结肠的一种高幅度传播序列波传播到乙状结肠时引起腹部不适感或者胀气样痛或者耻骨上区疼痛,而传播到直肠时可引起排便的急迫感
[24]。直肠是排便紧迫感产生的起始部位,直肠的膨胀启动直肠充盈感,大便团块进入直肠时使肠管变形改变了肠壁的压力和张力,刺激了肠壁上面能够引起反射性直肠收缩的机械性感受器。肠道膨胀越很,直肠收缩的幅度就越大。随着膨胀程度的增加,排便感发生如下变化:持续的欲排气感-持续急迫的欲排便感-感觉非常不适和强烈的欲排便 感
[25]。直肠末端的环肌层增厚(肛门内括约肌)并持续性张力收缩以闭合出口,该肌对扩张直肠的反应是作同步弛缓,且这种弛缓的程度和速度与直肠扩张的程度和速度相关,该特性精确协调直肠内容物容积与内括约肌开闭的关系,有利于直肠合理发挥其粪便自制与排出功能。
当粪便充满直肠刺激肠壁感受器,发出冲动传入腰骶部脊髓内的低级排便中枢,同时上传至大脑皮质而产生便意[26]。如环境许可,大脑皮质即发出冲动使排便中枢兴奋增强,产生排使反射,使乙状结肠和直肠收缩,肛门括约肌舒张,同时还须有意识地先行深吸气,声门关闭,增加胸腔压力,隔肌下降、腹肌收缩,增加腹内压力,促进粪便排出体外。人类排便机制是一个涉及多种因素复杂的生物调节过程[27]。
任何导致排便活动反射弧的任一环节的破坏便会导致大便失禁。对于那些症状较轻大便失禁患者,国外用了多种方法进行了有效的治疗,如药物治疗、注射治疗、生物反馈治疗、骶神经刺激、肛门括约肌修复、盆底肌修复、股薄肌成型等[28-34]。但是对于那些因直肠癌Miles手术等各种原因导致的盆底横纹肌、底前间隙、和肛管的严重破坏导致对肠内容物感知功能的缺失和完全大便失禁的患者,人工肛门括约肌的应用可能是一种有效的方法。人工肛门括约肌的出现给肛门失禁的患者带来了福音,人工肛门括约肌Acticon® Neosphincter在临床上已经有多年的应用[35-39]。但是,现有的人工肛门括约肌都缺乏感知大便的功能,给患者的排便带来了诸多不便和心理的障碍。
正常情况下,肛门内外括约肌之间和肛管黏膜表面感受器能够将局部感知的信息经传入神经纤维至感觉神经中枢,神经中枢经过综合判断能够分辨直肠内的粪便是气体、流体还是固体,即肛管对不同的肠内容物进行“取样”作用[40]。但是现有的人工肛门括约肌不能对肠内容物进行取样,因此研究有感知不同性状大便功能的人工肛门括约肌对肛门失禁患者有着重要的意义。
在实验中,超声波经超声波发射头发出之后,纵向波依次穿过发射头侧肠管壁、肠内容物、超声波接收头侧肠管,最后到达超声波接收头,接收头经过声-电转换将声能转化为电能,超声波经过路径内不同的介质便形成了不同的电压信号,因此,利用超声波的衰减变化量信息可能起到模拟肛管的取样作用。
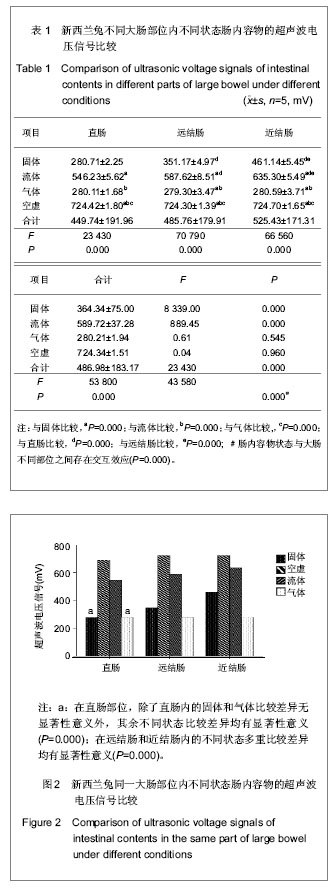
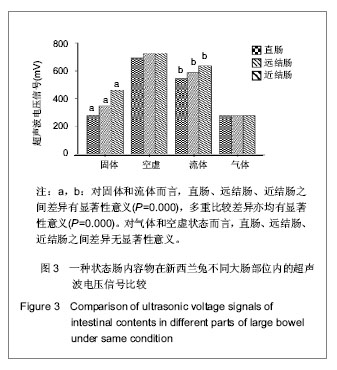
首先,从不同状态肠内容物来看,固体、流态、气体、空虚状态之间差异有显著性意义(F=53 800,P=0.000);直肠组、远结肠组、近结肠组的不同状态电压信号差异亦有显著性意义(F值分别为23 430,70 790和66 560,P值均小于0.001)。在不同的大肠部位内部的不同状态肠内容物的多重比较结果显示,在直肠部位,除了直肠内的固体和气体比较差异无显著性意义外,其余不同状态比较差异均有显著性意义;在远结肠和近结肠内的不同状态多重比较差异均有显著性意义。
对于气体来说,在水-气体的界面上,声强反射率大约为0.998,透射系数为0.002,因此超声从液体(固体更甚)向气体传播几乎是不可能的;反之,从气体向液体和固体中传播,同样也是几乎不可能的。因此,超声波接收换能器几乎接收不到超声波信号因而电压值最小。固体与液体的界面差比气体与液体界面差要小,因此有部分超声波通过固体大便而被超声波接收换能器接收而表现为比气体较高的电压信号。流体大便与固体大便比较起来,流体内含水较多,此时肠管与大便的界面差很小,发生的超声波反射量也较少,但是,与此同时,新西兰兔为草食性动物,流体大便内的纤维素颗粒反射和散射一部分超声波,进一步增加了超声波传播过程中的衰减,这可能是流体大便电压信号大于固体大便同时比肠管空虚状态电压信号小的原因。
其次,从大肠的不同部位来看,直肠、远结肠、近结肠之间差异有显著性意义(F=23 430,P=0.000);其中,固体和流体肠内容物在不同的大肠部位差异有显著性意义(固体组和半流体组的F值分别为8 339和889.45,二者P值均小于0.001),多重比较固体和流体各自不同的个大肠部位差异性均有显著性意义(P值均小于0.001)。但是,肠管空虚状态和气体各自在不同部位的肠腔里面的电压信号差异无显著性意义(P值分别为0.041和0.614,二者的值都大于0.05)。
虽然固体大便颗粒直径由近及远逐渐减小,但是随着肠管对肠内容物水的吸收固体大便内含水量逐渐减少,固体大便颗粒直径减少的速度要小于水减少量的速度可能是导致固体肠内容物超声波信号由大肠近端向远端逐渐减弱的原因;流体肠内容物如同固体肠内容物的变化可能是由于肠管内流体肠内容物由近及远含水量减少所致;气体在不同大肠部位无显著差异,可能与超声波不能穿透气体及在本实验超声波振子直径的范围内超声波接收头未能接收到信号所致。肠管空虚状态电压信号在不同大肠部位没有差异,可能为超声波在肠管壁内传播时对肠管壁微小的距离变化不敏感所致。
再次,不同的大肠部位的电压值和不同状态肠内容物分组之间存在交互效应(F=43 580,P=0.000)。
总之,实验中选择的超声波信号探测系统可以用来探测新西兰兔不同大肠部位内不同状态的肠内容物电压信号。统计学显示4种不同的肠内容物的电压值差异有显著性意义,提示本超声波探测系统具有初步区分肠管内“有或者无”(肠管空虚状态和其他状态相比差异性显著)以及区分不同状态肠内容物(固体、流体、气体相比差异有显著性意义)的作用。在不同的大肠部位之间固体大便信号差异有显著性意义,流体信号差异亦有显著性意义,提示由于不同的动物饮食成分、排便习性及肠内容物大小不同可能需要不同的超声波传感器频率、功率、换能器及电路才能得出有意义的测量结果。
.jpg)