mouse Scale for locomotion detects differences in recovery after spinal cord injury in five common mouse strains. J Neurotrauma. 2006;23(5):635-659.
[21] BASSO DM, BEATTIE MS, BRESNAHAN JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(1):1-21.
[22] YANG Z, WANG KK. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: from intermediate filament assembly and gliosis to neurobiomarker. Trends Neurosci. 2015;38(6):364-374.
[23] ROPPER AE, THAKOR DK, HAN I, et al. Defining recovery neurobiology of injured spinal cord by synthetic matrix-assisted hMSC implantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(5):E820-E829.
[24] NAKAJIMA H, UCHIDA K, GUERRERO AR, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells promotes an alternative pathway of macrophage activation and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29(8):1614-1625.
[25] SHIUE SJ, RAU RH, SHIUE HS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes as a cell-free therapy for nerve injury-induced pain in rats. Pain. 2019;160(1):210-223.
[26] ABBASZADEH HA, NIKNAZAR S, DARABI S, et al. Stem cell transplantation and functional recovery after spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anat Cell Biol. 2018;51(3):180-188.
[27] FU H, HU D, ZHANG L, et al. Efficacy of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Transplantation in Rat Models with Traumatic Thoracic Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(21):2507-2518.
[28] PAPA S, VISMARA I, MARIANI A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated into biomimetic hydrogel scaffold gradually release CCL2 chemokine in situ preserving cytoarchitecture and promoting functional recovery in spinal cord injury. J Control Release. 2018;278:49-56.
[29] SUN G, LI G, LI D, et al. hucMSC derived exosomes promote functional recovery in spinal cord injury mice via attenuating inflammation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89:194-204.
[30] RYU HH, KANG BJ, PARK SS, et al. Comparison of mesenchymal stem cells derived from fat, bone marrow, Wharton’s jelly, and umbilical cord blood for treating spinal cord injuries in dogs. J Vet Med Sci. 2012;74(12):1617-1630.
[31] YOUSEFIFARD M, NASSERI MALEKI S, ASKARIAN-AMIRI S, et al. A combination of mesenchymal stem cells and scaffolds promotes motor functional recovery in spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019;32(2):269-284.
[32] 潘晓明,吴玲玲,陈浩浩,等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植对脊髓损伤小鼠运动功能的修复和镇痛作用[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2020,43(1):3-9.
[33] KRUPA P, VACKOVA I, RUZICKA J, et al. The Effect of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Wharton’s Jelly in Spinal Cord Injury Treatment Is Dose-Dependent and Can Be Facilitated by Repeated Application. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(5):1503.
[34] LI G, CHE MT, ZHANG K, et al. Graft of the NT-3 persistent delivery gelatin sponge scaffold promotes axon regeneration, attenuates inflammation, and induces cell migration in rat and canine with spinal cord injury. Biomaterials. 2016;83:233-248.
[35] TAKAHASHI A, NAKAJIMA H, UCHIDA K, et al. Comparison of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Isolated from Murine Adipose Tissue and Bone Marrow in the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2018; 27(7):1126-1139.
[36] MUNISWAMI DM, KANTHAKUMAR P, KANAKASABAPATHY I, et al. Motor Recovery after Transplantation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Rat Models of Spinal Cord Injury. Ann Neurosci. 2019; 25(3):126-140.
[37] LIU AM, CHEN BL, YU LT, et al. Human adipose tissue- and umbilical cord-derived stem cells: which is a better alternative to treat spinal cord injury? Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(12):2306-2317.
[38] TIAN DZ, DENG D, QIANG JL, et al. Repair of spinal cord injury in rats by umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells through P38MAPK signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(3 Suppl):47-53.
|