| [1] Khaji A, Kowey PR. Update on atrial fibrillation J. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2017;27(1):14-25. [2] Fuster V, Ryden LE, Cannom DS, et al. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: full text: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2001 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation): developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association and the Heart Rhythm Society. Europace. 2006;8(9):651-745. [3] Bernstein SA, Wong B, Vasquez C, et al. Spinal cord stimulation protects against atrial fibrillation induced by tachypacing. Heart Rhythm. 2012;9(9):1426-1433. [4] Lanza GA, Barone L, Di Monaco A. Effect of spinal cord stimulation in patients with refractory angina: evidence from observational studies. Neuromodulation. 2012;15(6): 542-549. [5] Borjesson M, Andrell P, Mannheimer C, et al. Spinal cord stimulation for long-term treatment of severe angina pectoris: what does the evidence say? Future Cardiol. 2011;7(6):825-833. [6] Falowski S, Celii A, Sharan A. Spinal cord stimulation: an update. Neurotherapeutics. 2008;5(1):86-99. [7] Grimaldi R, de Luca A, Kornet L, et al. Can spinal cord stimulation reduce ventricular arrhythmias. Heart Rhythm. 2012;9(11):1884-1887. [8] Liu Y, Yue WS, Liao SY, et al. Thoracic spinal cord stimulation improves cardiac contractile function and myocardial oxygen consumption in a porcine model of ischemic heart failure. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012; 23(5):534-540. [9] Jesus S, Alo KM, Torre-Amtone G, et al. Initial experiencer with spinal cord stimulation for the treatment of advanced heart failure. J Card Fail. 2010;16(8):S67.[10] 侯月梅杨新春.心房颤动模型制作与评价[J].中国心脏起搏与心电生理杂志,2006,20(3):194-197.[11] Tan AY, Zhou S, Song J, et al. Neural mechanisms of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal atrial tachycardia in ambulatory canines. Circulation. 2008;118(9): 916. [12] Allessie M, Kirchhof C, Scheffer GJ, et al. Regional control of atrial fibrillation by rapid pacing in conscious dogs. Circulation. 1991;84(4):1689-1697. [13] Morillo CA, Klein GJ, Jones DL, et al. Chronic rapid atrial pacing: a structural, functional, and electrophysiological characteristics of a newmodel of sustained atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1995;91(5):1588-1595. [14] Sanders P, Pürerfellner H, Pokushalov E, et al. Performance of a new atrial fibrillation detection algorithm in a miniaturized insertable cardiac monitor: results from the reveal LINQ usability study. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13(7): 1425-1430. [15] Shen MJ, Zipes DP. Role of the autonomic nervous system in modulating cardiac arrhythmias. Circ Res. 2014;114(6): 1004. [16] Patterson E, Lazzara R, Szabo B, et al. Sodium-calcium exchange initiated by the Ca2+ transient: an arrhythmia trigger within pulmonary veins. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47: 1196-1206. [17] Coumel P, Attuel P, Lavallée J, et al. The atrial arrhythmia syndrome of vagal origin. Arch Mal Coeur Vais.1978;71(6): 645-656. [18] Schauerte P, Scherlag B, Patterson E, er al. Focal atrial fibrillation: experimental evidence for a pathophysiologic role of the autonomic nervous system. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010;12(5):592-599. [19] Shealy CN, Mortimer JT and Reswick JB. Electrical inhibition of pain by stimulation of the dorsal columns: preliminary clinical report. Anesth Analg. 1967;46:489-491. [20] Olgin JE, Takahashi T, Wilson E, et al. Effects of thoracic spinal cord stimulation on cardiac autonomic regulation of the sinus and atrioventricular nodes. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002;13(5):475-481. [21] Friedrichs K, Klinke A, Baldus S. Inflammatory pathways underlying atrial fibrillation. Trends Mol Med. 2011;17(10): 556-563. [22] Jalife J, Kaur K. Atrial remodeling, fibrosis, and atrial fibrillation. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2015;25(6):475-484. [23] Bruins P, Velthuis H, Yazdanbakhsh AP, et al. Activation of the complement system during and after cardiopulmonary bypass surgery: postsurgery activation involves c-reactive protein and is associated with postoperative arrhythmia. Circulation. 1997;96(10):3542-3548. [24] Frustaci A, Chimenti C, Bellocci F, et al. Histological substrate of atrial biopsies in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1997;96(4):1180-1184. [25] Aviles RJ, Martin DO, Apperson HC, et al. Inflammation as a risk factor for atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2003;108(24): 3006-3010. [26] Hu YF, Chen YJ, Lin YJ, et al. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015; 12(4):230-243. [27] Patel P, Dokainish H, Tsai P, et al. Update on the association of inflammation and atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010;21(9):1064-1070. [28] Kornej J, Reinhardt C, Kosiuk J, et al. Response of high-sensitive C-reactive protein to catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation and its relation with rhythm outcome. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44165. [29] Zheng LH, Yao Y, Wu LM, et al. Relationships of high-sensitive C-reactive protein and P-wave dispersion in lone atrial fibrillation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(11): 1450-1454. [30] Smit MD, Maass AH, De Jong AM, et al. Role of inflammation in early atrial fibrillation recurrence. Europace. 2012;14(6):810-817. [31] Wu N, Xu B, Xiang Y, et al. Association of inflammatory factors with occurrence and recurrence of atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2013;169(1):62-72. [32] Marcus GM, Smith LM, Ordovas K, et al. Intracardiac and extracardiac markers of inflammation during atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2010;7(2):149-154. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
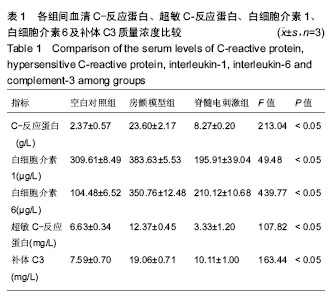
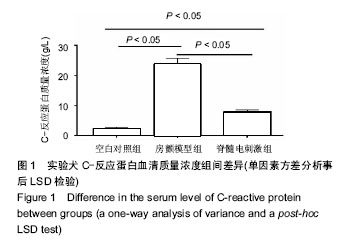
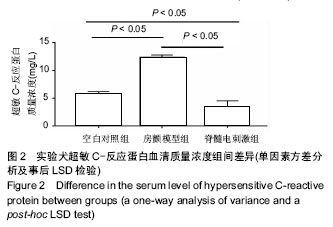
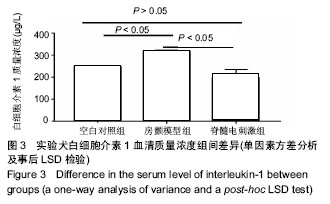
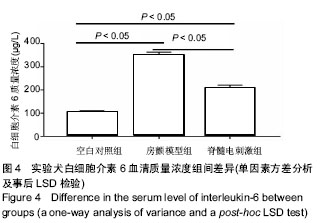
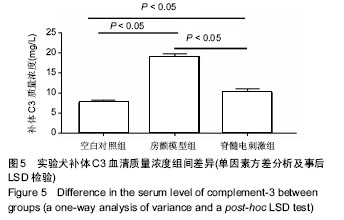
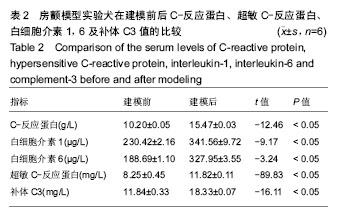
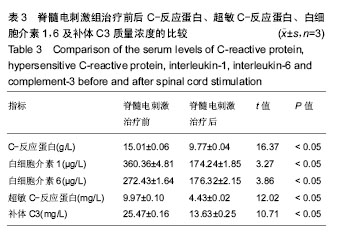
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
脊髓电刺激治疗:是通过向特定的脊髓节段发放低能量、高频率电刺激,以达到治疗疼痛或其他疾病的治疗形式。#br#
脊髓电刺激的应用:脊髓电刺激目前已广泛运用于顽固性心绞痛、心律失常风暴、顽固性心力衰竭等的治疗,近年来其对房颤的治疗作用越来越受到心内电生理界关注。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
脊髓电刺激治疗:是通过向特定的脊髓节段发放低能量、高频率电刺激,以达到治疗疼痛或其他疾病的治疗形式。#br#
脊髓电刺激的应用:脊髓电刺激目前已广泛运用于顽固性心绞痛、心律失常风暴、顽固性心力衰竭等的治疗,近年来其对房颤的治疗作用越来越受到心内电生理界关注。#br#
#br#