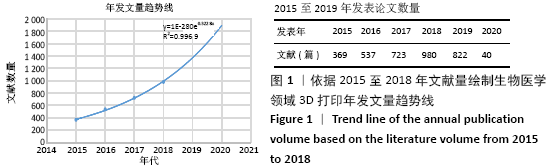
[1] BERMAN B. 3-d printing: the new industrial revolution. Bus Horiz. 2012;55(2):155-162.
[2] CAI H, LIU Z, WEI F, et al. 3D printing in spine surgery. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1093:345-359.
[3] DAWOOD A, MARTI MB, SAURET-JACKSON V, et al. 3D printing in dentistry. Br Dent J. 2015;219(11):521-529.
[4] ZHU W, MA X, GOU M, et al. 3D printing of functional biomaterials for tissue engineering. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2016;40:103-112.
[5] TRENFIELD SJ, AWAD A, MADLA CM, et al. Shaping the future: recent advances of 3D printing in drug delivery and healthcare. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019;16(10):1081-1094.
[6] VAN ECK NJ. Software suvey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523-538.
[7] 刘金花,崔金梅.基于VOSviewer的领域性热门研究主题挖掘[J].情报探索,2016(2):13-16.
[8] KOLESKY DB, TRUBY RL, GLADMAN AS, et al. 3D bioprinting of vascularized, heterogeneous cell-laden tissue constructs. Adv Mater. 2014;26(19):3124-3130.
[9] PATI F, JANG J, HA DH, et al. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3935.
[10] KANG HW, LEE SJ, KO IK, et al. A 3D bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity. Nat Biotechnol. 2016;34(3):312-319.
[11] MANNOOR MS, JIANG Z, JAMES T, et al. 3D printed bionic ears. Nano Lett. 2013;13(6):2634-2639.
[12] ZOPF DA, HOLLISTER SJ, NELSON ME, et al. Bioresorbable airway splint created with a three-dimensional printer. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368(21):2043-2045.
[13] ZEIN NN, HANOUNEH IA, BISHOP PD, et al. Three-dimensional print of a liver for preoperative planning in living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2013;19(12):1304-1310.
[14] GOYANES A, ROBLES MP, BUANZ A, et al. Effect of geometry on drug release from 3D printed tablets. Int J Pharm. 2015;494(2):657-663.
[15] GOYANES A, BUANZ AB, HATTON GB, et al. 3D printing of modified-release aminosalicylate (4-ASA and 5-ASA) tablets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;89:157-162.
[16] GOYANES A, BUANZ AB, BASIT AW, et al. Fused-filament 3D printing (3DP) for fabrication of tablets. Int J Pharm. 2014;476(1-2):88-92.
[17] ZEIN I, HUTMACHER D W, TAN K C, et al. Fused deposition modeling of novel scaffold architectures for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials. 2002;23(4):1169-1185.
[18] INZANA JA, OLVERA D, FULLER SM, et al. 3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2014;35(13):4026-4034.
[19] WILLIAMS JM, ADEWUNMI A, SCHEK RM, et al. Bone tissue engineering using polycaprolactone scaffolds fabricated via selective laser sintering. Biomaterials. 2005;26(23):4817-4827.
[20] 潘玮,郑鹏,黄锦泉,等.基于数据清洗“DEAN”流程的健康信息领域研究热点探测[J]. 现代情报,2018,38(10):73-77.
[21] PARK EK, LIM JY, YUN IS, et al. Cranioplasty enhanced by three-dimensional printing: custom-made three-dimensional-printed titanium implants for skull defects. J Craniofac Surg. 2016;27(4):943-949.
[22] RACHMIEL A, SHILO D, BLANC O, et al. Reconstruction of complex mandibular defects using integrated dental custom-made titanium implants. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;55(4):425-427.
[23] PERTICARINI L, ZANON G, ROSSI S M, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of a trabecular titanium acetabular component in hip arthroplasty: results at minimum 5 years follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:375.
[24] SHAH FA, SNIS A, MATIC A, et al. 3D printed Ti6Al4V implant surface promotes bone maturation and retains a higher density of less aged osteocytes at the bone-implant interface. Acta Biomater. 2016;30: 357-367.
[25] 沃金,袁峰,李威,等.钛支架微孔参数对成骨细胞黏附、增殖、分化的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(3):499-501.
[26] ARABNEJAD S, JOHNSTON B, TANZER M, et al. Fully porous 3D printed titanium femoral stem to reduce stress-shielding following total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(8):1774-1783.
[27] MACKEY A, NG JI, CORE J, et al. Three-dimensional-printed uterine model for surgical planning of a cesarean delivery complicated by multiple myomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133(4):720-724.
[28] GARAS M, VACCAREZZA M, NEWLAND G, et al. 3D-Printed specimens as a valuable tool in anatomy education: a pilot study. Ann Anat. 2018; 219:57-64.
[29] PLOCH CC, MANSI C, JAYAMOHAN J, et al. Using 3D Printing to Create Personalized Brain Models for Neurosurgical Training and Preoperative Planning. World Neurosurg. 2016;90:668-674.
[30] 田晓军,邱敏,颜野,等.3D打印肾脏模型和CT影像在住院医师教学过程中的对比应用[J].中国高等医学教育,2018,(9):74-75.
[31] LI P, XUAN M, LIAO C, et al. Application of intraoperative navigation for the reconstruction of mandibular defects with microvascular fibular flaps-preliminary clinical experiences. J Craniofac Surg. 2016;27(3): 751-755.
[32] HUANG H, HSIEH M F, ZHANG G, et al. Improved accuracy of 3D-printed navigational template during complicated tibial plateau fracture surgery. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2015;38(1):109-117.
[33] WEISSLER J M, SOSIN M, DORAFSHAR A H, et al. Combining virtual surgical planning, intraoperative navigation, and 3-dimensional printing in prosthetic-based bilateral microtia reconstruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75(7):1491-1497.
[34] JIANG Y, JI Z, GUO F, et al. Side effects of CT-guided implantation of (125)I seeds for recurrent malignant tumors of the head and neck assisted by 3D printing non co-planar template. Radiat Oncol. 2018;13(1):18.
[35] LIU JY, MAN QW, MA YQ, et al. I(125) brachytherapy guided by individual three-dimensional printed plates for recurrent ameloblastoma of the skull base. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;55(7): e38-e40.
[36] 鞠尔男,力武,李欣芯,等.生物医疗领域三维打印的研究与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(30):4906-4912.
[37] 余和东,张丽,夏凌云,等.3D打印成型纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/聚己内酯三元复合支架材料的构建及表征[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(10):1496-1501.
[38] 余程,刘凯,侯长江,等.3D打印纳米羟基磷灰石/聚己内酯支架生物相容性[J].青岛大学医学院学报,2017,53(1):1-4.
[39] HASSANAJILI S, KARAMI-POUR A, ORYAN A, et al. Preparation and characterization of PLA/PCL/HA composite scaffolds using indirect 3D printing for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109960.
[40] JAKUS AE, SHAH RN. Multi and mixed 3D-printing of graphene-hydroxyapatite hybrid materials for complex tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(1):274-283.
[41] HERMENEAN A, CODREANU A, HERMAN H, et al. Chitosan-graphene oxide 3d scaffolds as promising tools for bone regeneration in critical-size mouse calvarial defects. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16641.
[42] UNAGOLLA JM, JAYASURIYA AC. Enhanced cell functions on graphene oxide incorporated 3D printed polycaprolactone scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;102:1-11.
[43] CAVO M, SCAGLIONE S. Scaffold microstructure effects on functional and mechanical performance: Integration of theoretical and experimental approaches for bone tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;68:872-879.
[44] YANG F, CHEN C, ZHOU Q, et al. Laser beam melting 3D printing of Ti6Al4V based porous structured dental implants: fabrication, biocompatibility analysis and photoelastic study. Sci Rep. 2017;7:45360.
[45] ANONYMOUS. Spritam-a new formulation of levetiracetam for epilepsy. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2016;58(1497):78-79.
[46] ARAFAT B, QINNA N, CIESZYNSKA M, et al. Tailored on demand anti-coagulant dosing: an in vitro and in vivo evaluation of 3D printed purpose-designed oral dosage forms. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018; 128:282-289.
[47] GOYANES A, FINA F, MARTORANA A, et al. Development of modified release 3D printed tablets (printlets) with pharmaceutical excipients using additive manufacturing. Int J Pharm. 2017;527(1-2):21-30.
[48] SKOWYRA J, PIETRZAK K, ALHNAN MA. Fabrication of extended-release patient-tailored prednisolone tablets via fused deposition modelling (FDM) 3D printing. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015;68:11-17.
[49] GOYANES A, ROBLES MP, BUANZ A, et al. Effect of geometry on drug release from 3D printed tablets. Int J Pharm. 2015;494(2):657-663.
[50] KEMPIN W, FRANZ C, KOSTER LC, et al. Assessment of different polymers and drug loads for fused deposition modeling of drug loaded implants. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017;115:84-93.
[51] BECK R, CHAVES PS, GOYANES A, et al. 3D printed tablets loaded with polymeric nanocapsules: An innovative approach to produce customized drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2017;528(1-2):268-279.
[52] HE Y, GAO Q, WU WB, et al. 3D Printed Paper-Based Microfluidic Analytical Devices. Micromachines (Basel). 2016;7(7):108.
[53] 张慧,孟桐辉,刘琳,等.3D生物打印材料在生物医学领域中的应用及研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2019,13(2):157-160.
[54] 史建峰,王涵,赵蕾,等.3D生物打印支架材料的研究进展[J].中国药事,2018,32(10):1406-1411.
[55] CHIMENE D, LENNOX KK, KAUNAS RR, et al. Advanced bioinks for 3d printing: a materials science perspective. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016;44(6): 2090-2102.
[56] HONG S, SYCKS D, CHAN HF, et al. 3D Printing: 3D Printing of Highly Stretchable and Tough Hydrogels into Complex, Cellularized Structures. Adv Mater. 2015;27(27):4034.
[57] BENNING L, GUTZWEILER L, TRONDLE K, et al. Assessment of hydrogels for bioprinting of endothelial cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(4): 935-947.
[58] SHI P, LAUDE A, YEONG WY. Investigation of cell viability and morphology in 3D bio-printed alginate constructs with tunable stiffness. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(4):1009-1018.
[59] LEE SJ, HEO DN, PARK JS, et al. Characterization and preparation of bio-tubular scaffolds for fabricating artificial vascular grafts by combining electrospinning and a 3D printing system. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015; 17(5):2996-2999.
[60] LEE VK, KIM DY, NGO H, et al. Creating perfused functional vascular channels using 3D bio-printing technology. Biomaterials. 2014;35(28): 8092-8102.
[61] MARKSTEDT K, MANTAS A, TOURNIER I, et al. 3D Bioprinting human chondrocytes with nanocellulose-alginate bioink for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Biomacromolecules. 2015;16(5):1489-1496.
[62] APELGREN P, AMOROSO M, LINDAHL A, et al. Chondrocytes and stem cells in 3D-bioprinted structures create human cartilage in vivo. PLoS One. 2017;12(12):e189428.
|