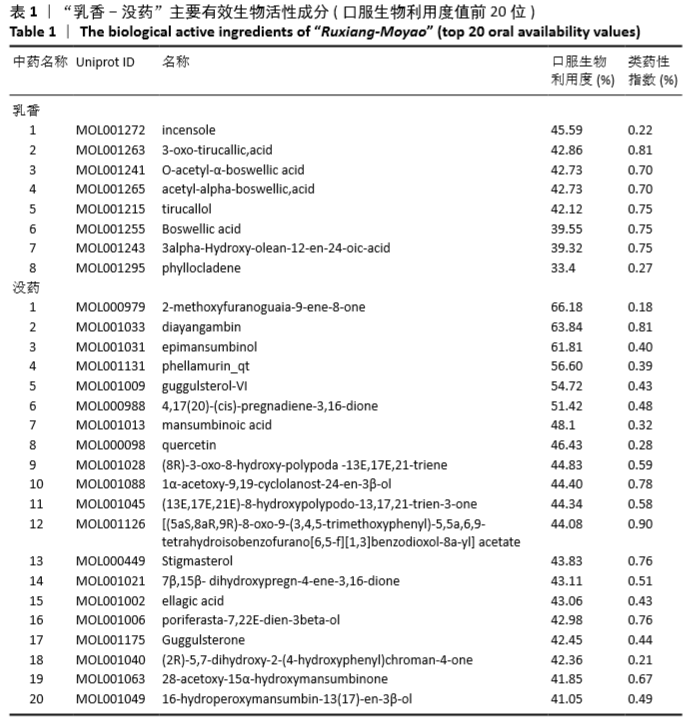
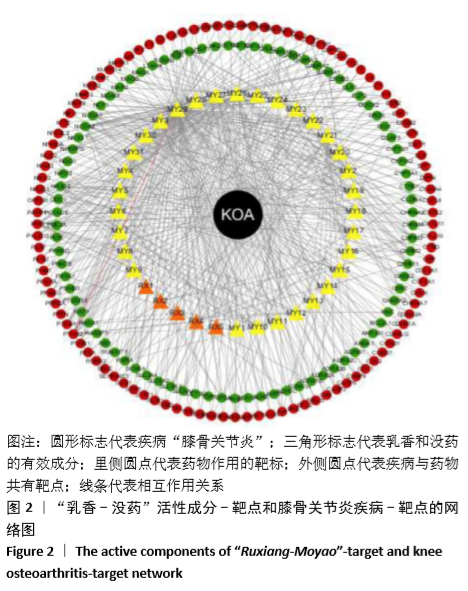
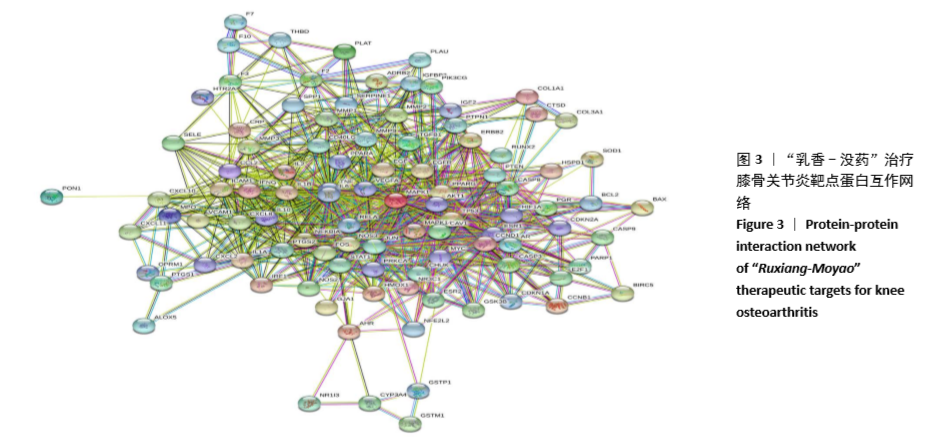
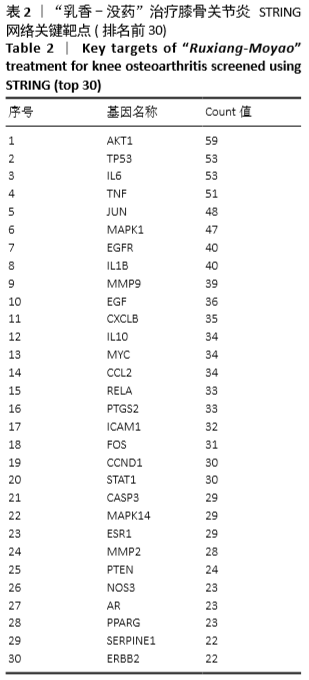
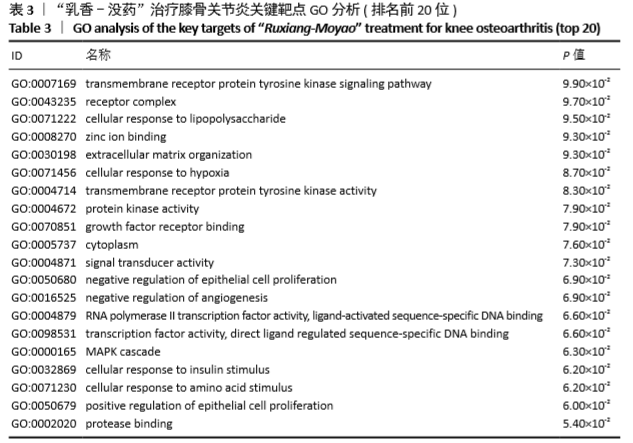
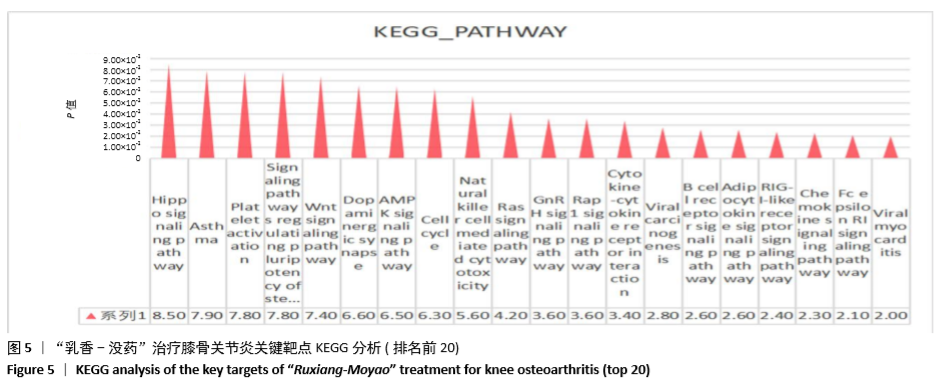
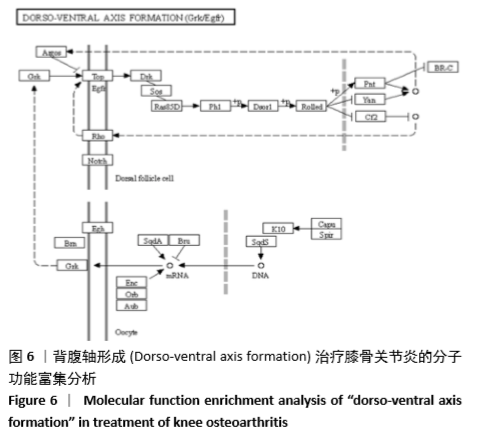
[1] 佟帅,吕海波,刘建桥.千山活血膏治疗膝骨关节炎30例疗效观察[J].中医药信息,2013,30(1):87-88.
[2] 刘维.中西医结合风湿免疫病学[M].武汉:华中科技大学出版社,2009:11.
[3] 施桂英.关节炎概要[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2000:339.
[4] 高欢欢,薛志鹏,李泰贤,等.治疗膝骨关节炎的中成药的组方规律分析[J].中国药房,2019,30(15):2096-2100.
[5] HOPKINS AL. Network pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4(11):682-690.
[6] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform.2014; 6:13.
[7] PIÑERO J, BRAVO À, QUERALT-ROSINACH N, et al. DisGeNET: a comprehensive platform integrating information on human disease-associated genes and variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D833-D839.
[8] 吴丹,高耀,向欢,等.基于网络药理学的柴胡抗抑郁作用机制研究[J].药学学报,2018,53(2):210-219.
[9] 刘增君.膝骨关节炎的治疗和进展[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(35):8064-8065.
[10] 魏玉玺.全膝关节置换术治疗膝重度骨性关节炎并内翻畸形的临床研究[D].贵州:贵阳医学院,2014.
[11] GOLDRING MB. The role of the chondrocyte in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43(9):1916-1926.
[12] 覃光辉.五色疗法治疗早中期膝骨关节炎[J].中国民间疗法,2018,26(4):14-15.
[13] 洪定钢.膝骨关节炎的中医药治疗[J].长春中医药大学学报,2009,25(5):698-699.
[14] 罗万华,王亮.强筋健骨汤治疗膝骨性关节炎60例临床疗效观察[J].四川中医, 2012,30(1):100-101.
[15] 杨少锋,姚共和.退行性骨关节炎与骨质疏松相关性的研究进展[J].湖南中医杂志,2006, 22(3):102-103.
[16] 朱良春.从痹病三个主证谈用药经验[J].北京中医药,1992(5):5-6.
[17] 马金石,王双青,杨国强.你身边的化学:化学创造美好生活[M].北京:科学出版社,2011.
[18] 周惠明.乳香没药, 制炭存性[J].浙江中医杂志,2000,35(6):268.
[19] 孙凯,魏戌,朱立国,等.“杜仲-牛膝”药对治疗腰痛机制的网络药理学探讨[J].中药新药与临床药理,2019,30(8): 935-942.
[20] 李强,张庆民,刘强,等.膝关节炎临床多种手段综合治疗的效果分析[J].中国现代药物应用,2013,7(3):39-40.
[21] 郭辉,张玲.乳香中化学成分和药理作用的研究进展[J].食品与药品,2007,9(5): 50-52.
[22] 常允平,韩英梅,张俊艳.乳香的化学成分和药理活性研究进展[J].现代药物与临床,2012,27(1):52-59.
[23] 赵金凤,周春兰,韩陆,等.没药研究进展[J].中国药房,2011,22(7):661-665.
[24] 魏昌勇. 几个BMP信号通路相关基因在斑马鱼胚胎早期发育过程的功能研究[D].北京:中国科学院大学, 2014.
[25] 周宇,李林.成骨分化和骨形成中BMP和TGF-β信号研究进展[J].医学信息,2015, 28(42):445-446.
[26] GUO X, WANG XF. Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 2009;19(1):71-88.
[27] NELSEN SM, CHRISTIAN JL. Site-specific cleavage of BMP4 by furin, PC6, and PC7. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(40):27157-27166.
[28] 朱瑜琪,王智耀,张帅,等.细胞因子与膝骨关节炎关节软骨损伤的修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(36):5873-5878.
[29] ZHANG P, ZHONG ZH, YU HT, et al. Exogenous expression of IL-1Ra and TGF-β1 promotes in vivo repair in experimental rabbit osteoarthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2015;44(5):404-411.
[30] ZHANG C, HUANG Y, ZHANG QZ, et al. Effect of Bushen Gujin Recipe on serum and synovia interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha of knee osteoarthritis model rabbits. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2015;35(3):355-358.
[31] LUO Z, JIANG L, XU Y, et al. Mechano growth factor (MGF) and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β3 functionalized silk scaffolds enhance articular hyaline cartilage regeneration in rabbit model. Biomaterials. 2015;52:463-475.
[32] WANG X, LI Y, HAN R, et al. Demineralized bone matrix combined bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor-β3 gene promoted pig cartilage defect repair. PLoS One. 2014; 9(12):e116061.
[33] LAPRAZ F, BESNARDEAU L, LEPAGE T. Patterning of the dorsal-ventral axis in echinoderms: insights into the evolution of the BMP-chordin signaling network. PLoS Biol. 2009;7(11):e1000248.
[34] 高红,朱正仑.背腹轴线形成的机制及其临床意义(英文)[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2012,44(5):673-677.
[35] YANG W, HAN W, QIN A, et al. The emerging role of Hippo signaling pathway in regulating osteoclast formation. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(6):4606-4617.
[36] SONG H, KIM H, LEE K, et al. Ablation of Rassf2 induces bone defects and subsequent haematopoietic anomalies in mice. EMBO J. 2012;31(5):1147-1159.
[37] LARSSON J, OHISHI M, GARRISON B, et al. Nf2/merlin regulates hematopoietic stem cell behavior by altering microenvironmental architecture. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(2):221-227.
[38] ALLEN NP, DONNINGER H, VOS MD, et al. RASSF6 is a novel member of the RASSF family of tumor suppressors. Oncogene. 2007;26(42):6203-6211.
[39] 王苹苹,孔繁平,陈学群,等.低氧细胞应激的HIF-1信号通路[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2011,40(5):559-566.
[40] NIZET V, JOHNSON RS. Interdependence of hypoxic and innate immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9(9):609-617.
|