中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (37): 6607-6612.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.37.011
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
基因芯片分析鱼藤素对斑马鱼胚胎发育的影响
李文浩1, 2,刘瑞瑾2,吴新荣1, 2
- 1解放军广州军区广州总医院药剂科,广东省广州市 510010
2华南理工大学轻工与食品学院,广东省广州市 510641
Deguelin treatment delays embryonic development of zebrafish: A gene chip analysis
Li Wen-hao1,2, Liu Rui-jin2, Wu Xin-rong1, 2
- 1Department of Pharmacy, General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Command of PLA, Guangzhou 510010, Guangdong Province, China
2School of Light Industry and Food, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510641, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
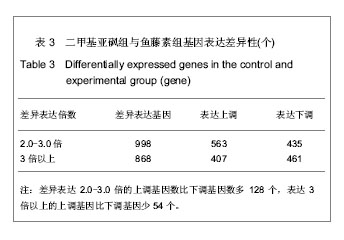
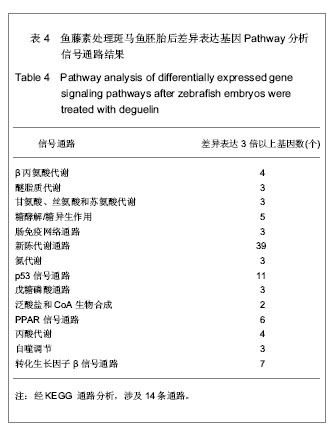
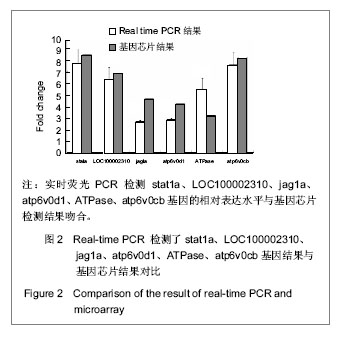
背景:鱼藤素具有延缓斑马鱼胚胎发育的作用,但其具体作用机制尚未明确。 目的:分析鱼藤素处理斑马鱼胚胎的基因与信号传导通路表达差异。 方法:斑马鱼胚胎来自于根据Zebrafish book中描述的方法养的殖斑马鱼。用0.6 μmol/L鱼藤素处理2-细胞期斑马鱼胚胎,以二甲基亚砜孵化液处理2-细胞期斑马鱼胚胎为对照。4 hpf 时期提取二甲基亚砜组及鱼藤素组总RNA,利用基因芯片技术检测鱼藤素处理斑马鱼胚胎后基因的差异表达,采用实时荧光定量PCR验证基因芯片结果,结合聚类分析及通路分析来探索鱼藤素的作用机制。 结果与结论:芯片结果显示,鱼藤素处理斑马鱼胚胎后差异表达上调3倍以上的基因407个,下调的461个。PCR 验证结果与芯片结果相符。经KEGG 通路分析,涉及14条通路。鱼藤素可能通过干扰细胞的代谢生长及影响其分化起作用。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)