| [1] Clarke LE, Richardson SM, Hoyland JA. Harnessing the Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for IVD Regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;10(4):296-306. [2] 李雷.不同手术方式对腰椎间盘突出症患者术后生活质量影响[D].泰安:泰山医学院,2015.[3] Bae WC, Masuda K. Emerging technologies for molecular therapy for intervertebral disk degeneration. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011; 42(4):585-601, ix. [4] Daly C, Ghosh P, Jenkin G, et al. A Review of Animal Models of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Pathophysiology, Regeneration, and Translation to the Clinic. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016: 5952165. [5] Sakai D, Nishimura K, Tanaka M, et al. Migration of bone marrow-derived cells for endogenous repair in a new tail-looping disc degeneration model in the mouse: a pilot study. Spine J. 2015;15(6):1356-1365. [6] 高元朝,赵志斌,支满霞,等.脉络宁注射液与激素对脊神经根炎所致脊髓损伤保护作用的比较[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2014;20(21): 187-192.[7] 刘洋,王东风,黄娜.复方南星蠲瘀软膏对大鼠神经根炎和足趾肿胀的药理作用研究[J].中国药房,2011,22(11):977-979.[8] 王林林,李明,金菲.电针疗法对神经根型颈椎病模型大鼠神经根保护作用机理研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报, 2014,16(6):111-114.[9] 舒小琴.SD大鼠断层解剖学彩色图谱的构建[D].武汉:华中科技大学, 2011.[10] 唐朝辉,曹亮,丁岗,等.腰痹通胶囊对大鼠腰椎神经根压迫致腰椎间盘突出模型药效及炎性因子的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2015, 21(5):155-158.[11] Hoy D, March L, Brooks P, et al. The global burden of low back pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):968-974. [12] 陈柏书.针刺治疗腰椎间盘突出症的去自由基镇痛机理研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2014.[13] 王美琴,郭长青,张义,等.针刀疗法对腰椎间盘突出症大鼠背根神经节局部微循环影响的实验研究[J].针灸临床杂志, 2016,32(1):72-75.[14] 刘进显,黎尚荣.大鼠腰神经根受压模型建立的实验研究[J].现代医院, 2010,10(5):23-24.[15] Cuéllar JM, Borges PM, Cuéllar VG, et al. Cytokine expression in the epidural space: a model of noncompressive disc herniation- induced inflammation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(1):17-23. [16] Zhu X, Cao S, Zhu MD, et al. Contribution of chemokine CCL2/CCR2 signaling in the dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord to the maintenance of neuropathic pain in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation. J Pain. 2014;15(5):516-526. [17] Vassilaki M, Hurwitz EL. Insights in public health: perspectives on pain in the low back and neck: global burden, epidemiology, and management. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2014;73(4):122-126. [18] Yuan W, Che W, Jiang YQ, et al. Establishment of intervertebral disc degeneration model induced by ischemic sub-endplate in rat tail. Spine J. 2015;15(5):1050-1059. [19] Fujioka Y, Stahlberg A, Ochi M, et al. Expression of inflammation/ pain-related genes in the dorsal root ganglion following disc puncture in rats. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2016;24(1):106-112. [20] Numaguchi S, Esumi M, Sakamoto M, et al. Passive cigarette smoking changes the circadian rhythm of clock genes in rat intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(1):39-47. [21] 赵赫,俞兴,唐向盛,等.炎性因子IL-1β?TNF-α与椎间盘退变关系的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2017,30(9):866-871.[22] Chung JM, Kim HK, Chung K. Segmental spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathic pain. Methods Mol Med. 2004;99:35-45. [23] Zamora T, Palma J, Andia M, et al. Effect of Propionibacterium acnes (PA) injection on intervertebral disc degeneration in a rat model: Does it mimic modic changes? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017;103(5):795-799. [24] Tong W, Lu Z, Qin L, et al. Cell therapy for the degenerating intervertebral disc. Transl Res. 2017;181:49-58. [25] Song H, Luo Y, Wang W, et al. Effects of alendronate on lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration with bone loss in ovariectomized rats. Spine J. 2017;17(7):995-1003. [26] Luo Y, Zhang L, Wang WY, et al. Alendronate retards the progression of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in ovariectomized rats. Bone. 2013;55(2):439-448. [27] Jia H, Ma J, Lv J, et al. Oestrogen and parathyroid hormone alleviate lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in ovariectomized rats and enhance Wnt/β-catenin pathway activity. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27521. [28] 徐海栋,刘晓伟,史新瑞,等.大鼠尾椎椎间盘退变静态压力模型的构建[J].脊柱外科杂志,2017,15(6):348-350,356.[29] Nakayama E, Matsumoto T, Kazama T, et al. Transplantation of dedifferentiation fat cells promotes intervertebral disc regeneration in a rat intervertebral disc degeneration model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;493(2):1004-1009. [30] 苏清,赵瑞青,任伟云.腹膜透析中预防腹腔感染的护理对策[J].中原医刊,2003,30(21):57. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
神经根炎:多种原因所致的神经根的炎性或变性病变。病变可侵及颈、胸、腰、骶任一节段的脊神经根,临床上以颈胸神经根和腰骶神经最常受累,可引起肩背痛及腰腿痛。
化学性神经根炎:在某些化学性因素的作用下,引起纤维环破裂,部分髓核液漏至椎间盘外并沿着神经根扩散引起神经根的一种炎症状态,常发生在L4、L5部位,如使用1%,2%,4%等一定浓度的甲醛溶液浸泡滤纸块后置于神经根旁,为一种常见的造成化学性神经根炎的方法。
文题释义:
神经根炎:多种原因所致的神经根的炎性或变性病变。病变可侵及颈、胸、腰、骶任一节段的脊神经根,临床上以颈胸神经根和腰骶神经最常受累,可引起肩背痛及腰腿痛。
化学性神经根炎:在某些化学性因素的作用下,引起纤维环破裂,部分髓核液漏至椎间盘外并沿着神经根扩散引起神经根的一种炎症状态,常发生在L4、L5部位,如使用1%,2%,4%等一定浓度的甲醛溶液浸泡滤纸块后置于神经根旁,为一种常见的造成化学性神经根炎的方法。.jpg) 文题释义:
神经根炎:多种原因所致的神经根的炎性或变性病变。病变可侵及颈、胸、腰、骶任一节段的脊神经根,临床上以颈胸神经根和腰骶神经最常受累,可引起肩背痛及腰腿痛。
化学性神经根炎:在某些化学性因素的作用下,引起纤维环破裂,部分髓核液漏至椎间盘外并沿着神经根扩散引起神经根的一种炎症状态,常发生在L4、L5部位,如使用1%,2%,4%等一定浓度的甲醛溶液浸泡滤纸块后置于神经根旁,为一种常见的造成化学性神经根炎的方法。
文题释义:
神经根炎:多种原因所致的神经根的炎性或变性病变。病变可侵及颈、胸、腰、骶任一节段的脊神经根,临床上以颈胸神经根和腰骶神经最常受累,可引起肩背痛及腰腿痛。
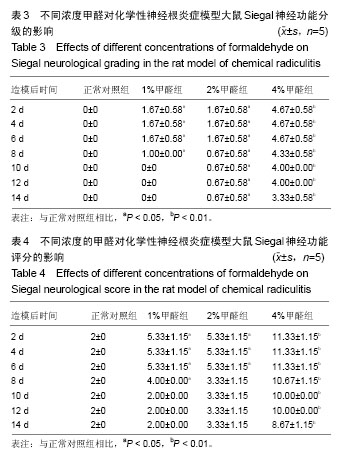
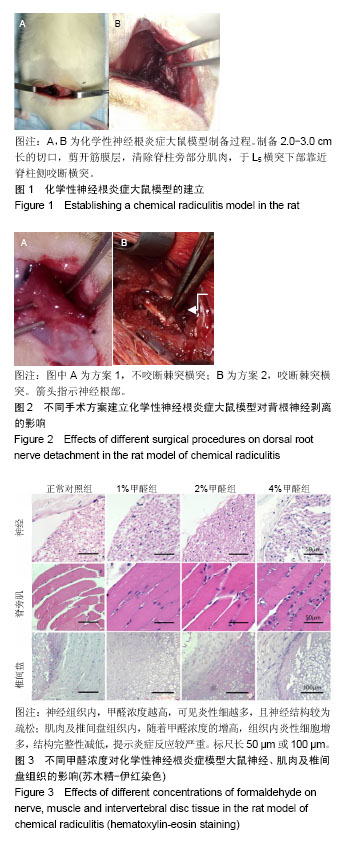
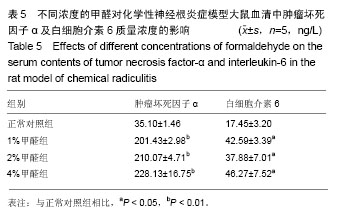
化学性神经根炎:在某些化学性因素的作用下,引起纤维环破裂,部分髓核液漏至椎间盘外并沿着神经根扩散引起神经根的一种炎症状态,常发生在L4、L5部位,如使用1%,2%,4%等一定浓度的甲醛溶液浸泡滤纸块后置于神经根旁,为一种常见的造成化学性神经根炎的方法。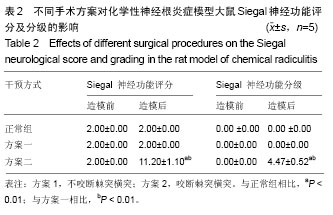
.jpg) 文题释义:
神经根炎:多种原因所致的神经根的炎性或变性病变。病变可侵及颈、胸、腰、骶任一节段的脊神经根,临床上以颈胸神经根和腰骶神经最常受累,可引起肩背痛及腰腿痛。
化学性神经根炎:在某些化学性因素的作用下,引起纤维环破裂,部分髓核液漏至椎间盘外并沿着神经根扩散引起神经根的一种炎症状态,常发生在L4、L5部位,如使用1%,2%,4%等一定浓度的甲醛溶液浸泡滤纸块后置于神经根旁,为一种常见的造成化学性神经根炎的方法。
文题释义:
神经根炎:多种原因所致的神经根的炎性或变性病变。病变可侵及颈、胸、腰、骶任一节段的脊神经根,临床上以颈胸神经根和腰骶神经最常受累,可引起肩背痛及腰腿痛。
化学性神经根炎:在某些化学性因素的作用下,引起纤维环破裂,部分髓核液漏至椎间盘外并沿着神经根扩散引起神经根的一种炎症状态,常发生在L4、L5部位,如使用1%,2%,4%等一定浓度的甲醛溶液浸泡滤纸块后置于神经根旁,为一种常见的造成化学性神经根炎的方法。