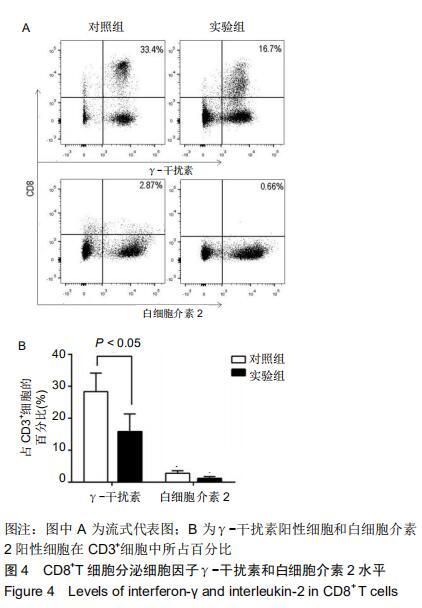
|
[1] SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, FEDEWA SA, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(3): 177-193.
[2] 孙洁,赵君宁.结直肠癌筛查的研究进展[J].实用老年医学,2019, 33(3):294-297.
[3] 董茜,王琪玮,张敬东.晚期结直肠癌靶向治疗的现状及进展[J].实用肿瘤杂志,2019,34(2):99-105.
[4] 刘天池,贾为国,赵荣华,等.结直肠癌免疫治疗的现状、挑战和出路[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2018,25(10):967-978.
[5] RAHBARGHAZI R, JABBARI N, SANI NA, et al. Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles: reliable tools for Cancer diagnosis and clinical applications. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):73.
[6] TKACH M, THÉRY C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell. 2016;164(6):1226-1232.
[7] ZHANG X, YUAN X, SHI H, et al. Exosomes in cancer: small particle, big player. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:83.
[8] TRAMS EG, LAUTER CJ, SALEM N JR, et al. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645(1):63-70.
[9] QIU GZ, JIN MZ, DAI JX, et al. Reprogramming of the Tumor in the Hypoxic Niche: The Emerging Concept and Associated Therapeutic Strategies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017;38(8): 669-686.
[10] LUDWIG N, HONG CS, LUDWIG S, et al. Isolation and Analysis of Tumor-Derived Exosomes. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2019;127(1):e91.
[11] GAO L, WANG L, DAI T, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes antagonize innate antiviral immunity. Nat Immunol. 2018; 19(3):233-245.
[12] YAO Y, CHEN L, WEI W, et al. Tumor cell-derived exosome-targeted dendritic cells stimulate stronger CD8+ CTL responses and antitumor immunities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;436(1):60-65.
[13] LI Q, HUANG Q, HUYAN T, et al. Bifacial effects of engineering tumour cell-derived exosomes on human natural killer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2018;363(2):141-150.
[14] 郑琦,侯炜.肿瘤外泌体在肿瘤调控中的作用[J].河北医药,2019, 41(9):1418-1422.
[15] KURYWCHAK P, TAVORMINA J, KALLURI R. The emerging roles of exosomes in the modulation of immune responses in cancer. Genome Med. 2018;10(1):23.
[16] ABUSAMRA AJ, ZHONG Z, ZHENG X, et al. Tumor exosomes expressing Fas ligand mediate CD8+ T-cell apoptosis. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2005;35(2):169-173.
[17] MAYBRUCK BT, PFANNENSTIEL LW, DIAZ-MONTERO M, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes induce CD8+ T cell suppressors. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5(1):65.
[18] 刘畅,王红艳.CD8+T细胞活化与分化的分子机制[J].中国免疫学杂志,2017,33(4):481-487.
[19] WHERRY EJ, AHMED R. Memory CD8 T-cell differentiation during viral infection. J Virol. 2004;78(11):5535-5545.
[20] KAECH SM, HEMBY S, KERSH E, et al. Molecular and functional profiling of memory CD8 T cell differentiation. Cell. 2002;111(6):837-851.
[21] YE SB, LI ZL, LUO DH, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes promote tumor progression and T-cell dysfunction through the regulation of enriched exosomal microRNAs in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5(14): 5439-5452.
[22] WHITESIDE TL. Exosomes and tumor-mediated immune suppression. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(4):1216-1223.
[23] CEREGHETTI DM, LEE PP. Tumor-Derived Exosomes Contain microRNAs with Immunological Function: Implications for a Novel Immunosuppression Mechanism. Microrna. 2014;2(3):194-204.
[24] ZHANG Y, WU XH, LUO CL, et al. Interleukin-12-anchored exosomes increase cytotoxicity of T lymphocytes by reversing the JAK/STAT pathway impaired by tumor-derived exosomes. Int J Mol Med. 2010;25(5):695-700.
[25] CLAYTON A, MITCHELL JP, COURT J, et al. Human tumor-derived exosomes selectively impair lymphocyte responses to interleukin-2. Cancer Res. 2007;67(15): 7458-7466.
[26] CHEN JH, XIANG JY, DING GP, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma- derived exosomes inhibit the antitumor activity of cytokine-induced killer cells by down-regulating the secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α and perforin. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016;17(7):537-544.
[27] LI P, LIU D, CHEN J, et al. Exosomes derived from hepatocellular carcinoma inhibit CD4+ and CD8+ T cell function through the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2019;12(5):5333-5340.
[28] XU HY, LI N, YAO N, et al. CD8+ T cells stimulated by exosomes derived from RenCa cells mediate specific immune responses through the FasL/Fas signaling pathway and, combined with GM‑CSF and IL‑12, enhance the anti‑renal cortical adenocarcinoma effect. Oncol Rep. 2019;42(2): 866-879.
|