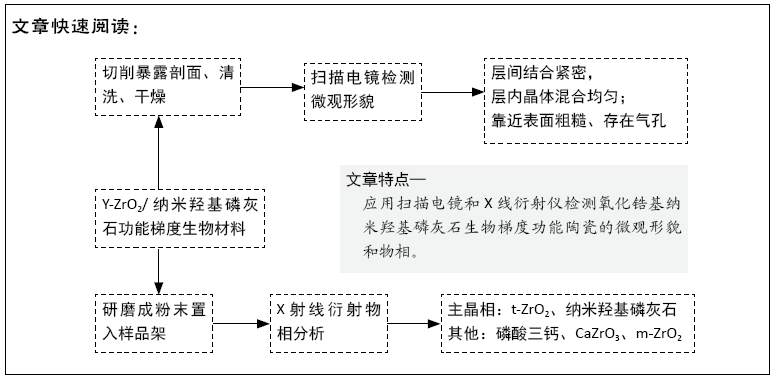
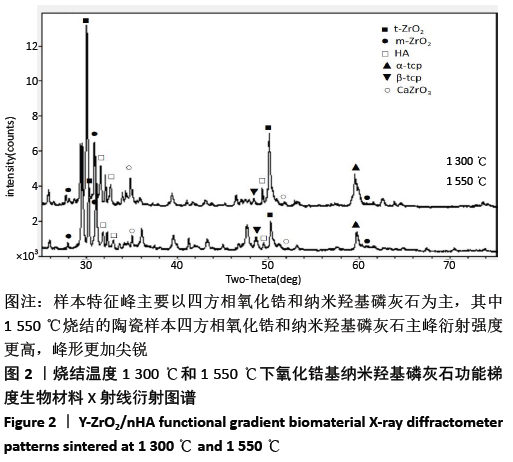
[1] 陈涛,付海洋,李岩,等.羟基磷灰石基复合骨修复材料研究进展[J].中国药事,2019,33(3):302-309.
[2] 于月苹,乌日开西·艾依提.钛合金植入物表面羟基磷灰石涂层的研究现状[J].热加工工艺,2019,48(2):23-27.
[3] 蒋媛,杨杨.二氧化锆的临床研究进展[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2017, 33(2):125-127.
[4] GEETHA M, SINGH AK, ASOKAM AR, et al. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants – A review. Prog Mater Sci. 2009; 54(3):397-425.
[5] NIINOMI M. Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2008;1(1): 30-42.
[6] 于婉琦,周延民,赵静辉.口腔种植体新材料的研究现状[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2019,46(4):488-496.
[7] SEO DS, CHAE HC. Fabrication and Microstructure of Hydroxyapatite Coatings on Zirconia by Room Temperature Spray Process. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015;15(8):6039-6043.
[8] HIROTA M, HAYAKAWA T, OHKUBO C, et al. Bone responses to zirconia implants with a thin carbonate-containing hydroxyapatite coating using a molecular precursor method. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(6):1277-1288.
[9] 鲍雨梅,徐哲玉,马龙,等.氧化锆增强HA涂层的制备及其磨损性能[J].中国陶瓷,2016,52(4):58-63.
[10] 鲍雨梅,马龙,徐哲玉,等.羟基磷灰石涂层制备及失效研究进展[J].材料导报,2016,30(9):70-74.
[11] 吴永智,栗卓新,李红,等.等离子喷涂羟基磷灰石/氧化锆复合涂层力学性能分析[J].新技术新工艺,2008(4):88-90.
[12] FARIA D, PIRES JM, BOCCACCINI AR, et al. Development of novel zirconia implant’s materials gradated design with improved bioactive surface. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;94:110-125.
[13] 黄勇,庞小峰,何从军,等.医用钛合金表面羟基磷灰石/二氧化锆梯度复合涂层的制备[J].电镀与涂饰,2011,30(1):78-82.
[14] 沈倩倩,潘育松.生物功能梯度材料的制备技术及性能评价[J].热加工工艺,2015,44(14):21-24.
[15] MAHMOUDI M, SAIDI AR, HASHEMIPOUR MA. The use of functionally graded dental crowns to improve biocompatibility: a finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2018;21(2): 161-168.
[16] 牛月月,王春燕,舒静媛,等.氧化锆基纳米羟基磷灰石功能梯度材料的制备及力学检测[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(10): 1528-1533.
[17] 朱东彬,宋艳军,梁金生,等.齿科用氧化锆陶瓷韧性研究进展[J].无机材料学报,2018,33(4):363-372.
[18] 蒋欣泉.骨缺损修复生物材料与骨再生[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2017, 52(10):600-604.
[19] Sivaraman K, Chopra A, Narayan AI. Is zirconia a viable alternative to titanium for oral implant? A critical review. J Prosthodont Res. 2018; 62(2):121-133.
[20] 屈银英,王珺璆.氧化锆种植体材料特性及改良的研究进展[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2018,5(19):26-27.
[21] RIGOLIN MSM, BARBUGLI PA, JORGE JH, et al. Effect of the aging of titanium and zirconia abutment surfaces on the viability, adhesion, and proliferation of cells and the adhesion of microorganisms. J Prosthet Dent. 2019;122(6):564.e1-564.e10.
[22] 邵荣学,全仁夫,张亮,等.梯度复合HA/ZrO2多孔支架材料在松质骨缺损应用的实验[J].中国比较医学杂志,2015,25(11):46-51.
[23] 王玉增,单志华.羟基磷灰石(HAP)的制备及应用概况[J].皮革科学与工程,2015,25(6):34-38.
[24] ROOP KR, WANG M. Functionally graded bioactive coatings of hydroxyapatite/titanium oxide composite system. Mater Lett. 2002; 55(3):133-137.
[25] EWAIS EM, AMIN AM, AHMED YM, et al. Combined effect of magnesia and zirconia on the bioactivity of calcium silicate ceramics at C\S ratio less than unity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 1):155-160.
[26] 刘丹,吴永豪,李向锋,等.纳米尺度表面粗糙度可影响羟基磷灰石陶瓷的生物学性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(18):2903-2909.
[27] ABOUSHELIB MN. Osteogenesis ability of CAD/CAM porous zirconia scaffolds enriched with nano-hydroxyapatite particles. Int J Implant Dent.2017;3(1):21.
[28] 游杰刚,张国栋,金永龙,等.烧结方式对合成锆酸钙材料结构和性能的影响[J].耐火材料,2015,49(2):110-112.
[29] BALHADDAD AA, KANSARA AA, HIDAN D, et al. Toward dental caries: Exploring nanoparticle-based platforms and calcium phosphate compounds for dental restorative materials. Bioact Mater. 2018;4(1): 43-55.
[30] 雷群,林东,黄文秀,等.钙离子对人成骨细胞迁移与成骨分化的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(6):602-608.
[31] 刘兆强,朱立国.磷酸钙材料在骨再生中的应用进展[J].中国医疗设备,2019,34(10):158-163.
[32] 文静,张喆轶,廖建国,等.α-磷酸三钙对磷酸镁骨水泥强度与体外降解性能的影响[J].硅酸盐通报,2019,38(02):574-579.
[33] 岑超德,张永,罗聪,等.3D打印PLLA/β-TCP复合人工骨及组织相容性研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(04):326-332.
[34] 史文涛,戴瑶,陈平波,等.鼻黏膜来源外胚间充质干细胞与磷酸钙骨水泥材料的体外相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(33): 5350-5355.
[35] 刘宁,朱勇,刘昌奎,等.仿生磷酸钙缓释涂层改性三维支架的制备及性能研究[J].山西医科大学学报,2019,50(1):35-39.
[36] CURRAN DJ, FLEMING TJ, TOWLER MR. Mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite-zirconia compacts sintered by two different sintering methods. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(4):1109-1120.
[37] 魏兆冬.ZrO2-HA生物陶瓷的制备及微观结构研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2006.
[38] 胡金凤,郭卫春,余铃,等.氧化锆改性磷酸镁骨水泥的生物力学性能体外初步测试[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(11):15-18,22.
[39] BOLLINO F, ARMENIA E, TRANQUILLO E. Zirconia/Hydroxyapatite Composites Synthesized Via Sol-Gel: Influence of Hydroxyapatite Content and Heating on Their Biological Properties. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(7):757.
[40] LI X, YOSHIHARA K, DE MUNCK J, et al. Modified tricalcium silicate cement formulations with added zirconium oxide. Clin Oral Investig. 2017;21(3):895-905.
|