中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (20): 3267-3274.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3201
• 组织构建循证医学 evidence-based medicine in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
补阳还五汤预防骨科术后深静脉血栓形成的系统评价及试验序贯分析
靖金鹏1,张 玥2,刘效敏3,刘 壹1
- 1山东中医药大学第一临床医学院,山东省济南市 250014;山东中医药大学附属医院,2周围血管病科,3运动损伤骨科,山东省济南市 250014
Buyang Huanwu Decoction in prevention of deep venous thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
Jing Jinpeng1, Zhang Yue2, Liu Xiaomin3, Liu Yi1
- 1First Clinical Medicine School, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Peripheral Vascular Disease, 3Department of Orthopedics for Athletic Injuries, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
试验序贯分析:试验序贯分析用于系统综述或Meta分析样本量估算,克服了经典的系统综述或Meta分析的不足,能增加结果的可信度和合理性。亦为Meta分析的更新提供了参考,相比于传统的Meta分析能及时建议终止无效的试验,防止医疗资源的浪费,更加符合伦理的要求。
Meta分析:是系统综述中应用的一种统计学方法,它将多个临床试验的数据结果进行系统的、定量的综合分析,通过增大样本量来增加研究结论的可信度,被广泛应用于治疗、诊断、病因、预后甚至疾病的流行病学研究中。
目的:目前部分临床随机对照研究证明补阳还五汤能有效预防骨科术后患者发生深静脉血栓,但尚缺乏循证医学证据的支持。文章系统评价补阳还五汤加减预防骨科患者术后发生深静脉血栓的临床疗效及安全性。
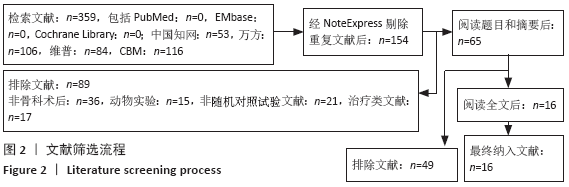
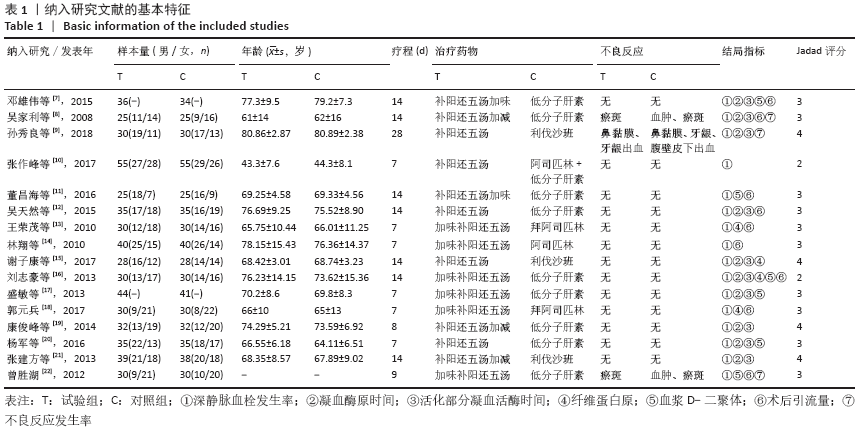
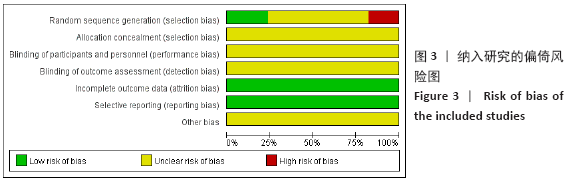
方法:截止至2020年3月,检索PubMed、Embase、Cochrane Library、中国知网、维普、万方、中国生物医学数据库收录的关于补阳还五汤加减预防骨科术后深静脉血栓的临床随机对照试验文献。试验对象为骨科术后患者,试验组为补阳还五汤预防患者术后发生深静脉血栓,对照组为常规西药预防。根据Cochrane Handbook 5.1.0评价标准及改良Jadad评分量表对纳入文献进行质量评估,采用RevMan 5.3和Stata 16软件进行Meta分析,TSA 0.9.5.10 Beta 软件进试验序贯分析,比较试验组与对照组患者术后深静脉血栓的发生率、凝血酶原时间、活化部分凝血活酶时间、纤维蛋白原、D-二聚体、术后引流量和不良反应发生率方面的差异。
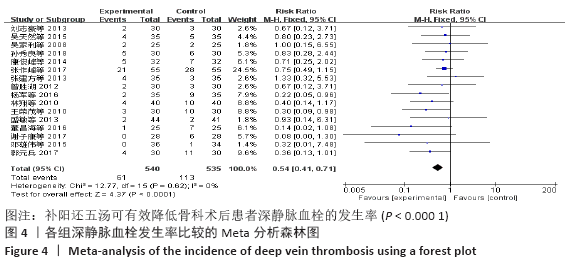
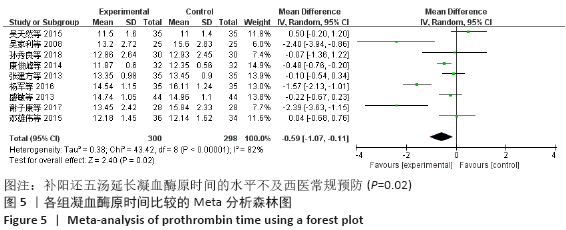
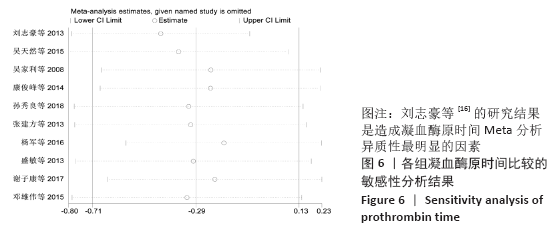
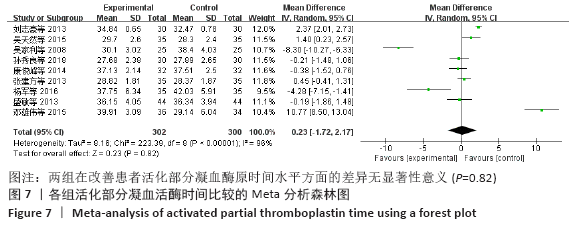
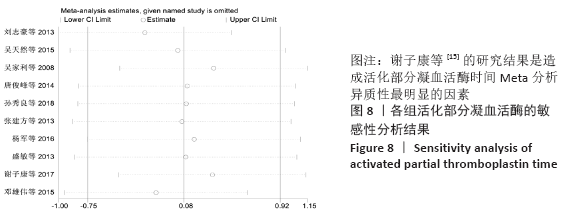
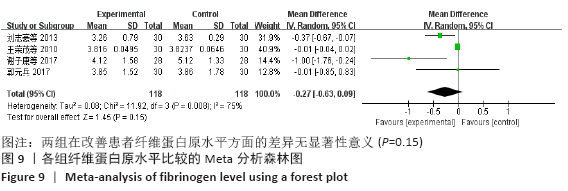
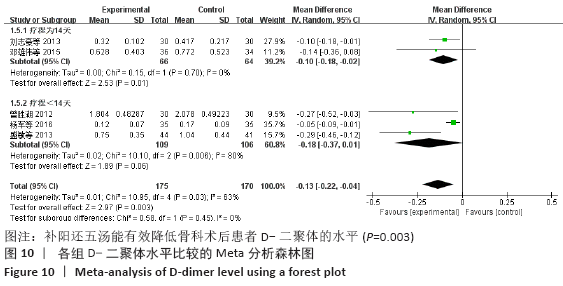
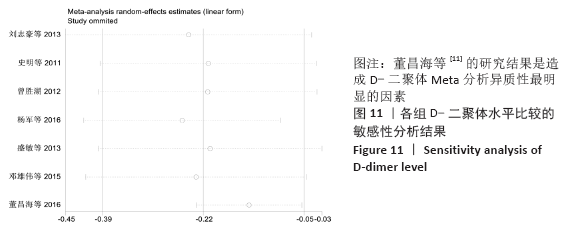
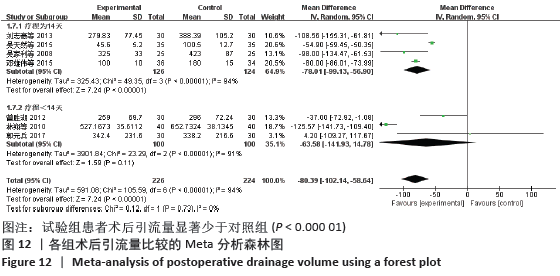
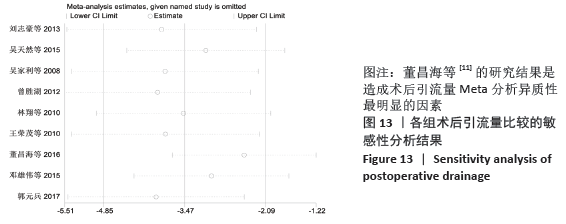
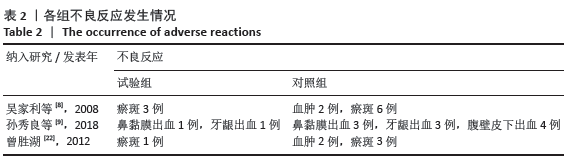
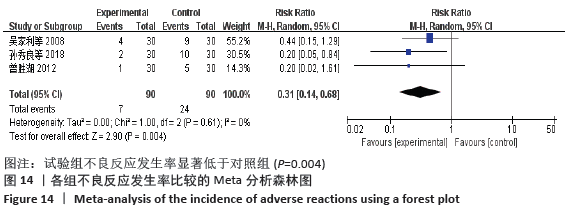
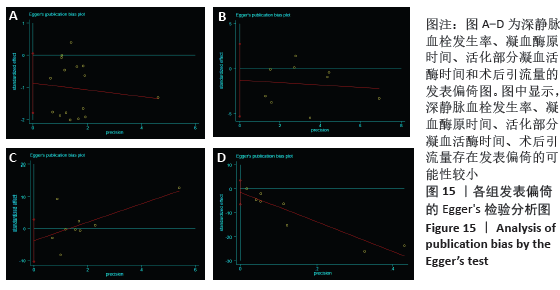
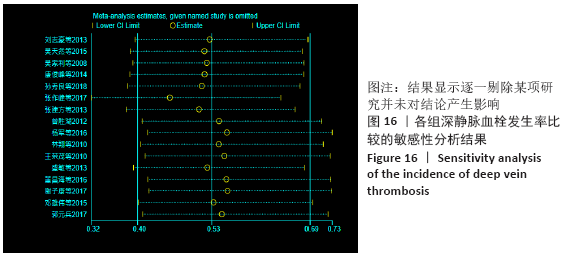
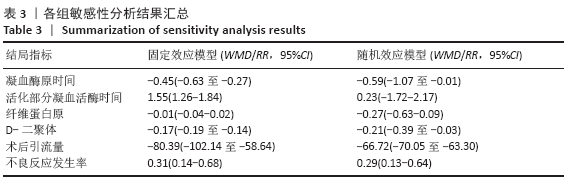
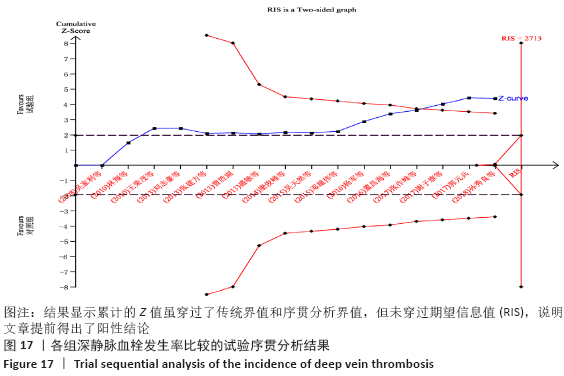
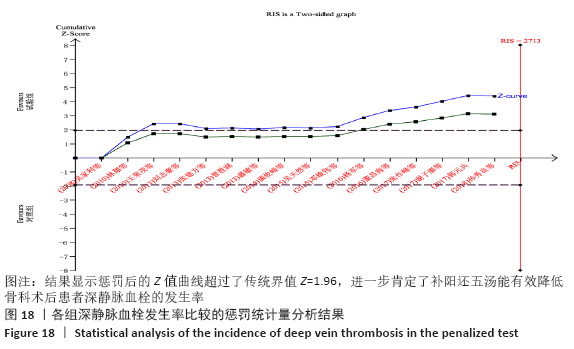
结果:①所纳入文献Jadad评分均在4分及以下,文献总体质量不高;②共纳入文献16篇,涉及1 075例患者,其中试验组540例,对照组535例;③Meta分析结果显示:试验组深静脉血栓发生率(RR=0.54,95%CI:0.41-0.71,P < 0.000 1)、D-二聚体(WMD=-0.13,95%CI:-0.22至-0.04,P=0.003)和术后引流量(WMD=-80.39,95%CI:-102.14至-58.64,P < 0.000 01)均显著低于对照组,延长凝血酶原时间不及对照组(WMD=-0.59,95%CI:-1.07至-0.01,P=0.02),活化部分凝血活酶时间(WMD=0.23,95%CI:-1.72-2.17,P=0.82)及纤维蛋白原(WMD= -0.27,95%CI:-0.63-0.09,P=0.15)指标的改善水平两组无显著性差异,不良反应发生率显著低于对照组(RR=0.31,95%CI:0.14-0.68,P=0.004);④试验序贯分析(TSA)显示,深静脉血栓发生率累积纳入的研究穿过了传统界值和序贯分析界值,进一步肯定了其临床疗效。
结论:补阳还五汤加减能有效降低骨科术后患者深静脉血栓的发生率,且具有一定的安全性,但仍需纳入更多高质量的随机对照试验进一步验证。
中图分类号: