中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (30): 4835-4840.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0971
• 药物控释材料 drug delivery materials • 上一篇 下一篇
麻醉诱导期梯度效应室靶控输注丙泊酚应用对老年患者围术期血流动力学和苏醒期的影响
刘 霞,王文娟,吴雪梅,谢 红
- 苏州大学附属第二医院,江苏省苏州市 215004
Effect of target controlled infusion of propofol on perioperative hemodynamics and awakening period in elderly patients
Liu Xia, Wang Wen-juan, Wu Xue-mei, Xie Hong
- Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215004, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
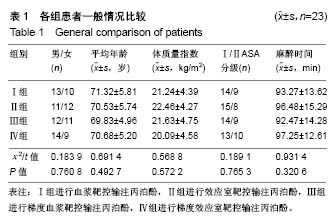
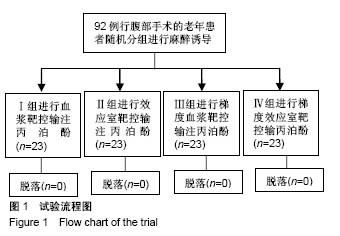
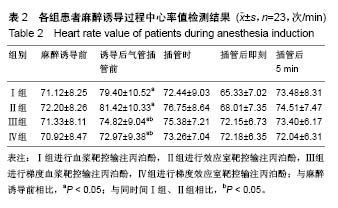
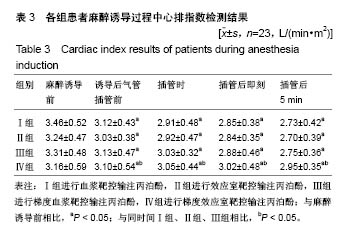
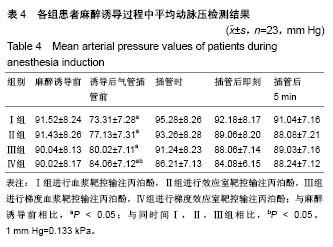
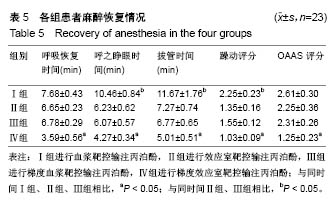
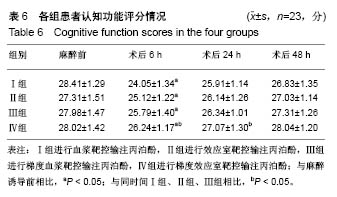
结果与结论:①与麻醉诱导前比较,4组诱导后气管插管前的心排指数、平均动脉压均降低(P < 0.05),心率明显升高(P < 0.05);在诱导后气管插管前,Ⅳ组的心排指数、平均动脉压下降幅度明显低于其余3组(P < 0.05),心率明显低于其余3组(P < 0.05);在插管时、插管后即刻及插管后5 min,4组间各指标比较无差异;②Ⅳ组的呼吸恢复时间、呼之睁眼时间、拔管时间明显短于其余3组(P < 0.05),躁动评分、OAAS评分明显低于其余3组(P < 0.05);③与麻醉诱导前比较,4组术后MMSE评分均有降低;Ⅳ组术后6,24 h的MMSE评分均高于其余3组(P < 0.05);④结果表明:对老年患者进行麻醉时,采用梯度效应室靶控输注丙泊酚进行诱导麻醉,不仅不影响麻醉效果,还可减轻对患者循环系统的影响,且术后麻醉恢复较快。
ORCID: 0000-0002-4658-4916(刘霞)
中图分类号: