中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (8): 1182-1187.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0582
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后椎体再骨折的危险:回顾性多因素分析
庞巨涛,张新虎,孙建华,周连军,刘 斌,李凤国,李文哲
- 哈励逊国际和平医院骨三科,河北省衡水市 053000
Risk factors for vertebral re-fracture after percutaneous kyphoplasty: retrospective multivariate analysis
Pang Jutao, Zhang Xinhu, Sun Jianhua, Zhou Lianjun, Liu Bin, Li Fengguo, Li Wenzhe
- Third Department of Orthopedics, Harrison International Peace Hospital, Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术(percutaneous kyphoplasty,PKP):是治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的一种新方法,即通过经皮穿刺向椎体内放置可膨胀性气囊(IBT),扩张后再注入骨水泥。PKP手术不仅可以迅速缓解患者疼痛症状,而且可以部分恢复被压缩椎体的高度,矫正椎体后凸畸形,增强椎体的强度和硬度,提高术中灌注骨水泥的安全性。
骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折:是因椎体骨基质中钙盐沉积量减少,导致骨组织微细结构破坏、强度下降、脆性增加,轻微应力及损伤即可诱发的椎体骨折,是骨质疏松严重的并发症之一。
摘要
背景:已有一些研究分析了经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后再骨折的高危因素,但对经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后椎体再骨折的高危风险因素及干预措施尚存有争议。
目的:分析经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后椎体再骨折的风险因素,探讨针对性的风险因素干预在预防经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后再骨折中的应用价值。
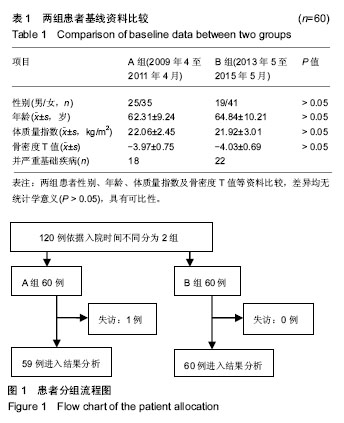
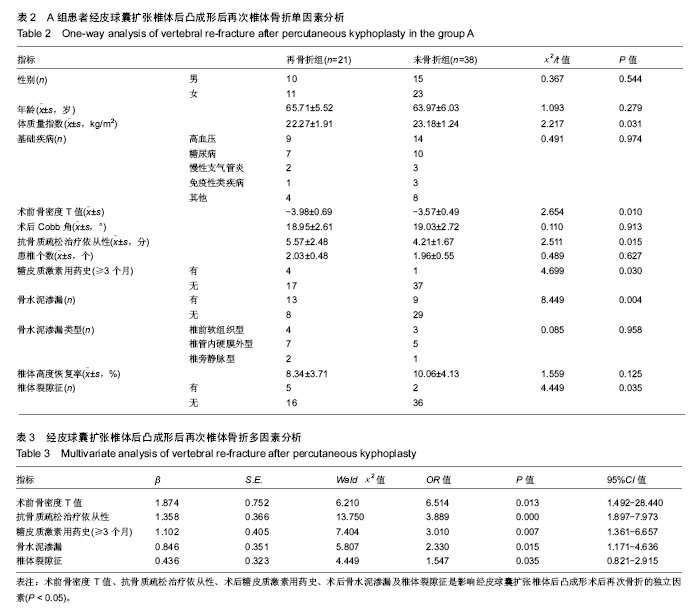
方法:纳入骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折患者,2009年4月至2011年4月接受经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形治疗的60例作为A组,采用Logistic多因素分析经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后再次椎体骨折的高危因素,并针对高危因素制定相应的干预措施;2013年5至2015年5月60例接受经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形治疗的患者,作为B组,接受针对性干预处理(对患椎邻近存在椎体真空裂隙征的椎体,予以预防性注入骨水泥;服用抗骨质疏松药物,并进行健康用药指导等),术后随访记录并比较两组椎体再骨折发生率等情况。
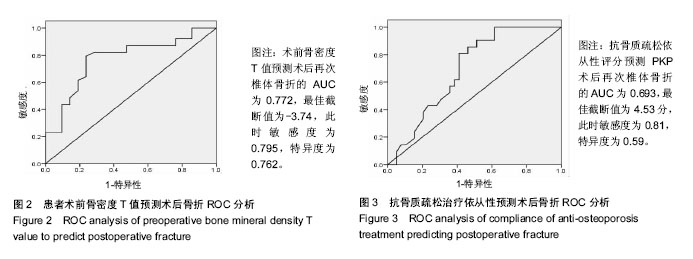
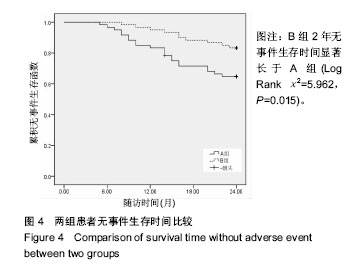
结果与结论:①A组术后平均随访18个月,21例再次发生骨折,38例未发生骨折;B组10例患者再次出现椎体骨折,B组2年无事件生存时间显著长于A组(P=0.015);②Logistic多因素模型分析结果显示,术前骨密度T值、抗骨质疏松治疗依从性、糖皮质激素用药史、术中骨水泥渗漏及椎体裂隙征是影响经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后再次骨折的独立因素(P < 0.05);③经ROC分析显示,术前骨密度T值和抗骨质疏松依从性评分预测患者经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后再次骨折的AUC分别为0.772和0.693(β=0.064,0.067,95%CI=0.646-0.898,0.562-0.823,P=0.001,0.014),最佳截断值分别为-3.74和4.53分,敏感度分别为0.795和0.81,特异度分别为0.762和0.59;④结果说明,经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后重视术前骨密度、术后抗骨质疏松治疗依从性、糖皮质激素用药史等高危风险因素警示作用,给予针对性干预有助于降低术后再骨折发生率,改善预后。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-9033-815X(庞巨涛)
中图分类号:
.jpg)