中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (20): 3117-3124.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3199
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 下一篇
高压氧、振动训练与虾青素联合干预糖尿病骨质疏松模型大鼠骨密度、糖代谢及氧化应激的变化
刘玉琳1,李国泰2
- 1重庆城市管理职业学院智慧康养学院,重庆市 401331;2重庆大学体育学院,重庆市 400044
Combined effects of hyperbaric oxygen, vibration training and astaxanthin on bone mineral density, glucose metabolism and oxidative stress in diabetic osteoporosis rats
Liu Yulin1, Li Guotai2
- 1Wisdom Health Care School, Chongqing City Management College, Chongqing 401331, China; 2College of Physical Education, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
摘要: 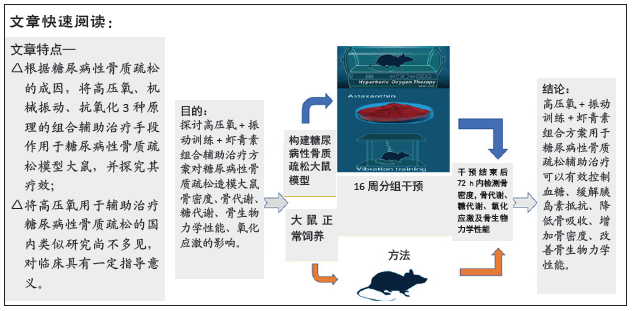
文题释义:
糖尿病性骨质疏松症:1 型或 2 型糖尿病患者经常性地发生骨矿物含量减少、骨密度降低及出现各种骨质疏松症的临床症状,糖尿病性骨质疏松症是一种发生在骨骼系统严重而常见的糖尿病并发症。
高压氧:为一种物理治疗手段,通过提高氧分压增加血氧含量和促进氧弥散而改善组织的血液供应,对多种创伤有显著疗效。
虾青素:是一种红色类胡萝卜素,名变胞藻黄素、虾红素、虾黄素等,广泛分布在海洋细菌、藻类、甲壳类和鱼类中,天然虾青素是迄今为止发现的自然界最强大的天然抗氧化剂之一。
背景:糖尿病性骨质疏松是一种发生在骨骼系统严重而常见的糖尿病并发症,具有较高致残、致死率。目前尚无针对糖尿病性骨质疏松的特异治疗方案,主要是采用降血糖和抗骨质疏松药物联合治疗。与单用药物治疗相比,加入非药物辅助手段的联合治疗对患者的骨密度提升效果可能会更显著。
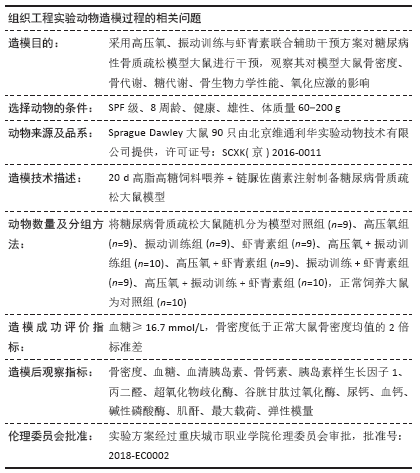
目的:探讨高压氧+振动训练+虾青素组合辅助治疗方案对糖尿病性骨质疏松造模大鼠的骨密度、骨代谢、糖代谢、骨生物力学性能及氧化应激的影响。
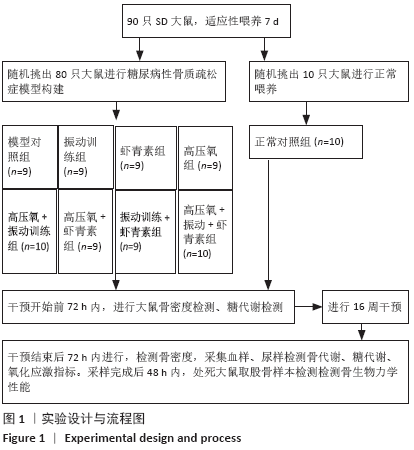
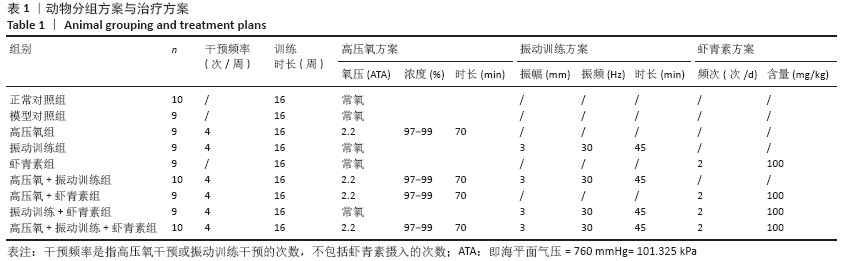
方法:纳入90只大鼠,10只大鼠正常饲养列为正常对照组;80只大鼠构建糖尿病性骨质疏松模型后随机分为8组(n=10),即模型对照组、高氧组、振动训练组、虾青素组、高压氧+振动训练组、高压氧+虾青素组、振动训练+虾青素组、高压氧+振动训练+虾青素组。执行16周干预,干预结束进行骨密度、糖代谢、氧化应激等检测。
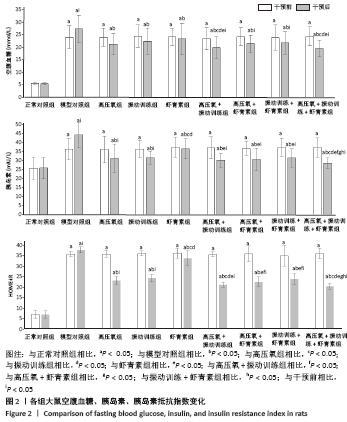
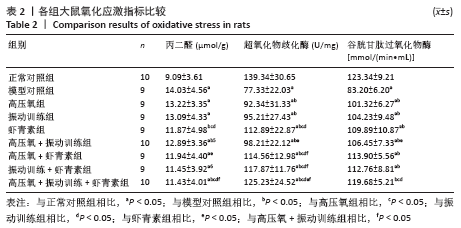
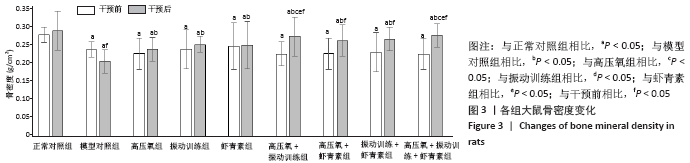
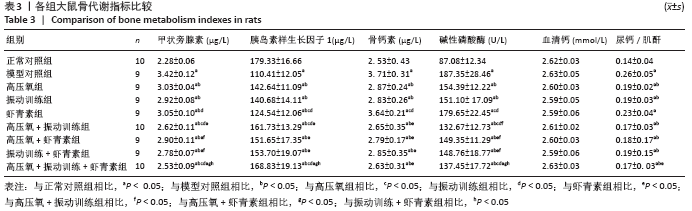
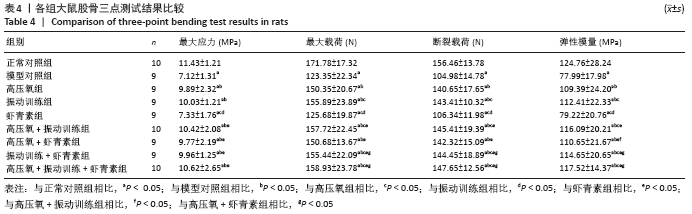
结果与结论:①经过16周干预,血糖、血清胰岛素、胰岛素抵抗方面,高压氧+振动训练组、高压氧+振动训练+虾青素组显著低于模型对照组、高氧组、振动训练组、虾青素组、高压氧+虾青素组、振动训练+虾青素组(P < 0.05);②丙二醛方面,高压氧+振动训练+虾青素组显著低于高氧组、振动训练组、高压氧+振动训练组(P < 0.05);③超氧歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶方面,高压氧+振动训练+虾青素组显著高于模型对照组、高氧组、振动训练组、高压氧+振动训练组(P < 0.05);④骨密度方面,高压氧+振动训练+虾青素组显著高于模型对照组、高压氧组、虾青素组(P < 0.05);⑤甲状旁腺激素、碱性磷酸酶方面,高压氧+振动训练组、高压氧+振动训练+虾青素组显著低于高氧组、振动训练组、虾青素组、高压氧+虾青素组、振动训练+虾青素组(P < 0.05);⑥胰岛素样生长因子1水平方面,高压氧+振动训练+虾青素组显著高于高氧组、振动训练组、虾青素组、高压氧+虾青素组、振动训练+虾青素组(P < 0.05);⑦股骨最大载荷、断裂载荷和弹性模量方面,高压氧+振动训练组、高压氧+振动训练+虾青素组、振动训练组、振动训练+虾青素组显著高于模型对照组、高氧组、虾青素组、高压氧+虾青素组(P < 0.05);⑧提示高压氧+振动训练+虾青素组合方案用于糖尿病性骨质疏松辅助治疗可以有效控制血糖、缓解胰岛素抵抗、降低骨吸收、增加骨密度、改善骨生物力学性能,且效果明显优于单独使用高压氧或振动训练。
中图分类号: