| [1]Sadeqi M,Klouche S,Bohu Y,et al.Progression of the Psychological ACL RSI Score and Return to Sport After Anterior CruciateLigament Reconstruction: A Prospective 2-Year Follow-up Study From the French ProspectiveAnterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Cohort Study (FAST). Orthop J Sports Med.2018;6(12):1-6.[2]宋斌,李卫平,陈仲,等.前交叉韧带重建术后早期感染的治疗[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2014, 33(4):292-296.[3]Waterman BR,Arroyo W,Cotter EJ,et al.Septic Arthritis After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Clinical and Functional Outcomes Based on Graft Retention or Removal. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(3):2325967118758626. [4]Saper M,Stephenson K,Heisey M.Arthroscopic irrigation and debridement in the treatment of septic arthritis after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Arthroscopy. 2014;30: 747-754.[5]Calvo R,Figueroa D,Anastasiadis Z,et al.Septic arthritis in ACL reconstruction surgery with hamstring autografts.Eleven years of experience.Knee.2014;21:717-720.[6]Cadet ER, Makhni EC, Mehran N,et al.Management of septic arthritis following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A review of current practices and recommendations.J Am AcadOrthop Surg.2013;21: 647-656.[7]杨松杰,张清旭,陈绪彪,等.关节镜下膝交叉韧带重建中自体与异体肌腱移植物的疗效比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(34): 5513-5518.[8]Dekker TJ,Godin JA,Dale KM,et al.Return to Sport After Pediatric Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction and Its Effect on Subsequent Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(11):897-904.[9]Gupta AK,Moorman CR.Nocardia nova infection afterprimary anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with tibialis anterior allograft.Am J Sports Med.2010;38(7):1483-1486.[10]Nakayama H,Yagi M,Yoshiya S,et al.Micro- organismcolonization and intraoperative contamination in patientsundergoing arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligamentreconstruction.Arthroscopy. 2012;28(5):667-671.[11]Tuman J,Diduch DR,Baumfeld JA,et al.Joint infection unique tohamstring tendon harvester used during anterior cruciate ligamentreconstruction surgery.Arthroscopy. 2008;24(5): 618-620.[12]Schollin-Borg M, Michaëlsson K, Rahme H. Presentation, outcome, and cause of septic arthritis after anterior cruciateligament reconstruction:a case control study. Arthroscopy.2003;19(9):941-947.[13]Katz LM,Battaglia TC,Patino P,et al.A retrospectivecomparison of the incidence of bacterial infection followinganterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with autograft versus allograft.Arthroscopy. 2008;24(12): 1330-1335.[14]Maletis GB,Inacio MC,Reynolds S,et al.Incidence of postoperative anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction infections: graft choice makes a difference.Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(8):1780-1785.[15]Greenberg DD,Robertson M,Vallurupalli S,et al. Allograftcompared with autograft infection rates in primary anteriorcruciate ligament reconstruction.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92(14):2402-2408.[16]Barker JU,Drakos MC,Maak TG,et al. Effect of graft selection on the incidence of postoperative infection in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(2): 281-286.[17]Murphy MV, Du DT, Hua W,et al.Risk Factors for Surgical SiteInfections Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol.2016; 37(7): 827-833.[18]Yazdi H, Moradi A, Herbort M.The effect of gentamicin inirrigating solutions on articular infection prophylaxis duringarthroscopic ACL reconstruction.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2014;134(2):257-261.[19]Pérez-Prieto D, Torres-Claramunt R, Gelber PE, et al. Autograftsoaking in vancomycin reduces the risk of infection afteranterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg SportsTraumatolArthrosc.2016;24(9):2724-2728.[20]Vertullo CJ, Quick M, Jones A,et al.A surgical technique usingpresoaked vancomycin hamstring grafts to decrease the riskof infection after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(3):337-342.[21]刘玉杰.关注前交叉韧带重建术后影响疗效的因素与对策[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(11): 883-885.[22]Matava MJ,Evans TA,Wright RW,et al.Septic arthritis of theknee following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: results of a survey of sports medicine fellowship directors. Arthroscopy. 1998;14(7):717-725.[23]陈拿云,敖英芳.前交叉韧带重建术后关节感染的风险因素?病理?诊断和治疗研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志. 2019,38(1): 54-60.[24]赵阳, 张春礼.关节镜下自体肌腱移植重建前交叉韧带术后并发症的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015,4(5):422-426.[25]Riordan T,Doyle D,Tabaqchali S.Synovial fluid lactic acid measurement in the diagnosis and management of septic arthritis. J Clin Pathol. 1982;35(4):390-394.[26]徐长明,杨 乐,胡传亮,等.前交叉韧带重建后的感染[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(5):938-944.[27]Kim SJ ,Postigo R,Koo S,et al.Infection After Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Orthopedics. 2014;37(7):477.[28]Kim YM,Joo YB.Clinical Presentation of Staphylococcusepidermidis Septic Arthritis Following Anterior CruciateLigament Reconstruction.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2012;24(1):46-51.[29]Viola R, Marzano N, Vianello R. An unusual epidemic ofStaphylococcus-negative infections involving anterior cruciateligament reconstruction with salvage of the graft andfunction. Arthroscopy.2000. 16(2):173-177.[30]Wang C,Ao YF,Wang JQ,et al.Diagnosis and management of septic arthritis after arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction]. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi.2008;46(10): 745-748.[31]Gianotti SM,Marshall SW, Hume PA,et al.Incidence of anterior cruciate ligament injury and other knee ligament injuries: a national population-based study. J Sci Med Sport. 2009;12(6): 622-627.[32]Torres-Claramunt R, Pelfort X, Erquicia J, et al. Kneejointinfection after ACL reconstruction: prevalence, managementand functional outcomes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(12):2844-2849.[33]Odio CM,Ramirez T,Arias G,et al.Double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of dexamethasone therapy for hematogenous septic arthritis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22(10):883-889.[34]Philipp S, Martin S, Micha I , et al. Septic Arthritis After Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Evaluation of an Arthroscopic Graft-Retaining Treatment Protocol.Am J Sports Med.2015; 43(12):3005-3012.[35]Abdelaziz A,Radwan YA,Rizk A.Multiple arthroscopic debridement and graft retention in septic knee arthritis after ACL reconstruction: a prospective case-control study. Int Orthop. 2014;38(1):73-82.[36]Pogorzelski J,Themessl A,Achtnich A,et al.Septic Arthritis After Anterior CruciateLigamentReconstruction;How Important Is Graft Salvage?Am J Sports Med.2018;46(10): 2376-2383.[37]Wang C,Lee YH,Siebold R.Recommendations for the management of septic arthritis after ACL reconstruction.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(9):2136-2144. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
前交叉韧带重建术:前交叉韧带是控制膝关节前向稳定的一个重要结构,包括前内侧和后外侧束。前交叉韧带对膝关节稳定提供了强有力的支持,当其完全断裂,膝关节会出现明显不稳定的情况。目前最常用的治疗方案为采用关节镜取腘绳肌等肌腱来重建交叉韧带,恢复膝关节的稳定性。
红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate,ESR):是指红细胞在一定条件下沉降的速度,简称血沉。在健康人血沉数值波动于一个较狭窄范围内,在许多病理情况下血沉明显增快。红细胞沉降是多种因素互相作用的结果。将抗凝的血静置于垂直竖立的小玻璃管中,由于红细胞的比重较大,受重力作用而自然下沉,正常情况下下沉十分缓慢,常以红细胞在第1小时末下沉的距离来表示红细胞沉降的速度,称红细胞沉降率。
文题释义:
前交叉韧带重建术:前交叉韧带是控制膝关节前向稳定的一个重要结构,包括前内侧和后外侧束。前交叉韧带对膝关节稳定提供了强有力的支持,当其完全断裂,膝关节会出现明显不稳定的情况。目前最常用的治疗方案为采用关节镜取腘绳肌等肌腱来重建交叉韧带,恢复膝关节的稳定性。
红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate,ESR):是指红细胞在一定条件下沉降的速度,简称血沉。在健康人血沉数值波动于一个较狭窄范围内,在许多病理情况下血沉明显增快。红细胞沉降是多种因素互相作用的结果。将抗凝的血静置于垂直竖立的小玻璃管中,由于红细胞的比重较大,受重力作用而自然下沉,正常情况下下沉十分缓慢,常以红细胞在第1小时末下沉的距离来表示红细胞沉降的速度,称红细胞沉降率。.jpg) 文题释义:
前交叉韧带重建术:前交叉韧带是控制膝关节前向稳定的一个重要结构,包括前内侧和后外侧束。前交叉韧带对膝关节稳定提供了强有力的支持,当其完全断裂,膝关节会出现明显不稳定的情况。目前最常用的治疗方案为采用关节镜取腘绳肌等肌腱来重建交叉韧带,恢复膝关节的稳定性。
红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate,ESR):是指红细胞在一定条件下沉降的速度,简称血沉。在健康人血沉数值波动于一个较狭窄范围内,在许多病理情况下血沉明显增快。红细胞沉降是多种因素互相作用的结果。将抗凝的血静置于垂直竖立的小玻璃管中,由于红细胞的比重较大,受重力作用而自然下沉,正常情况下下沉十分缓慢,常以红细胞在第1小时末下沉的距离来表示红细胞沉降的速度,称红细胞沉降率。
文题释义:
前交叉韧带重建术:前交叉韧带是控制膝关节前向稳定的一个重要结构,包括前内侧和后外侧束。前交叉韧带对膝关节稳定提供了强有力的支持,当其完全断裂,膝关节会出现明显不稳定的情况。目前最常用的治疗方案为采用关节镜取腘绳肌等肌腱来重建交叉韧带,恢复膝关节的稳定性。
红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate,ESR):是指红细胞在一定条件下沉降的速度,简称血沉。在健康人血沉数值波动于一个较狭窄范围内,在许多病理情况下血沉明显增快。红细胞沉降是多种因素互相作用的结果。将抗凝的血静置于垂直竖立的小玻璃管中,由于红细胞的比重较大,受重力作用而自然下沉,正常情况下下沉十分缓慢,常以红细胞在第1小时末下沉的距离来表示红细胞沉降的速度,称红细胞沉降率。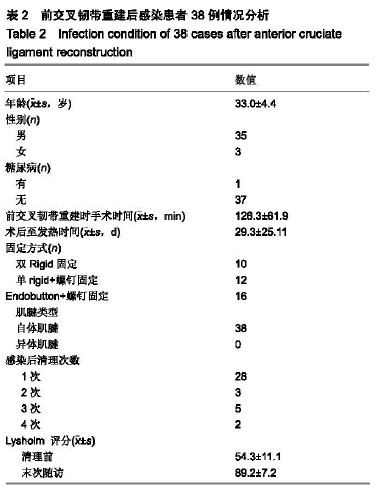
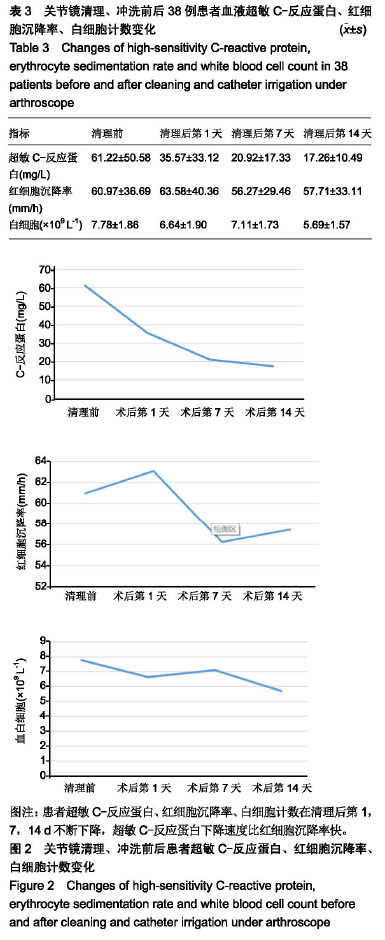
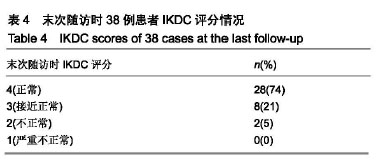
.jpg)
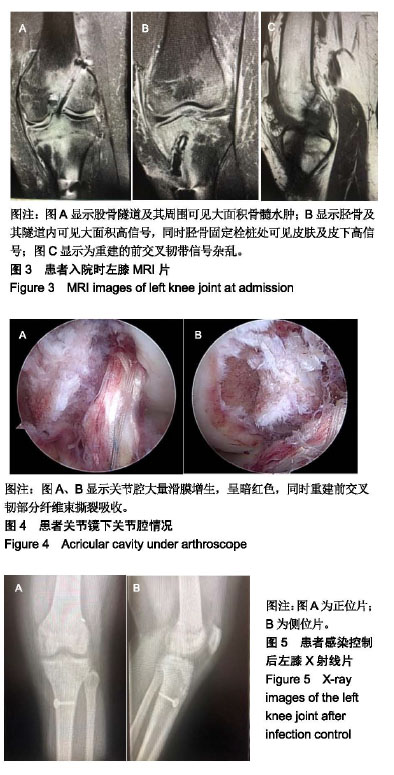
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
前交叉韧带重建术:前交叉韧带是控制膝关节前向稳定的一个重要结构,包括前内侧和后外侧束。前交叉韧带对膝关节稳定提供了强有力的支持,当其完全断裂,膝关节会出现明显不稳定的情况。目前最常用的治疗方案为采用关节镜取腘绳肌等肌腱来重建交叉韧带,恢复膝关节的稳定性。
红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate,ESR):是指红细胞在一定条件下沉降的速度,简称血沉。在健康人血沉数值波动于一个较狭窄范围内,在许多病理情况下血沉明显增快。红细胞沉降是多种因素互相作用的结果。将抗凝的血静置于垂直竖立的小玻璃管中,由于红细胞的比重较大,受重力作用而自然下沉,正常情况下下沉十分缓慢,常以红细胞在第1小时末下沉的距离来表示红细胞沉降的速度,称红细胞沉降率。
文题释义:
前交叉韧带重建术:前交叉韧带是控制膝关节前向稳定的一个重要结构,包括前内侧和后外侧束。前交叉韧带对膝关节稳定提供了强有力的支持,当其完全断裂,膝关节会出现明显不稳定的情况。目前最常用的治疗方案为采用关节镜取腘绳肌等肌腱来重建交叉韧带,恢复膝关节的稳定性。
红细胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate,ESR):是指红细胞在一定条件下沉降的速度,简称血沉。在健康人血沉数值波动于一个较狭窄范围内,在许多病理情况下血沉明显增快。红细胞沉降是多种因素互相作用的结果。将抗凝的血静置于垂直竖立的小玻璃管中,由于红细胞的比重较大,受重力作用而自然下沉,正常情况下下沉十分缓慢,常以红细胞在第1小时末下沉的距离来表示红细胞沉降的速度,称红细胞沉降率。