[1] NICHOLAS SB. Use of urinary proteomics in diagnosis and monitoring of diabetic kidney disease. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.2020; 8(4):261-262.
[2] GAO Y. Urine-an untapped goldmine for biomarker discovery?. Sci China Life Sci. 2013;56(12):1145-1146.
[3] JING J, GAO Y. Urine biomarkers in the early stages of diseases: current status and perspective. Discov Med. 2018;25(136):57-65.
[4] WU J, GAO Y. Physiological conditions can be reflected in human urine proteome and metabolome. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015;12(6):623-636.
[5] QIN W, DU Z, GAO Y. Collection and preservation of urinary proteins, using a fluff pulp diaper. Sci China Life Sci. 2018;61(6):671-674.
[6] JIA L, LIU X, LIU L, et al. Urimem, a membrane that can store urinary proteins simply and economically, makes the large-scale storage of clinical samples possible. Sci China Life Sci. 2014;57(3): 336-339.
[7] DASKALAKI E, BLACKBURN G, KALNA G, et al. A study of the effects of exercise on the urinary metabolome using normalisation to individual metabolic output. Metabolites. 2015;5(1):119-139.
[8] LIU C, ZHENG T, DUAN R, et al. On the Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1232:409-414.
[9] LIU C, LIU G, HU S, et al. Quantitative Biology of Exercise-Induced Signal Transduction Pathways. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;977:419-424.
[10] LIU C, TANG XM, DUAN R, et al. The Mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger is Necessary but Not Sufficient for Ca2+ Homeostasis and Viability. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1072:281-285.
[11] SUN SS, HU CL, PAN JH, et al. Trait Mindfulness Is Associated With the Self-Similarity of Heart Rate Variability. Front Psychol. 2019;10:314.
[12] WASINGER VC, SMITH HI, WILLIAMS KL, et al. Progress with Gene-product Mapping of the Mollicutes:Mycoplasma Genitalium. Electrophoresis. 1995;16(7):1090-1094.
[13] REUSZ GS. Urinary proteomics: fancy gadgetry or a clinically useful diagnostic instrument? The end-user’s perspective. Transpl Int. 2019;32(1):25-27.
[14] MARSHALL T, WILLIAMS K. Two dimensional electrophoresis of human urinary proteins following concentration by dye precipitation. Electrophoresis. 1996;17(7):1265-1272.
[15] JONATHAN B, PETER T. Urine proteomics: the present and future of measuring urinary protein components in disease. CMAJ. 2007;177(4): 361-368.
[16] MOHAN SV, NAYAKANTI DS, SATHE G, et al. Targeted Proteomics as a Tool for Quantifying Urine-Based Biomarkers. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2051:277-295.
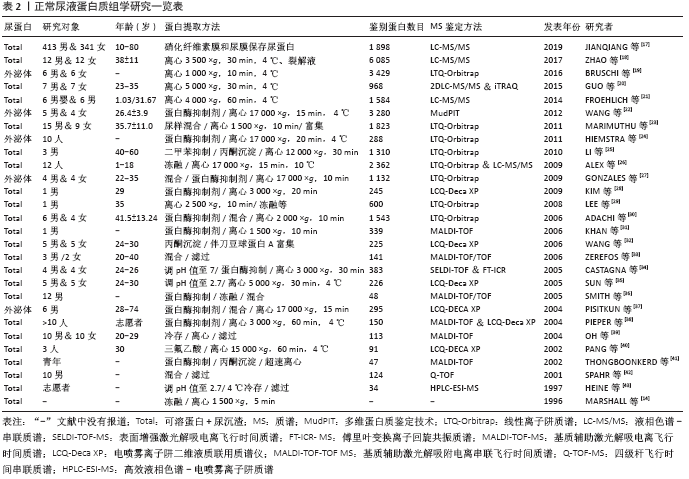
[17] JIANQIANG WU, WEIWEI QIN, LI PAN, et al. Regional Differences of the Urinary Proteomes in Healthy Chinese Individuals. Chin Med Sci J. 2019;34(3):157-167.
[18] ZHAO M, LI M, YANG Y, et al. A comprehensive analysis and annotation of human normal urinary proteome. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3024.
[19] BRUSCHI M, SANTUCCI L, RAVERA S, et al. Human urinary exosome proteome unveils its aerobic respiratory ability. J Proteomics. 2016; 136:25-34.
[20] GUO Z, ZHANG Y, ZOU L, et al. A Proteomic Analysis of Individual and Gender Variations in Normal Human Urine and Cerebrospinal Fluid Using iTRAQ Quantification. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0133270.
[21] FROEHLICH J W, VAEZZADEH A R, KIRCHNER M, et al. An in-depth comparison of the male pediatric and adult urinary proteomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1844(5):1044-1050.
[22] WANG Z, HILL S, LUTHER JM, et al. Proteomic analysis of urine exosomes by multidimensional protein identification technology (MudPIT). Proteomics. 2012;12(2):329-338.
[23] MARIMUTHU A, O’MEALLY RN, CHAERKADY R, et al. A Comprehensive Map of the Human Urinary Proteome. J Proteome Res. 2011;10(6): 2734-2743.
[24] HIEMSTRA TF, CHARLES PD, HESTER SS, et al. Uromodulin exclusion list improves urinary exosomal protein identification. J Biomol Tech. 2011; 22(4):136-145.
[25] LI QR, FAN KX, LI RX, et al. A comprehensive and non-prefractionation on the protein level approach for the human urinary proteome: touching phosphorylation in urine. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2010;24(6):823-832.
[26] ALEX K, FLAVIO M, KEVIN D, et al. Urine proteomics for profiling of human disease using high accuracy mass spectrometry. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2009;3(9):1052-1061.
[27] GONZALES P A, PISITKUN T, HOFFERT JD, et al. Large-scale proteomics and phosphoproteomics of urinary exosomes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(2):363-379.
[28] KIM KH, MOON MH. High speed two-dimensional protein separation without gel by isoelectric focusing-asymmetrical flow field flow fractionation: application to urinary proteome. J Proteome Res. 2009;8(9):4272-4278.
[29] LEE RS, MONIGATTI F, BRISCOE AC, et al. Optimizing sample handling for urinary proteomics. J Proteome Res. 2008;7(9):4022-4030.
[30] ADACHI J, KUMAR C, ZHANG Y, et al. The human urinary proteome contains more than 1500 proteins, including a large proportion of membrane proteins. Genome Biol. 2006;7(9):R80.
[31] KHAN A, PACKER NH. Simple urinary sample preparation forproteomic analysis. J Proteome Res. 2006;5(10):2824-2838.
[32] WANG LJ, LI FX, SUN W, et al. Concanavalin A-captured Glycoproteins in Healthy Human Urine. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5(3):560-562.
[33] ZEREFOS PG, VOUGAS K, DIMITRAKI P, et al. Characterization of the human urine proteome by preparative electrophoresis in combination with 2-DE. Proteomics. 2006;6(15):4346-4355.
[34] CASTAGNA A, CECCONI D, SENNESL I, et al. Exploring the hidden human urinary proteome via ligand library beads. J Proteome Res. 2005;4(6): 1917-1930.
[35] SUN W, LI F, WU S, et al. Human urine proteome analysis by three separation approaches. Proteomics. 2005;5(18):4994-5001.
[36] SMITH G, BARRATT D, ROWLINSON R, et al. Development of a high-throughput method for preparing human urine for two-dimensional electrophoresis. Proteomics. 2005;5(9):2315-2318.
[37] PISITKUN T, SHEN RF, KNEPPER MA. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004; 101(36):13368-13373.
[38] PIEPER R, GATLIN CL, MCGRATH AM, et al. Characterization of the human urinary proteome: a method for high-resolution display of urinary proteins on two-dimensional electrophoresis gels with a yield of nearly 1400 distinct protein spots. Proteomics. 2004;4(4): 1159-1174.
[39] OH J, PYO JH, JO EH, et al. Establishment of a nearstandard two-dimensional human urine proteomic map. Proteomics. 2004;4(11): 3485-3497.
[40] PANG JX, GINANNI N, DONGRE AR, et al. Biomarker discovery in urine by proteomics. J Proteome Res. 2002;1(2):161-169.
[41] THONGBONKERD V, MCLEISH KR, ARTHUR JM, et al. Proteomic analysis of normal human urinary proteins isolated by acetone precipitation or ultracentrifugation. Kidney Int. 2002;62(4):1461-1469.
[42] SPAHR CS, DAVIS MT, MCGINLEY MD, et al. Towards defining the urinary proteome using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.I.Profiling an unfractionated tryptic digest. Proteomics. 2001;1(1): 93-107.
[43] HEINE G, RAIDA M, FOLRSSMANN WG. Mapping of peplide and protein fragments in human urine using liquid chromatography 2-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 1997;776(1):117-124.
[44] POORMANS JR, ENGELS MF, SELLIER M, et al. Urine protein excretion and swimming events. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1991;23(7):831-835.
[45] POORTMANS J R, LABILLOY D. The influence of work intensity on postexercise proteinuria. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1988;57: 260-263.
[46] 冯美云, 冯炜权, 王民享. 足球训练和比赛时尿蛋白总量和β2-微球蛋白的变化[J].体育科学, 1988,8(2):52-55.
[47] 冯炜权, 冯美云, 张爱芳, 等. 应用尿蛋白评定运动员身体机能状态[J]. 北京体育学院学报,1992,15(1):1-12.
[48] YASUDA N, RUBY BC. Assessment of urinary protein composition in response to consecutive days of wildland firefighting. Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2019;25(1):27-34.
[49] LI X, GAO Y. Potential urinary aging markers of 20-month-old rats. PeerJ. 2016;4:e2058.
[50] GAUDREAU P, MORAIS JA, SHATENSTEIN B, et al. Nutrition as a determinant of successful aging: description of the Quebec longitudinal study Nuage and results from cross-sectional pilot studies. Rejuvenation Res. 2007;10(3):377-386.
[51] VALEEVA OA, PASTUSHKOV LK, PAKHARUKOVA NA, et al. Variability of urine proteome of healthy persons during 105-daily isolation. Fiziol cheloveka. 2011;37(3):98-102.
[52] LARINA IM, KOLCHANOV NA, DOBROKHOTOV IV, et al. Reconstruction of associative protein networks connected with processes of sodium exchange’ regulation and sodium deposition in healthy volunteers by urine proteome analysis. Fiziol Cheloveka. 2012;38(3):107-115.
[53] PARKER TJ, SAMPSON DL, BROSZCZAK D, et al. A fragment of the LG3 peptide of endorepellin is present in the urine of physically active mining workers: a potential marker of physical activity. PloS One. 2012;7(3):e33714.
[54] FRAGKAKI AG, PETROPOULOU G, ATHANASIADOU I, et al. Determination of anabolic androgenic steroids as imidazole carbamate derivatives in human urine using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci. 2020;43(11):2154-2161.
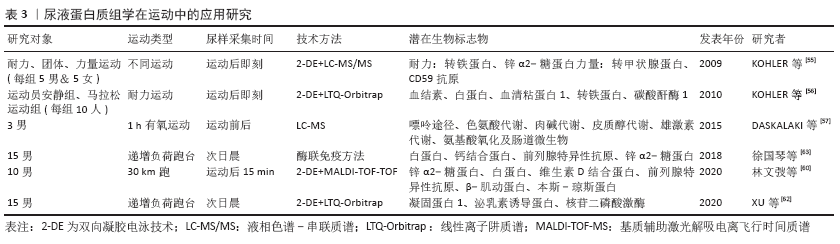
[55] KOHLER M, FRANZ S, REGENITER A, et al. Comparison of the urinary protein patterns of athletes by 2D-gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry-a pilot study. Drug Test Anal. 2009;1(8):382-386.
[56] KOHLER M, WALPURGIS K, THOMAS A, et al. Effects of endurance exercise on the urinary proteome analyzed by 2-D PAGE and Orbitrap MS. Proteomics Clin. 2010;4:568-576.
[57] DASKALAKI E, BLACKBURN G, KALNA G, et al. A study of the effects of exercise on the urinary metabolome using normalisation to individual metabolic output. Metabolites. 2015;5(1):119-139.
[58] 林文弢, 蔺海旗, 翁锡全. 蛋白质组学及其技术在运动人体科学中的研究[J]. 西安体育学院学报,2012,29(1):78-83.
[59] 林文弢, 徐国琴, 翁锡全. 尿液蛋白质组学研究现状及其在体育科学中的应用[J]. 广州体育学院学报,2010,30(6):72-76.
[60] 林文弢,蔺海旗,杨玲,等.男子30 km跑后尿液蛋白质组差异性表达的研究[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2020,35(1):7-12.
[61] 蔺海旗,林文弢,翁锡全,等.男子30km跑对肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统的影响[J]. 广州体育学院学报,2015,35(2):94-97.
[62] XU G, LIN W, MCAINCH AJ, et al. Identification of Urinary Biomarkers for Exercise-Induced Immunosuppression by iTRAQ Proteomics. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:3030793.
[63] 徐国琴,翁锡全,孟艳,等.运动性免疫机能低下发生过程中尿蛋白质组分变化特点研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(11): 921-926.
[64] REICHEL T, BOßLAU TK, PALMOWSKI J, et al. Reliability and suitability of physiological exercise response and recovery markers . Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):11924.
[65] LEE EC, FRAGALA MS, KAVOURAS SA, et al. Biomarkers in Sports and Exercise: Tracking Health, Performance, and Recovery in Athletes. J Strength Cond Res. 2017;31(10):2920-2937.
[66] 井健, 高友鹤. 尿液作为新型生物标志物来源的探索[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2016,43(11):1019-1028.
[67] Sampson DL, Broadbent JA, Parker AW, et al. Urinary biomarkers of physical activity: candidates and clinical utility. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014;11(1):91-106.
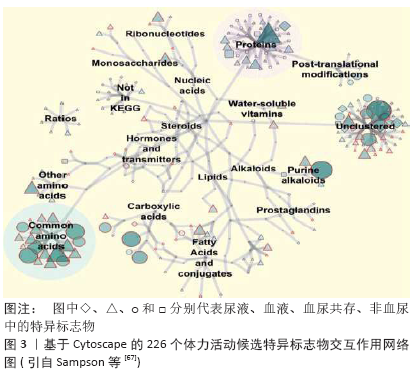
[68] 李江华, 刘承宜, 徐晓阳, 等. 2006年多哈亚运会短距离游泳男运动员代谢组学研究[J].体育科学,2008,28(2):42-46.
[69] ATKINSON TS, KAHN MJ. Blood doping: Then and now. A narrative review of the history, science and efficacy of blood doping in elite sport. Blood Rev. 2020;39:100632.
[70] WONG JKY, KWOK WH, CHAN GHM, et al. Doping control study of AICAR in post-race urine and plasma samples from horses. Drug Test Anal. 2017;9(9):1363-1371.
[71] 刘永涛, 赵敏迪, 潘宣圳, 等. 健康人的尿液中为什么会有蛋白质?[J].中国科学:生命科学,2020,50(3):338-348.
[72] PECHLIVANIS A, PAPAIOANNOU KG, TSALIS G, et al. Monitoring the Response of the Human Urinary Metabolome to Brief Maximal Exercise by a Combination of RP-UPLC-MS and (1)H NMR Spectroscopy. J Proteome Res. 2015;14(11):4610-4622.
|