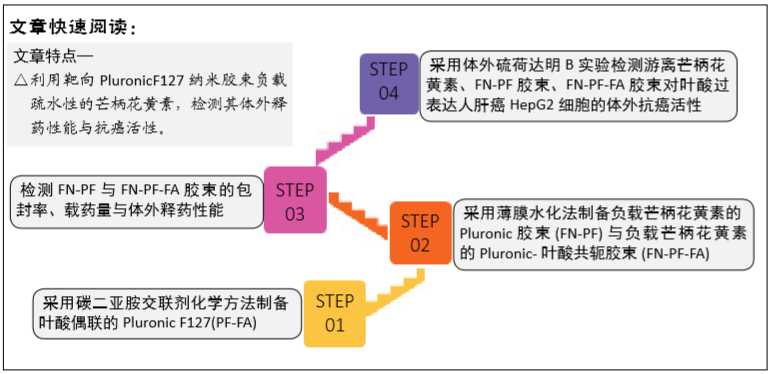
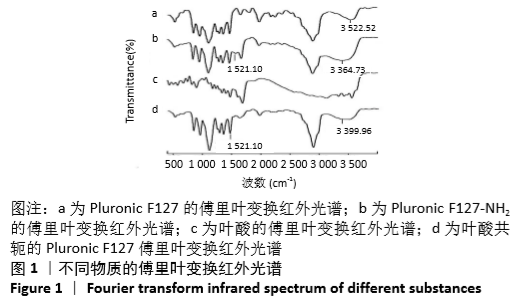
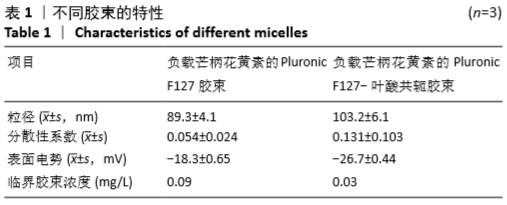
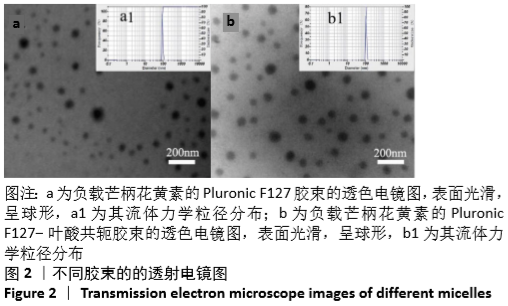
[1] HU Y, RAN J, ZHENG Z, et al. Exogenous stromal derived factor-1 releasing silk scaffold combined with intra-articular injection of progenitor cells promotes bone-ligament-bone regeneration. Acta Biomater.2018;71:168-183.
[2] MANSOORI MN, TYAGI AM, SHUKLA P, et al. Methoxyisoflavones formononetin and isoformononetin inhibit the differentiation of Th17 cells and B-cell lymphopoesis to promote osteogenesis in estrogen-deficient bone loss conditions.Menopause.2016;23(5):565-576.
[3] LI L, XU J, MA Y, et al. Local Upregulation of Stromal Cell–Derived Factor-1 After Ligament Injuries Enhances Homing Rate of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells in Rats.Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(8):2277-2284.
[4] WANG XH, SUN ZG, LUO L, et al. Formononetin promotes apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells via activation of mitochondria-dependent MAPK pathway. Trop J Pharm Res.2019;18(2):243-249.
[5] FERREIRA FM, CASTRO RA, BATISTA MA, et al. Association of water extract of green propolis and liposomal meglumine antimoniate in the treatment of experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Parasitol Res. 2014;113(2):533-543.
[6] LIU J, YONG H, YAO X, et al. Recent advances in phenolic–protein conjugates: synthesis, characterization, biological activities and potential applications.RSC Adv.2019;9 (61):35825-35840.
[7] PRAKASH I, JETTI R, TAN C, et al. Steviol Glycoside Sweeteners with Improved Flavor Profiles. U.S. Patent Application No.15/765,095.
[8] DAVIS JJ, COLEMAN KS, AZAMIAN BR, et al. Chemical and biochemical sensing with modified single walled carbon nanotubes.Chem Eur J. 2003;9(16):3732-3739.
[9] CAPEK I. Degradation of kinetically-stable o/w emulsions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci.2004;2107(2-3):125-155.
[10] PAWAR A, PATEL R, ARULMOZHI S, et al. D-α-Tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate conjugated folic acid nanomicelles: towards enhanced bioavailability, stability, safety, prolonged drug release and synergized anticancer effect of plumbagin.RSC Adv.2016;6(81): 78106-78121.
[11] HU H, YU J, LI Y, et al. Engineering of a novel pluronic F127/graphene nanohybrid for pH responsive drug delivery.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(1):141-148.
[12] YASIR M, SARA U S, CHAUHAN I, et al. Solid lipid nanoparticles for nose to brain delivery of donepezil: formulation, optimization by Box–Behnken design, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(8):1838-1851.
[13] RAJPOOT K, JAIN SK. Colorectal cancer-targeted delivery of oxaliplatin via folic acid-grafted solid lipid nanoparticles: preparation, optimization, and in vitro evaluation.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(6):1236-1247.
[14] LOW PS, HENNE WA, DOORNEWEERD DD. Discovery and development of folic-acid-based receptor targeting for imaging and therapy of cancer and inflammatory diseases.Acc Chem Res. 2007;41(1):120-129.
[15] HAO J, TONG T, JIN K, et al. Folic acid-functionalized drug delivery platform of resveratrol based on Pluronic 127/D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate mixed micelles.Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:2279-2292.
[16] ZHANG RY, WANG ZY, YANG XQ, et al. Folic acid modified Pluronic F127 coating Ag2S quantum dot for photoacoustic imaging of tumor cell-targeting.Nanotechnol.2018;29(5):055101.
[17] GRIMAUDO MA, PESCINA S, PADULA C, et al. Poloxamer 407/TPGS mixed micelles as promising carriers for cyclosporine ocular delivery.Mol Pharm.2018;15(2):571-584.
[18] CHENG XL, ZHOU TY, LI B, et al. Methotrexate and 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside exert synergistic anticancer action against human breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma.Acta Pharm Sin B.2013;34(7):951.
[19] KWAK M, MUSSER AJ, LEE J, et al. DNA-functionalised blend micelles: mix and fix polymeric hybrid nanostructures.Chem Commun. 2010; 46(27):4935-4937.
[20] MOHAPATRA S, MALLICK SK, MAITI TK, et al. Synthesis of highly stable folic acid conjugated magnetite nanoparticles for targeting cancer cells.Nanotechnol.2007;18(38):385102.
[21] TAY KC, TAN LTH, CHAN CK, et al. Formononetin: A review of its anticancer potentials and mechanisms.Front Pharmacol.2019.DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00820
[22] PATIL S, CHOUDHARY B, RATHORE A, et al. Enhanced oral bioavailability and anticancer activity of novel curcumin loaded mixed micelles in human lung cancer cells.Phytomedicine.2015;22(12):1103-1111.
[23] DRBOHLAVOVA J, CHOMOUCKA J, ADAM V, et al. Nanocarriers for anticancer drugs-new trends in nanomedicine.Curr Drug Metab. 2013:14(5):547-564.
[24] VIDYA PRIYADARSINI R, NAGINI S. Cancer chemoprevention by dietary phytochemicals: promises and pitfalls.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13(1):125-136.
[25] UN E, HAVA AM. A near-state PWM method with reduced switching losses and reduced common-mode voltage for three-phase voltage source inverters. IEEE Trans Ind Appl.2009;45(2):782-793.
[26] SUTHIWANGCHAROEN N, NAGARAJAN R. Controlled design and construction of multifunctional nanoparticles by molecular self-assembly. RSC Adv.2014;4(20):10076-10089.
[27] SONG X, GAN K, QIN S, et al. Preparation and characterization of general-purpose gelatin-based co-loading flavonoids nano-core structure. Sci Rep.2019;9(1):1-11.
[28] ZHAO X, LIU P. Reduction-responsive core–shell–corona micelles based on triblock copolymers: novel synthetic strategy, characterization, and application as a tumor microenvironment-responsive drug delivery system.ACS Appl Mater Inter.2014;7(1):166-174.
[29] PINDIPROLU SKS, KRISHNAMURTHY PT, CHINTAMANENI PK, et al. Nanocarrier based approaches for targeting breast cancer stem cells.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol.2018;46(5):885-898. |