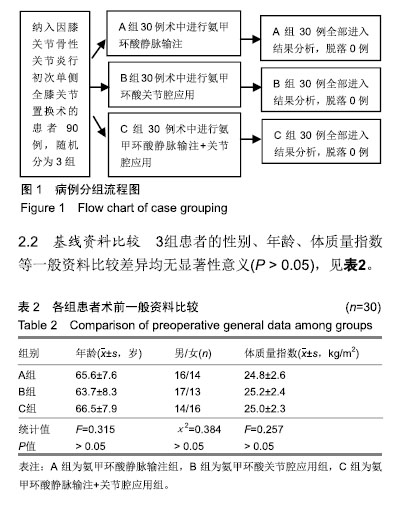
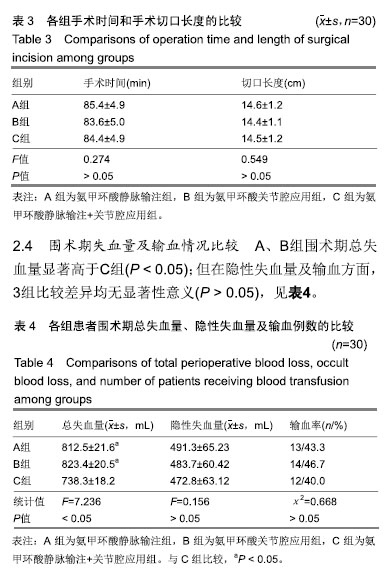
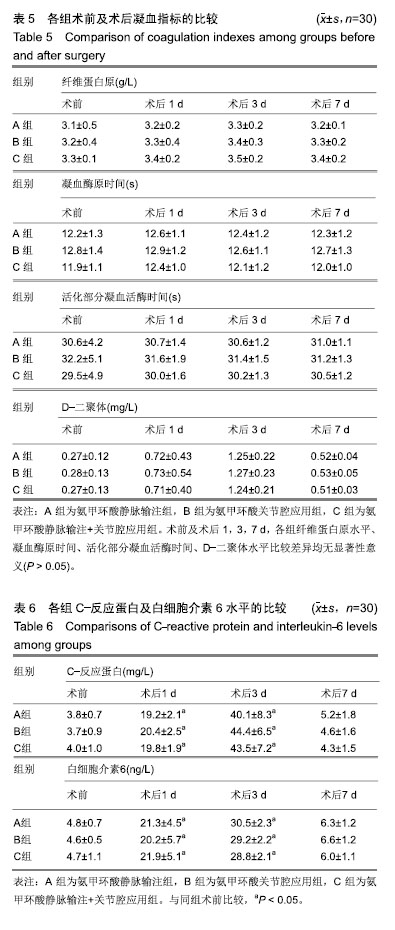
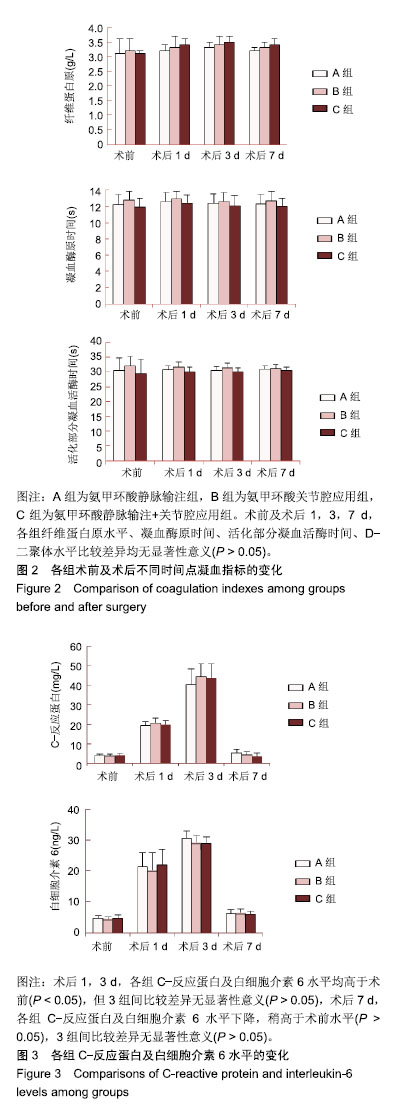
| [1]Kim YH,Pandey K,Park JW,et al.Comparative Efficacy of Intravenous With Intra-articular Versus Intravenous Only Administration of Tranexamic Acid to Reduce Blood Loss in Knee Arthroplasty.Orthopedics.2018;41(6):e827-e830. [2]Wang F,Zhao KC,Zhao MM,et al.The efficacy of oral versus intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss after primary total knee and hip arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Medicine(Baltimore). 2018;97(36):e12270. [3]Han YH, Huang HT, Pan JK, et al. Is the combined application of both drain-clamping and tranexamic acid superior to the single use of either application in patients with total-knee arthroplasty?: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine(Baltimore).2018;97(36):e11573. [4]Xiong H,Liu Y,Zeng Y,et al.The efficacy and safety of combined administration of intravenous and topical tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2018;19(1):321. [5]彭慧明,翁习生,翟吉良,等.氨甲环酸结合术后引流管临时夹闭降低单侧全膝置换术后失血量的有效性及安全性[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(4):400-405.[6]Li H,Bai L,Li Y,et al.Oral tranexamic acid reduces blood loss in total-knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(45):e12924.[7]Wu YG,Zeng Y,Hu QS,et al.Tranexamic Acid Plus Low-dose Epinephrine Reduces Blood Loss in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Orthop Surg. 2018; 10(4):287-295. [8]Almeida MDC,Albuquerque RPE,Palhares GM,et al. Evaluation of the use of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty.Rev Bras Ortop.2018;53(6):761-767.[9]Cao G,Xie J,Huang Z,et al.Efficacy and safety of multiple boluses of oral versus intravenous tranexamic acid at reducing blood loss after primary total knee arthroplasty without a tourniquet: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Thromb Res.2018;171:68-73. [10]Wang D,Wang HY,Luo ZY,et al.Blood-conserving efficacy of multiple doses of oral tranexamic acid associated with an enhanced-recovery programme in primary total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial.Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(8):1025-1032.[11]Kim YT, Kang MW, Lee JK, et al.Combined use of topical intraarticular tranexamic acid and rivaroxaban in total knee arthroplastysafely reduces blood loss, transfusion rates, and wound complications without increasing the risk of thrombosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2018;19(1):227.[12]Grant AL,Letson HL,Morris JL,et al.Tranexamic acid is associated with selective increase in inflammatory markers following total knee arthroplasty (TKA): a pilot study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):149. [13]Li R,Yin S,Zhong H,et al.[Effect on time of temporarily-closed wound drainage on blood loss of primary total knee arthroplasty after intravenous and intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017;31(4):417-421.[14]Guo P,He Z,Wang Y,et al.Efficacy and safety of oral tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine(Baltimore). 2018;97(18): e0587. [15]李大坤,高忠,邢刚,等.局部应用与静脉注射氨甲环酸减少全髋关节置换术术后失血量有效性与安全性的研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(8):843-844.[16]Yozawa S,Ogawa H,Matsumoto K,et al.Periarticular injection of tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and the necessity for allogeneic transfusion after total knee arthroplasty using autologous transfusion: a retrospective observational study.J Arthroplasty.2018;33(1):86-89.doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.08.018. [17]Abdel MP,Chalmers BP,Taunton MJ,et al.Intravenous versus topical tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: both effective in a randomized clinical trial of 640 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(12):1023-1029.[18]马瑞,杨佩,王春生,等.不同氨甲环酸给药途径在全膝关节置换术的有效性和安全性[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2018,12(5): 666-670.[19]高麟超.氨甲环酸的三种给药途径在全膝关节置换术中的有效性及安全性的对比研究[D].宁波:宁波大学,2016.[20]Sun Q,Li J,Chen J,et al.Comparison of intravenous, topical or combined routes of tranexamic acid administration in patients undergoing total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.BMJ Open.2019;9(1):e024350. [21]Jimenez JJ,Iribarren JL,Lorente L,et al.Tranexamic acid attenuates inflammatory response in cardiopulmonary bypass surgery through blockade of fibrinolysis: a case control study followed by a randomized double-blind controlled trial.Crit Care.2007;11(6):R117.[22]Hu Y,Li Q,Wei BG,et al.Blood loss of total knee arthroplasty in osteoarthritis: an analysis of influential factors.J Orthop Surg Res.2018;13(1):325.[23]Li ZJ,Zhao MW,Zeng L.Additional Dose of Intravenous Tranexamic Acid after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty Further Reduces Hidden Blood Loss.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018; 131(6):638-642. [24]Mufarrih SH,Malik AT,Qureshi NQ,et al.The effect of tranexamic acid in unilateral and bilateral total knee arthroplasty in the South Asian population: A retrospective cohort study.Int J Surg.2018;52:25-29.[25]Subramanyam KN,Khanchandani P,Tulajaprasad PV,et al.Efficacy and safety of intra-articular versus intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing perioperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized double-blind equivalence trial.Bone Joint J.2018;100-B(2):152-160. [26]Yuan X,Wang J,Wang Q,et al.Synergistic effects of intravenous and intra-articular tranexamic acid on reducing hemoglobin loss in revision total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled study.Transfusion. 2018;58(4):982-988. [27]George J,Eachempati KK,Subramanyam KN,et al.The comparative efficacy and safety of topical and intravenous tranexamic acid for reducing perioperative blood loss in Total knee arthroplasty- A randomized controlled non-inferiority trial.Knee.2018;25(1):185-191.[28]Zhang LK,Ma JX,Kuang MJ,et al.The efficacy of tranexamic acid using oral administration in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):159. [29]Wang Z,Shen X.The efficacy of combined intra-articular and intravenous tranexamic acid for blood loss in primary total knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Oct;96(42):e8123. [30]Yen SH,Lin PC,Chen B,et al.Topical Tranexamic Acid Reduces Blood Loss in Minimally Invasive Total Knee Arthroplasty Receiving Rivaroxaban.Biomed Res Int. 2017; 2017:9105645.[31]Wang D,Zhu H,Meng WK,et al.Comparison of oral versus intra-articular tranexamic acid in enhanced-recovery primary total knee arthroplasty without tourniquet application: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2018;19(1):85. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)