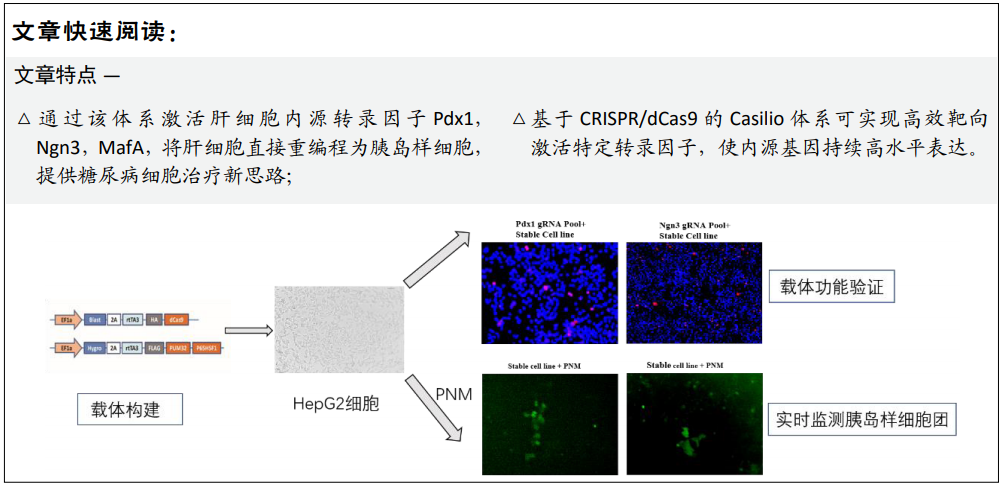
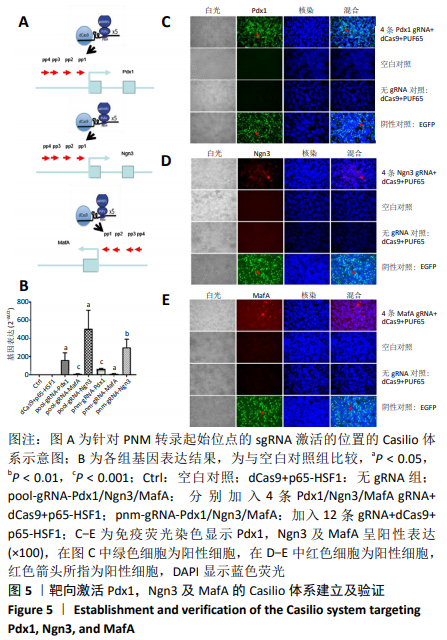
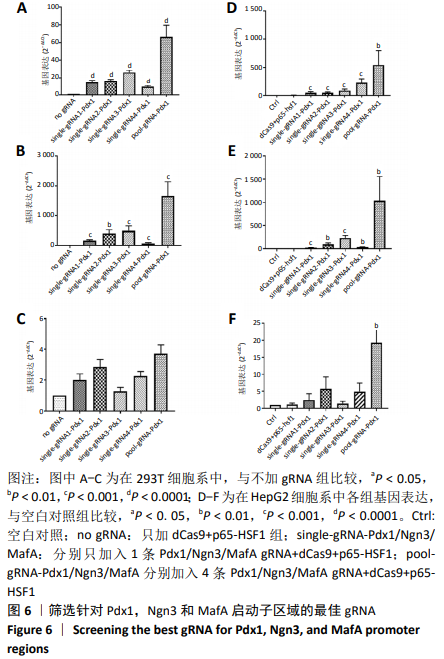
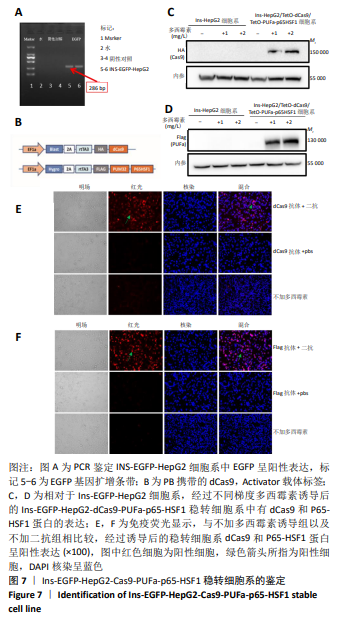
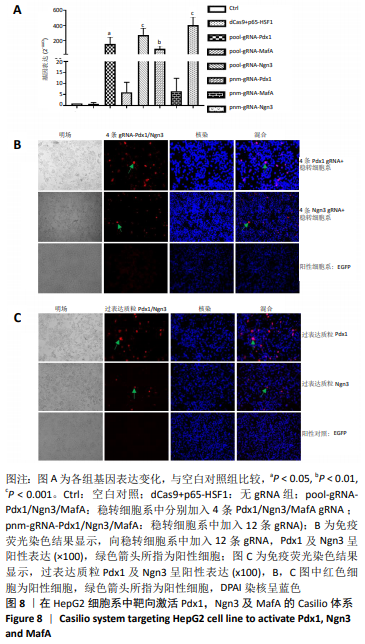
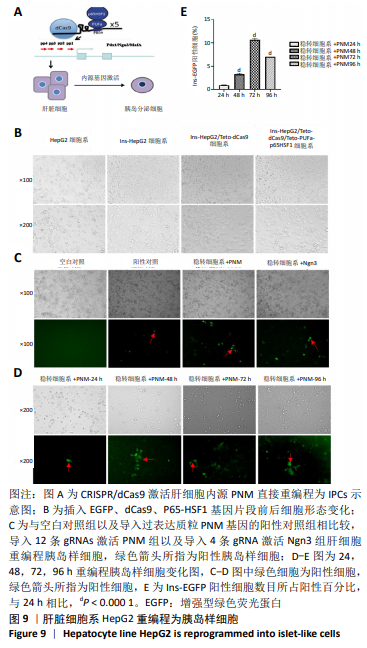
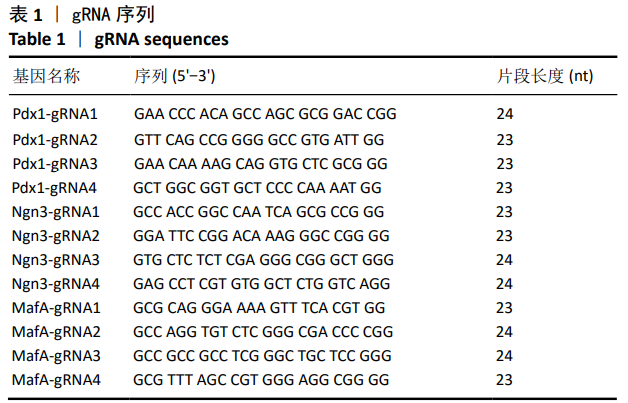
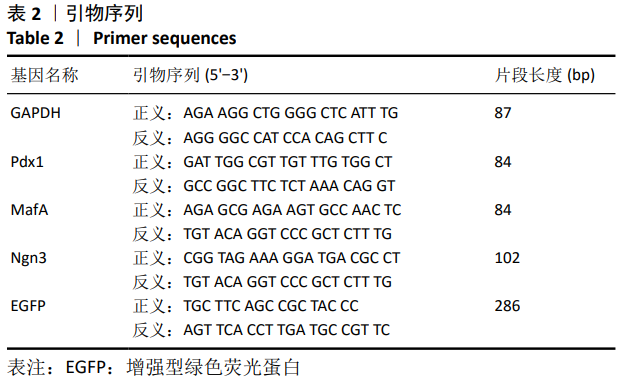
[1] BECK RW, BERGENSTAL RM, LAFFEL LM, et al. Advances in technology for management of type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 2019;394(10205): 1265-1273.
[2] BRUNI A, GALA-LOPEZ B, PEPPER AR, et al. Islet cell transplantation for the treatment of type 1 diabetes: recent advances and future challenges. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2014;7:211.
[3] ABREU J, ROEP B. Immune monitoring of islet and pancreas transplant recipients. Curr Diab Rep. 2013;13(5):704-712.
[4] KANAK MA, TAKITA M, KUNNATHODI F, et al. Inflammatory response in islet transplantation. Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:451035.
[5] SHAPIRO AJ, LAKEY JR, RYAN EA, et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(4):230-238.
[6] MANOHAR R, LAGASSE E. Transdetermination: a new trend in cellular reprogramming. Mol Ther. 2009;17(6):936-938.
[7] THOWFEEQU S, LI WC, SLACK JM, et al. Reprogramming of liver to pancreas. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;482:407-418.
[8] 任丽伟,杨晓菲,李富荣.细胞直接重编程—治疗糖尿病的新技术[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2014;30(12):2284-2288.
[9] AKINCI E, BANGA A, TUNGATT K, et al. Reprogramming of various cell types to a beta-like state by Pdx1, Ngn3 and MafA. PLoS One. 2013; 8(11):e82424.
[10] BANGA A, AKINCI E, GREDER LV, et al. In vivo reprogramming of Sox9+ cells in the liver to insulin-secreting ducts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(38):15336-15341.
[11] YECHOOR V, LIU V, ESPIRITU C, et al. Neurogenin3 is sufficient for transdetermination of hepatic progenitor cells into neo-islets in vivo but not transdifferentiation of hepatocytes. Dev Cell. 2009;16(3): 358-373.
[12] HICKEY RD, GALIVO F, SCHUG J, et al. Generation of isletlike cells from mouse gall bladder by direct ex vivo reprogramming. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11:503-515.
[13] HANNA J, SAHA K, PANDO B, et al. Direct cell reprogramming is a stochastic process amenable to acceleration. Nature. 2009;462(7273): 595-601.
[14] YOU L, TONG R, LI M, et al. Advancements and obstacles of CRISPR-Cas9 technology in translational research. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2019;13:359-370.
[15] RAPOSO VL. CRISPR-Cas9 and the Promise of a Better Future. Eur J Health Law. 2019;26(4):308-329.
[16] GLEESON A, SAWYER A. CRISPR/Cas9: the gold standard of genome editing? Biotechniques. 2018;64(6):239-243.
[17] LI D, ZHOU H, ZENG X. Battling CRISPR-Cas9 off-target genome editing. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2019;35(5):403-406.
[18] JEHUDA RB, SHEMER Y, BINAH O, et al. Genome editing in induced pluripotent stem cells using CRISPR/Cas9. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018; 14(3):323-336.
[19] CERMAK T, DOYLE EL, CHRISTIAN M, et al. Efficient design and assembly of custom TALEN and other TAL effector-based constructs for DNA targeting. Nucleic Acids Research. 2011;39(12):e82.
[20] HOCKEMEYER D, WANG H, KIANI S, et al. Genetic engineering of human pluripotent cells using TALE nucleases. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(8): 731-734.
[21] TAGHBALOUT A, DU M, JILLETTE N, et al. Enhanced CRISPR-based DNA demethylation by Casilio-ME-mediated RNA-guided coupling of methylcytosine oxidation and DNA repair pathways. Nat Commun Vol. 2019;10(1):1-12.
[22] CHENG AW, WANG H, YANG H, et al. Multiplexed activation of endogenous genes by CRISPR-on, an RNA-guided transcriptional activator system. Cell Res. 2013;23(10):1163-1171.
[23] SUN S, XIAO J, HUO J, et al. Targeting ectodysplasin promotor by CRISPR/dCas9-effector effectively induces the reprogramming of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into sweat gland-like cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):8.
[24] HUANG H, ZHONG L, ZHOU J, et al. Leydig-like cells derived from reprogrammed human foreskin fibroblasts by CRISPR/dCas9 increase the level of serum testosterone in castrated male rats. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(7):3971-3981.
[25] HUANG H, ZOU X, ZHONG L, et al. CRISPR/dCas9-mediated activation of multiple endogenous target genes directly converts human foreskin fibroblasts into Leydig-like cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(9):6072-6084.
[26] LIU P, CHEN M, LIU Y, et al. CRISPR-based chromatin remodeling of the endogenous Oct4 or Sox2 locus enables reprogramming to pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(2):252-261.
[27] ZHOU H, LIU J, ZHOU C, et al. In vivo simultaneous transcriptional activation of multiple genes in the brain using CRISPR–dCas9-activator transgenic mice. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(3):440-446.
[28] LIAO H-K, HATANAKA F, ARAOKA T, et al. In vivo target gene activation via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated trans-epigenetic modulation. Cell. 2017; 171(7):1495-1507.
[29] KAWAKAMI K, SHIMA A, KAWAKAMI N. Identification of a functional transposase of the Tol2 element, an Ac-like element from the Japanese medaka fish, and its transposition in the zebrafish germ lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(21):11403-11408.
[30] MITRA R, FAIN-THORNTON J, CRAIG NL. piggyBac can bypass DNA synthesis during cut and paste transposition. EMBO J. 2008;27(7):1097-1109.
[31] CHENG AW, JILLETTE N, LEE P, et al. Casilio: a versatile CRISPR-Cas9-Pumilio hybrid for gene regulation and genomic labeling. Cell Res. 2016;26(2):254.
[32] 王皓毅,李劲松,李伟.基于CRISPR-Cas9新型基因编辑技术研究[J].生命科学, 2016;28(8):867-870.
[33] YUSA K, ZHOU L, LI MA, et al. A hyperactive piggyBac transposase for mammalian applications. PNAS. 2011;108(4):1531-1536.
[34] PEREZ-PINERA P, KOCAK DD, VOCKLEY CM, et al. RNA-guided gene activation by CRISPR-Cas9–based transcription factors. Nat Methods. 2013;10(10):973.
[35] MAEDER ML, LINDER SJ, CASCIO VM, et al. CRISPR RNA–guided activation of endogenous human genes. Nat Methods. 2013;10(10): 977-979.
[36] ZHU S, RUSS HA, WANG X, et al. Human pancreatic beta-like cells converted from fibroblasts. Nat Commun. 2016;7(1):1-13.
[37] SCHERTZER MD, THULSON E, BRACEROS KC, et al. A piggyBac-based toolkit for inducible genome editing in mammalian cells. RNA. 2019;25(8):1047-1058.
[38] HAZELBAKER DZ, BECCARD A, ANGELINI G, et al. A multiplexed gRNA piggyBac transposon system facilitates efficient induction of CRISPRi and CRISPRa in human pluripotent stem cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1-10.
[39] WANG J, HUANG J, XU R. Seamless genome editing in Drosophila by combining CRISPR/Cas9 and piggyBac technologies. Yi Chuan. 2019; 41(5):422-429.
|