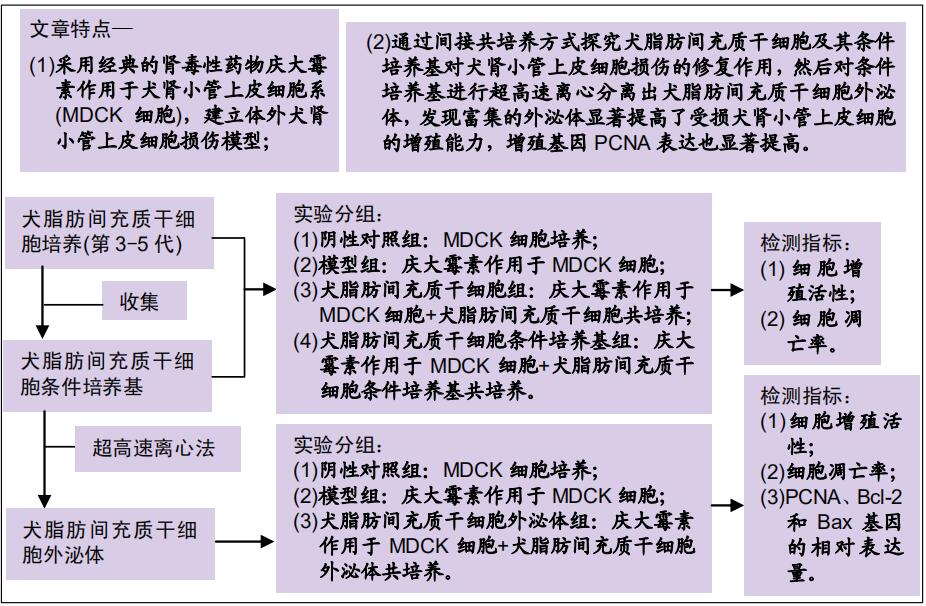
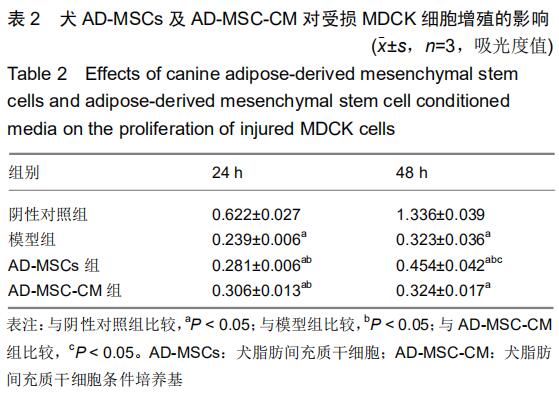
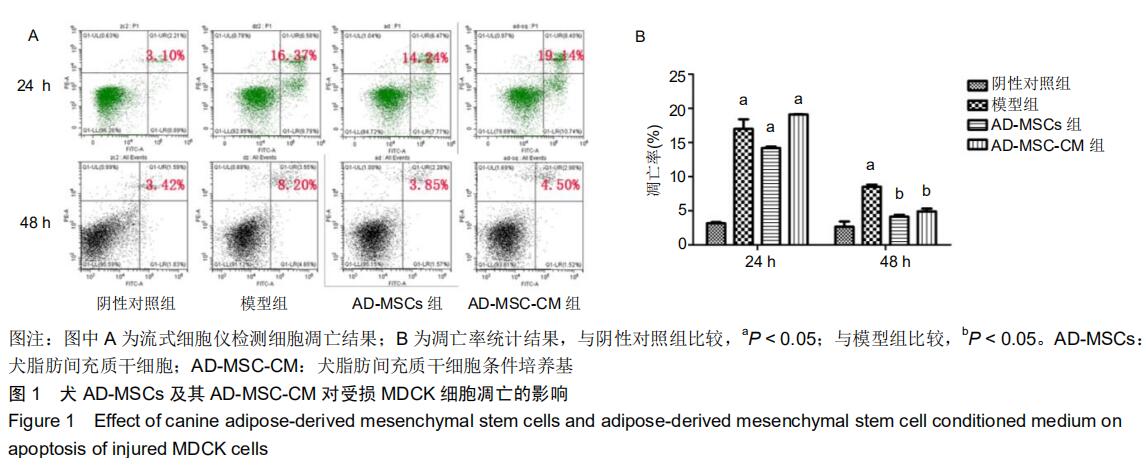
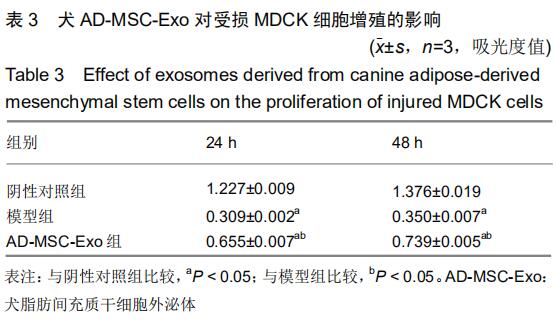
|
[1] LOPEZ-NOVOA JM, QUIROS Y, VICENTE L, et al. New insights into the mechanism of aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity: an integrative point of view. Kidney Int. 2011;79(1):33-45.
[2] LI J, LI QX, XIE XF, et al. Differential roles of dihydropyridine calcium antagonist nifedipine, nitrendipine and amlodipine on gentamicin-induced renal tubular toxicity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009;620(1-3):97-104.
[3] EL MOUEDDEN M, LAURENT G, MINGEOT-LECLERCQ MP, et al. Apoptosis in renal proximal tubules of rats treated with low doses of aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44(3):665-675.
[4] HEO JS, CHOI Y, KIM HS, et al. Comparison of molecular profiles of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta and adipose tissue. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(1):115-125.
[5] REGMI S, PATHAK S, KIM JO, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for the treatment of inflammatory diseases: Challenges, opportunities, and future perspectives. Eur J Cell Biol. 2019;98(5-8):151041.
[6] MORIGI M, IMBERTI B, ZOJA C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells are renotropic, helping to repair the kidney and improve function in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15(7): 1794-1804.
[7] BI B, SCHMITT R, ISRAILOVA M, et al. Stromal cells protect against acute tubular injury via an endocrine effect. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(9):2486-2496.
[8] YIN S, JI C, WU P, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes: bioactive ways of tissue injury repair. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(3):1230-1240.
[9] PHINNEY DG, PITTENGER MF. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4):851-858.
[10] LIM CY, HAN JI, KIM SG, et al. Evaluation of autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on renal regeneration after experimentally induced acute kidney injury in dogs. Am J Vet Res. 2016;77(2):208-217.
[11] 罗冬章,罗惠娜,李心怡,等.脂肪源间充质干细胞治疗犬急性肾衰竭的疗效观察[J].中国兽医杂志,2019,55(5):68-71,123.
[12] 李艳平,汪登如,施云平,等.犬干细胞修复因子治疗犬急性肾衰竭效果初探[J].上海畜牧兽医通讯,2016(5):16-18.
[13] YOO JH, PARK C, JUNG DI, et al.In vivo cell tracking of canine allogenic mesenchymal stem cells administration via renal arterial catheterization and physiopathological effects on the kidney in two healthy dogs. J Vet Med Sci. 2011;73(2): 269-274.
[14] ZHAN XS, EL-ASHRAM S, LUO DZ, et al. A Comparative Study of Biological Characteristics and Transcriptome Profiles of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Different Canine Tissues. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(6): E1485.
[15] 詹小舒,罗惠娜,罗冬章,等.犬脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体对血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移和凋亡的调控作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(29):4637-4643.
[16] 严磊,张绘艳,杨小康,等.庆大霉素致原代大鼠肾小管上皮细胞凋亡的研究[J].畜牧与兽医,2017,49(7):46-49.
[17] 刘翔,张白玉,王荣.四种急性肾衰竭模型的制作与体会[J].实验动物科学,2009,26(4):16-19,69.
[18] 严磊,张绘艳,杨小康,等.细胞凋亡在庆大霉素致MDCK细胞急性肾损伤中的作用[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医,2018(9):118-121.
[19] 傅鹏,袁伟杰,崔若兰,等.庆大霉素诱导肾小管上皮细胞凋亡及细胞周期调节蛋白表达[J].第二军医大学学报,2003,24(12): 1312-1315.
[20] FRIEDENSTEIN AJ, GORSKAJA JF, KULAGINA NN. Fibroblast precursors in normal and irradiated mouse hematopoietic organs. Exp Hematol. 1976;4(5):267-274.
[21] RUSSELL KA, CHOW NH, DUKOFF D, et al. Characterization and Immunomodulatory Effects of Canine Adipose Tissue- and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0167442.
[22] 李艳琪,王洪一,姚尧,等.人脐带源和胎盘源间充质干细胞的生物学特性比较[J].军事医学,2015,39(6):418-422.
[23] 蔡金宏,林春博,杨渊. 间充质干细胞分离方法的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(45):7375-7380.
[24] 韩之波,杨舟鑫,池颖,等. 人脐带、胎盘绒毛膜来源间充质干细胞的生物学特性比较研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2012,20(3): 692-696.
[25] FERNANDES M, VALENTE SG, SABONGI RG, et al.Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells versus adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for peripheral nerve regeneration.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(1):100-104.
[26] JIANG W, TAN Y, CAI M, et al. Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl4-Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:6079642.
[27] 魏兆明,江文胜,高艺,等.脂肪间充质干细胞的生物学特性及潜在临床应用[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2019,24(1):116-120.
[28] HERRERA MB, BUSSOLATI B, BRUNO S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells contribute to the renal repair of acute tubular epithelial injury. Int J Mol Med. 2004;14(6): 1035-1041.
[29] TÖGEL F, WEISS K, YANG Y, et al. Vasculotropic, paracrine actions of infused mesenchymal stem cells are important to the recovery from acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292(5):F1626-1635.
[30] HERRERA MB, BUSSOLATI B, BRUNO S, et al. Exogenous mesenchymal stem cells localize to the kidney by means of CD44 following acute tubular injury. Kidney Int. 2007;72(4): 430-441.
[31] DE ALMEIDA DC, DONIZETTI-OLIVEIRA C, BARBOSA-COSTA P, et al. In search of mechanisms associated with mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies for acute kidney injury. Clin Biochem Rev. 2013;34(3):131-144.
[32] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420.
[33] PAN BT, TENG K, WU C, et al. Electron microscopic evidence for externalization of the transferrin receptor in vesicular form in sheep reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1985;101(3):942-948.
[34] ZITVOGEL L, REGNAULT A, LOZIER A, et al. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med.1998;4(5): 594-600.
[35] THÉRY C, REGNAULT A, GARIN J, et al. Molecular characterization of dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Selective accumulation of the heat shock protein hsc73. J Cell Biol. 1999;147(3):599-610.
[36] BLANCHARD N, LANKAR D, FAURE F, et al. TCR activation of human T cells induces the production of exosomes bearing the TCR/CD3/zeta complex. J Immunol. 2002;168(7): 3235-3241.
[37] WOLFERS J, LOZIER A, RAPOSO G, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of shared tumor rejection antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nat Med. 2001;7(3):297-303.
[38] ANDRE F, SCHARTZ NE, MOVASSAGH M, et al. Malignant effusions and immunogenic tumour-derived exosomes. Lancet. 2002;360(9329):295-305.
[39] LAI CP, BREAKEFIELD XO. Role of exosomes/microvesicles in the nervous system and use in emerging therapies. Front Physiol. 2012;3:228.
[40] EIRIN A, RIESTER SM, ZHU XY, et al. MicroRNA and mRNA cargo of extracellular vesicles from porcine adipose tissue- derived mesenchymal stem cells. Gene. 2014;551(1): 55-64.
[41] EIRIN A, ZHU XY, PURANIK AS, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of extracellular vesicles isolated from porcine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:36120.
[42] YAGHOUBI Y, MOVASSAGHPOUR A, ZAMANI M, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived-exosomes in diseases treatment. Life Sci. 2019;233: 116733.
[43] ZHANG B, SHEN L, SHI H, et al. Exosomes from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Identification, Purification, and Biological Characteristics. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1929536.
[44] NARYZHNY SN. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen: a proteomics view. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008;65(23):3789-3808.
[45] TAIT SW, GREEN DR. Mitochondria and cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(9):621-632.
[46] DILLON CP, GREEN DR. Molecular Cell Biology of Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;930:1-23.
[47] 杨涛. 氨基糖苷类抗生素的肾毒性比较及毒理基因组学研究[D].上海:上海医药工业研究院,2006.
[48] BEHR L, HEKMATI M, LUCCHINI A, et al. Evaluation of the effect of autologous mesenchymal stem cell injection in a large-animal model of bilateral kidney ischaemia reperfusion injury. Cell Prolif. 2009;42(3):284-297.
|