中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (8): 1188-1195.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1082
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
Neer分型二、三部分肱骨近端骨折不同治疗方式的临床经济学随访分析
邱忠鹏,李 珂,李 刚,刘克宇,杜新辉,孟德峰,史晨辉,王维山
- 石河子大学医学院第一附属医院骨科中心,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832002
Different treatments for two-part and three-part proximal humeral fractures by Neer classification: follow-up results analyzed using clinical economics
Qiu Zhongpeng, Li Ke, Li Gang, Liu Keyu, Du Xinhui, Meng Defeng, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan
- Orthopedic Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of the Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
成本-效果分析:是通过评价使用一定量的卫生资源(成本)后获得的健康效果来确定最优化临床方案的分析方法。在医疗服务中,很多卫生服务结果并不适宜用货币来衡量或者难以货币化,但可以用方案实施后的效果指标来表示,这些指标是能够直接反映人群健康效果的指标。成本-效果分析的基本思想是以最低的成本去实现确定的计划目标,通过对目标实现程度的描述来反映方案的效果。基本原则是:①治疗方案的成本尽可能低,且取得的效果尽可能好;②成本-效果分析中成本采用货币形式,而效果却采用健康指标,疾病状态改善指标或卫生服务利用指标等,因此要保证在成本效果分析过程中不同方案之间效果的可比性。
肱骨近端骨折的Neer分型:是Neer于1970年提出肱骨近端骨折的四部分分类法。将肱骨上端4个组成部分即肱骨头、大结节、小结节和肱骨上端(关节部或解剖颈、大结节、小结节、骨干或外科颈)相互移位程度分6个基本类型,移位>1 cm或成角> 45°,否则不能认为是移位骨块。肱骨近端骨折多为此类型,只要肱骨近端的骨折块移位<1 cm或成角< 45°,无论骨折线是否多个部分,均为一部分骨折;单纯外科颈骨折,解剖颈骨折,单纯大结节骨折,单纯小结节骨折为二部分骨折;外科颈骨折合并大结节骨折或外科颈骨折合并小结节骨折为三部分骨折。
摘要
背景:医保总额预付制对医院医疗费用控制的影响进一步加强,给患者提供适宜技术,提高医疗资源使用效率,减轻患者负担,控制医疗成本,同时保障医疗质量,已经成为医院管理很重要的决策考量因素,并且深刻影响临床医生的临床医疗决策及服务行为。
目的:探讨二、三部分肱骨近端骨折不同治疗方式的临床疗效和总体成本,利用临床经济学方法对不同治疗方案进行对比研究。
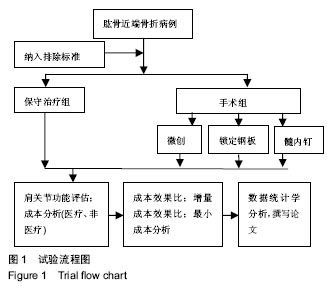
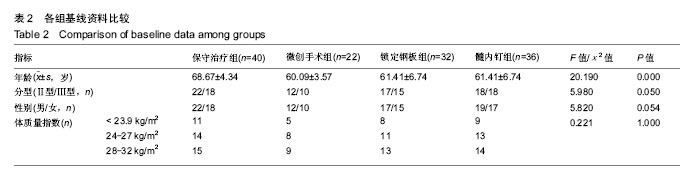
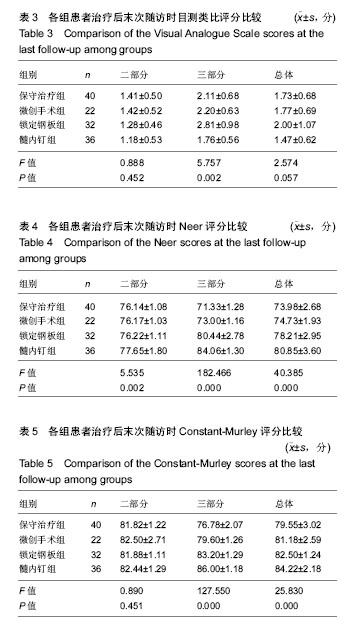
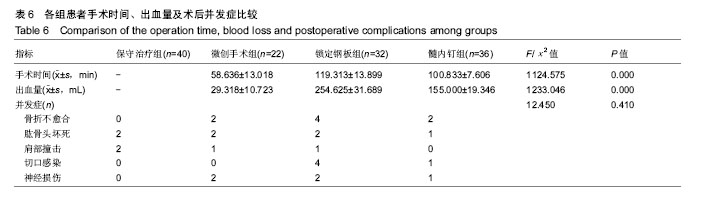
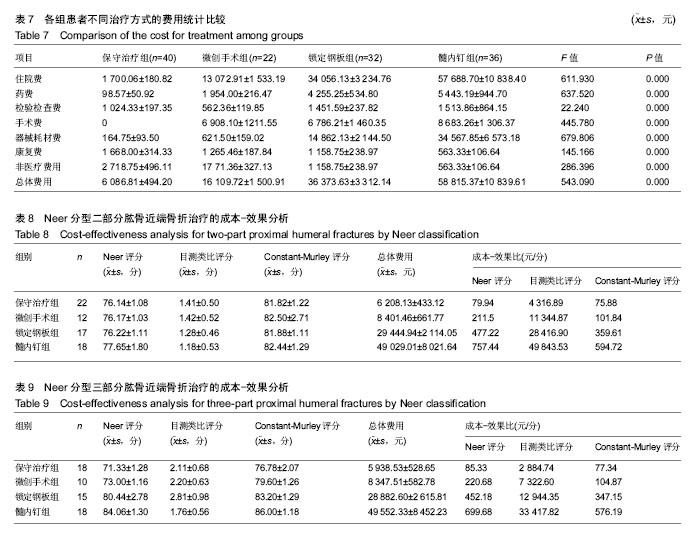
方法:将2011 年1月至2016年12月于石河子大学医学院第一附属医院骨科接受治疗的130例二、三部分肱骨近端骨折患者纳入研究,按治疗方式分为4组,保守治疗组(n=40)、微创手术组(n=22)、锁定钢板组(n=32)和髓内钉内固定组(n=36)。保守治疗组患者给予悬吊皮肤牵引或骨折手法复位石膏固定,各手术干预组患者均接受不同内固定手术,使用标准费用法统计患者治疗后 1年内因治疗产生的总体费用。治疗后使用Constant-Murley评分、目测类比评分、Neer评分对患者进行评估登记,使用临床经济学分析的方法对不同治疗组患者进行最小成本分析和成本效果分析。
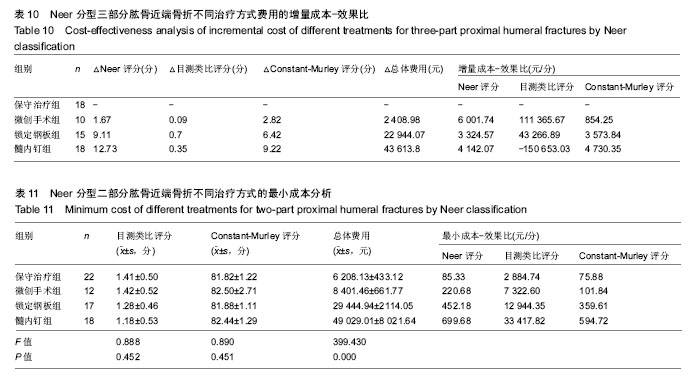
结果与结论:①成本效果分析结果显示,对于Neer二部分肱骨近端骨折,各手术干预组与保守治疗组疗效差异无显著性意义,但保守治疗组患者治疗支付成本更低。对于Neer三部分肱骨近端骨折,各手术干预组治疗效果优于保守治疗组,但手术干预组患者治疗支付成本高于保守治疗组;②根据增量成本效果比结果,对于Neer三部分肱骨近端骨折,微创手术组、锁定钢板组、髓内钉组患者肩关节功能Constant-Murley评分每提高1分需分别花费854.25,3 573.84,4 730.35元;③最小成本分析结果显示,对于Neer二部分肱骨近端骨折,4组患者疗效差异无显著性意义,但各手术干预组治疗成本较高,保守治疗组成本较低,保守治疗组具有与手术组相同的疗效和更好的经济学效果;④综上所述,保守治疗与手术干预治疗二、三部分肱骨近端骨折均有效,二部分肱骨近端骨折采取保守治疗是更经济、有效的治疗方案;而三部分肱骨近端骨折手术干预组治疗效果优于保守治疗组,但各手术组治疗支付成本比保守治疗组更高。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程 ORCID:0000-0001-5569-8205(邱忠鹏)
结果与结论:①成本效果分析结果显示,对于Neer二部分肱骨近端骨折,各手术干预组与保守治疗组疗效差异无显著性意义,但保守治疗组患者治疗支付成本更低。对于Neer三部分肱骨近端骨折,各手术干预组治疗效果优于保守治疗组,但手术干预组患者治疗支付成本高于保守治疗组;②根据增量成本效果比结果,对于Neer三部分肱骨近端骨折,微创手术组、锁定钢板组、髓内钉组患者肩关节功能Constant-Murley评分每提高1分需分别花费854.25,3 573.84,4 730.35元;③最小成本分析结果显示,对于Neer二部分肱骨近端骨折,4组患者疗效差异无显著性意义,但各手术干预组治疗成本较高,保守治疗组成本较低,保守治疗组具有与手术组相同的疗效和更好的经济学效果;④综上所述,保守治疗与手术干预治疗二、三部分肱骨近端骨折均有效,二部分肱骨近端骨折采取保守治疗是更经济、有效的治疗方案;而三部分肱骨近端骨折手术干预组治疗效果优于保守治疗组,但各手术组治疗支付成本比保守治疗组更高。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程 ORCID:0000-0001-5569-8205(邱忠鹏)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)