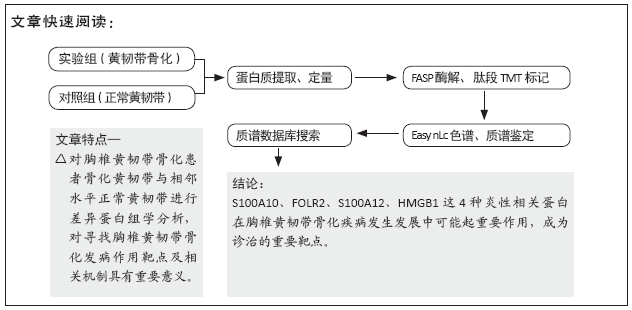
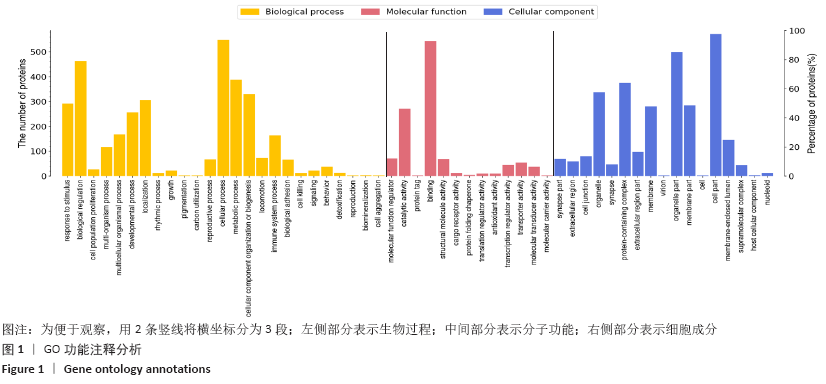
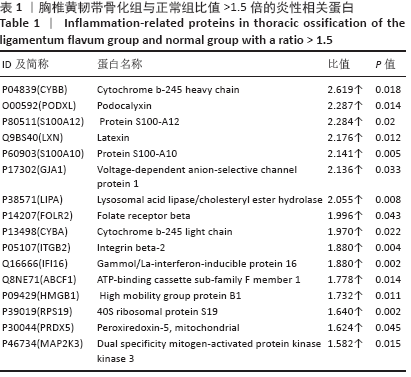
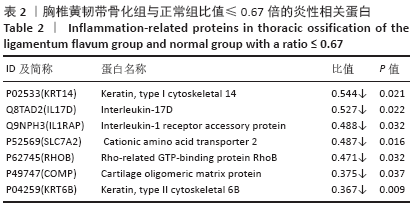
[1] Hirabayashi S. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2017;1(4):158-163.
[2] Wang B, Chen Z, Meng X, et al. iTRAQ quantitative proteomic study in patients with thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;487(4):834-839.
[3] Feng FB, Sun CG, Chen ZQ. Progress on clinical characteristics and identification of location of thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Orthop Surg. 2015;7(2):87-96.
[4] Fan D, Chen Z, Chen Y, et al. Mechanistic roles of leptin in osteogenic stimulation in thoracic ligament flavum cells. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282(41):29958-29966.
[5] Mobbs RJ, Dvorak M. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum: diet and genetics. J Clin Neurosci. 2007;14(7):703-705.
[6] Wang W, Kong L, Zhao H, et al. Thoracic ossification of ligamentum flavum caused by skeletal fluorosis. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(8):1119-1128.
[7] Uchida K, Yayama T, Cai HX, et al. Ossification process involving the human thoracic ligamentum flavum: role of transcription factors. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(5):R144.
[8] Park JO, Lee BH, Kang YM, et al. Inflammatory cytokines induce fibrosis and ossification of human ligamentum flavum cells. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(1):E6-12.
[9] Hanash SM, Bobek MP, Rickman DS, et al. Integrating cancer genomics and proteomics in the post-genome era. Proteomics. 2002; 2(1):69-75.
[10] Oh YM, Lee WJ, Kim MG, et al. Comparative proteomic tissue analysis in patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. World Neurosurg. 2014;82(1-2):e353-359.
[11] 张志强, 李春雯, 潘定权, 等. 蛋白组学在骨质疏松中的应用[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2014,32(6):1316-1319.
[12] 李大河. 强直性脊柱炎韧带组织比较蛋白质组学研究及膜联蛋白A2功能验证[D].上海:第二军医大学,2016.
[13] Kamita M, Mori T, Sakai Y, et al. Proteomic analysis of ligamentum flavum from patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Proteomics. 2015; 15(9):1622-1630.
[14] 王翀,田征,宋兴华,等.应用iTRAQ技术对尤文肉瘤的蛋白组学研究[J]. 新疆医学,2017,47(4):347-349+362.
[15] 冯瑞宾,罗世兴,赵劲民,等.蛋白组学在骨关节炎中的研究进展[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2018,12(6):830-834.
[16] 姜宇. 胸椎黄韧带骨化的血清比较蛋白质组学研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2012.
[17] Rescher U, Gerke V. S100A10/p11: family, friends and functions. Pflugers Arch. 2008;455(4):575-582.
[18] Bharadwaj A, Bydoun M, Holloway R, et al. Annexin A2 heterotetramer: structure and function. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(3): 6259-6305.
[19] Ker D, Wang D, Sharma R, et al. Identifying deer antler uhrf1 proliferation and s100a10 mineralization genes using comparative RNA-seq. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):292.
[20] Li H, Li J, Jiang J, et al. An osteogenesis/angiogenesis-stimulation artificial ligament for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Acta Biomater. 2017;54:399-410.
[21] Cmoch A, Strzelecka-Kiliszek A, Palczewska M, et al. Matrix vesicles isolated from mineralization-competent Saos-2 cells are selectively enriched with annexins and S100 proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;412(4):683-687.
[22] Ke CY, Mathias CJ, Green MA. The folate receptor as a molecular target for tumor-selective radionuclide delivery. Nucl Med Biol. 2003; 30(8):811-817.
[23] Salazar MD, Ratnam M. The folate receptor: what does it promise in tissue-targeted therapeutics. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26(1): 141-152.
[24] Low PS, Antony AC. Folate receptor-targeted drugs for cancer and inflammatory diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56(8):1055-1058.
[25] Nogueira E, Gomes AC, Preto A, et al. Folate-targeted nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(4):1113-1126.
[26] Tsuneyoshi Y, Tanaka M, Nagai T, et al. Functional folate receptor beta-expressing macrophages in osteoarthritis synovium and their M1/M2 expression profiles. Scand J Rheumatol. 2012;41(2):132-140.
[27] Winkel LC, Groen HC, van Thiel BS, et al. Folate receptor–targeted single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography to detect activated macrophages in atherosclerosis: can it distinguish vulnerable from stable atherosclerotic plaques? Mol Imaging. 2014;13. doi: 10.2310/7290.2013.00061.
[28] Müller A, Beck K, Rancic Z, et al. Imaging atherosclerotic plaque inflammation via folate receptor targeting using a novel 18F-folate radiotracer. Mol Imaging. 2014;13:1-11.
[29] Moroz OV, Burkitt W, Wittkowski H, et al. Both Ca2+ and Zn2+ are essential for S100A12 protein oligomerization and function. BMC Biochem. 2009;10:11.
[30] Bagheri V, Hassanshahi G, Zeinali M, et al. Elevated levels of S100A12 in the seminal plasma of infertile men with varicocele. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016;48(3):343-347.
[31] Yan WX, Armishaw C, Goyette J, et al. Mast cell and monocyte recruitment by S100A12 and its hinge domain. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283(19):13035-13043.
[32] Nazari A, Khorramdelazad H, Hassanshahi G, et al. S100A12 in renal and cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci. 2017;191:253-258.
[33] Hofmann Bowman MA, Gawdzik J, Bukhari U, et al. S100A12 in vascular smooth muscle accelerates vascular calcification in apolipoprotein E-null mice by activating an osteogenic gene regulatory program. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31(2):337-344.
[34] Choi BH, Ro H, Jung ES, et al. Circulating S100A12 Levels Are Associated with Progression of Abdominal Aortic Calcification in Hemodialysis Patients. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0150145.
[35] Park JS, Arcaroli J, Yum HK, et al. Activation of gene expression in human neutrophils by high mobility group box 1 protein. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;284(4):C870-879.
[36] Lin F, Zhang W, Xue D, et al. Signaling pathways involved in the effects of HMGB1 on mesenchymal stem cell migration and osteoblastic differentiation. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(3):789-797.
[37] Chen MQ, Luan JJ. HMGB1 promotes bone fracture healing through activation of ERK signaling pathway in a rat tibial fracture model. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019;35(9):550-558. |