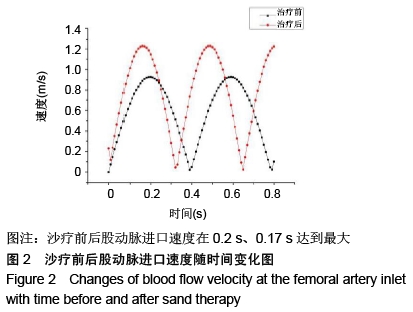
[1] 刘龙,迪丽娜尔•马合木提,富荣昌,等.室内沙疗对人体股动脉血流动力学影响的实验研究[J].新疆医科大学学报, 2014,37(1): 29-31.
[2] 布热比•依明,富荣昌,阿达依•谢尔亚孜旦,等.维医沙疗对股动脉分叉的血流动力学影响[J].医用生物力学杂志,2016,31(5): 431-436.
[3] 布热比•依明,富荣昌,维医沙疗下股动脉双向流固耦合血流动力学数值模拟[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2017,36(4): 507-511.
[4] 王克强,杨俊华,吴国强,等.腹主动脉分叉处粥样斑块分布及其意义[J].上海医科大学学报, 1989,16(6):427-430.
[5] 李珊. 冠状动脉分叉病变斑块分布特点研究——多排螺旋CT和血管内超声分析[D].北京:中国人民解放军军医进修学院.2007.
[6] GAO H, LONG Q, KUMAR DAS S,et al.Study of carotid arterial plaque stress for symptomatic and asymptomatic patients.J Biomech. 2011;44(14):2551-2557.
[7] KRISHNAN B.CHANDRAN, STANLEY E.RITTGERS, AJIT P. Yoganathan. Biofluid Mechanics-The Human Circulation. CRC Press.2012.
[8] 鲍觅夏,周平,郭凤,等.过载负荷下分叉血管的流动数值模拟[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(4):551-555.
[9] DERBEL H, KOBEITER H, PIZAINE G, et al.Accuracy of a Cone-Beam CT Virtual Parenchymal Perfusion Algorithm for Liver Cancer Targeting during Intra-arterial Therapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018;29(2):254-261.e2.
[10] 张梅,张运,高月花.颈动脉及股动脉内膜-中膜层厚度正常值的对比研究[J].中国医学影像技术,2002,18(1):32-33.
[11] 章德发,刘莹,毕勇强,等.不同狭窄率的颈动脉内血流动力学数值模拟[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(7):1872-1875.
[12] 杨文慧,何燕,魏云鸿,等.超声检测颈动脉粥样硬化对冠心病的预测价值[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2014;16(8) :880-882.
[13] 杨眉.下肢动脉斑块形成所致血管狭窄的彩超诊断及分析[J].双足与保健,2018,27(2):131+133.
[14] 戴正行,居敏昊,王婷,等.MSCTA不同图像后处理技术诊断常见下肢动脉病变的准确性观察[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2017,15(8): 149-152.
[15] 冯元桢.生物力学[M] .北京:科学出版社,1983.
[16] 邓小燕,孙安强,刘肖,等.生物流体力学[M].北京:机械工业出版社, 2014.
[17] 王勖成.有限单元法[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2003.
[18] LIU GY, WU JH, GHISTA DN, et al. Hemodynamic characterizationof transient blood flow in right coronary arteries with varying curvature and side-branch bifurcation angles. Comput Biol Med.2015;64:117-126.
[19] 豆中强.动脉血管中脉动血流的数值模拟[D].重庆:重庆大学, 2006.
[20] XU P, LIU X, SONG Q, et al.Patient-specific structural effects on hemodynamics in the ischemic lower limb artery. Sci Rep. 2016;6:39225.
[21] COSTAS CH, STANLEY AB. Fully developed pulsatile flow in a curved pipe.J Fluid Mech.2011;195:23.
[22] CHAICHANA T, SUN Z, JEWKES J. Computation of hemodynamics in the left coronary artery with variable angulations.J Biomech. 2011;44(10):1869-1878.
[23] SHAHCHERAGHI N,DWYER HA,CHEER AY,et al. Unsteady and three-dimensional simulation of blood flow in the human aortic arch.J Biomech Eng. 2002;124(4):378-87.
[24] LIU JY, CHEN CC, WANG WH, et al.Comparison of blood flow dynamics in thoracic aortic dissection and normal aortic based on CT images.BME Clin Med.2010;14(5):390-393.
[25] 刘莹,章德发,殷艳飞,等.颈动脉双向流固耦合模型非稳态血流数值分析[J].介入放射学杂志,2015,24(10):885-889.
[26] CAN Y, KILIÇ H, AKSOY M,et al. OP-204 [AJC » Interventions for peripheral arterial diseases] Endovascular Treatment of Arteriovenous Fistula. The American Journal of Cardiology. 2017;23-26:e64.
[27] LANGE U, MÜLLER-LADNER U, SCHMIDT KL. Balneotherapy in rheumatic diseases–an overview of novel and known aspects. Rheumatology International. 2006;26(6):497-499.
[28] ZUNNUNOV ZR, MAMATMURADOV SO.Hemodynamics in patients with hypertension after ammotherapy.Vopr Kurortol Fizioter Lech Fiz Kult. 2004;(3):13-15.
[29] 尼加提•外力,居来提•买提肉孜,李艳娜,等.沙疗温度对骨重建实验的影响及传热数值模拟研究[J].中国实验动物学报,2017, 25(2):181-185
[30] 王小龙,陈弼沧,吴秋英.维吾尔医学埋沙疗法治疗骨关节炎研究现状[J].光明中医,2015,30(6):1374-1375.
[31] CHEN H, LI Z, HONG H, et al.Relationship between visible branch arteries distal to the stenosis on magnetic resonance angiography and stroke recurrence in patients with severe middle cerebral artery trunk stenosis: a one-year follow up study.BMC Neurol. 2015;15:167.
[32] 于洁,高传玉,许文克,等.超声检查和血管造影对兔动脉粥样硬化狭窄模型的评价[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(40):51-53+193.
[33] MATSAGKAS M, KOUVELOS G, ARNAOUTOGLOU E,et al. Hybrid Procedures for Patients With Critical Limb Ischemia and Severe Common Femoral Artery Atherosclerosis.Ann Vasc Surg. 2011;25(8):1063-1069.
[34] SHAALAN WE, FRENCH-SHERRY E, CASTILLA M, et al. Reliability of common femoral artery hemodynamics in assessing the severity of aortoiliac inflow disease.J Vasc Surg. 2003;37(5):960-969.
[35] XU P, LIU X, SONG Q, et al. Patient-specific structural effects on hemodynamics in the ischemic lower limb artery. Sci Rep. 2016;6:39225.
[36] 陈玲婷,王荩,彭飞,等.下肢动脉硬化性闭塞症发病机制的研究进展[J].心理月刊,2018(12):111.
[37] 王慧琴,王思博,刘亢丁,等.局部血液动力学对颈动脉粥样硬化斑块的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2017,34(7):667-669.
[38] BAKSI AJ, DAVIES JE, HADJILOIZOU N, et al. Attenuation of reflected waves in man during retrograde propagation from femoral artery to proximal aorta. Int J Cardiol. 2016;202: 441-445.
[39] HODGES GJ, STEWART DG, DAVISON PJ, et al. The role of shear stress on cutaneous microvascular endothelial function in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117(12):2457-2468.
[40] THIM T,HAGENSEN MK,HORLYCK A,et al.Wall shear stress and local plaque development in stenosed carotid arteries of hypercholesterolemic minipigs.J Cardiovasc Dis Res. 2012; 3(2):77.
|
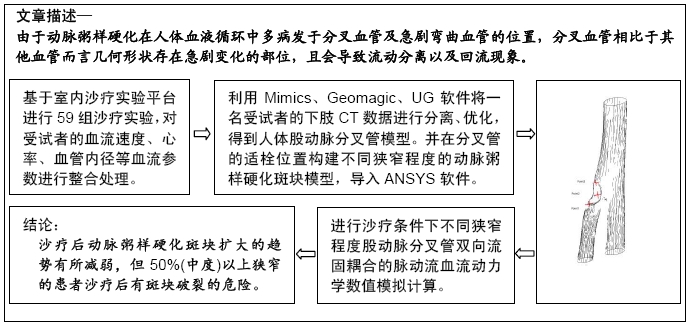
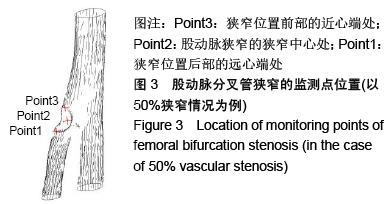

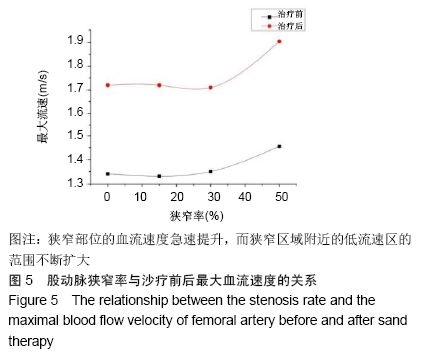

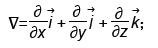
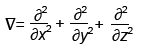
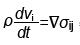 ,
,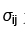
 tij
tij