中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 754-760.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3011
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
转化生长因子β1诱导心肌成纤维细胞转分化过程中Hedgehog信号通路的作用机制
聂慧娟,黄织春
- 内蒙古医科大学附属医院心血管内科,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010059
The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation
Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun
- Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010059, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
上皮间质转分化:是人体正常发育过程中或者机体在各种致病因素刺激下,上皮表型向间质表型转分化的过程,进而失去正常功能,组织器官发生纤维化异常增殖。
Hedgehog信号通路:是与人体生长、发育及疾病的发生发展有着密切关系的细胞通路,参与胚胎发育、器官形成及多种疾病损伤发病过程,但在心肌纤维化中的相关作用不明确,此次研究探讨其参与心肌纤维化的作用机制。
背景:近年来越来越多的研究表明Hedghog信号通路异常活化广泛参与全身多组织器官疾病的损伤修复过程,但其在心肌纤维化中的相关作用尚不明确。
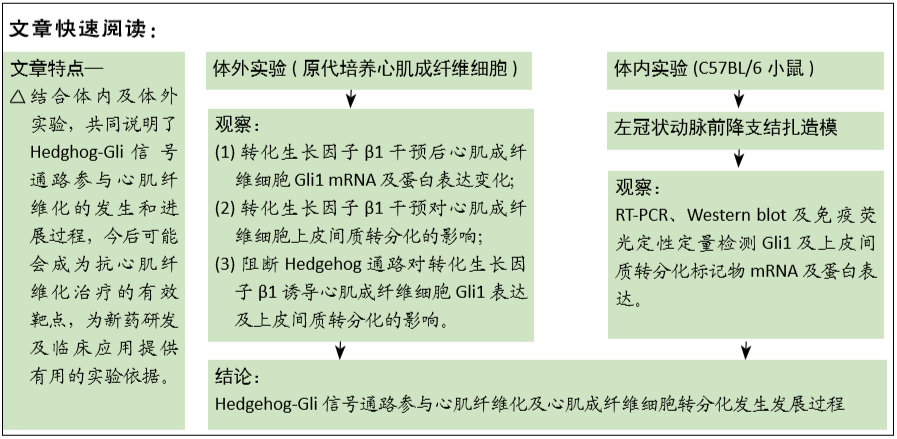
目的:研究阻断Hedgehog-Gli信号通路对转化生长因子β1诱导的心肌成纤维细胞上皮间质转分化过程的影响。
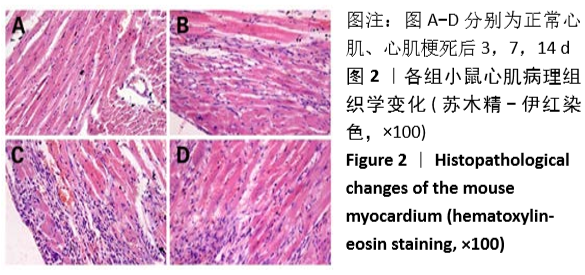
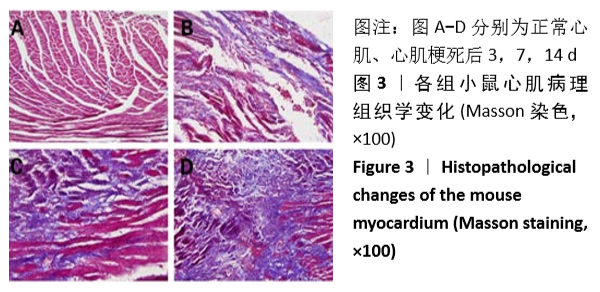
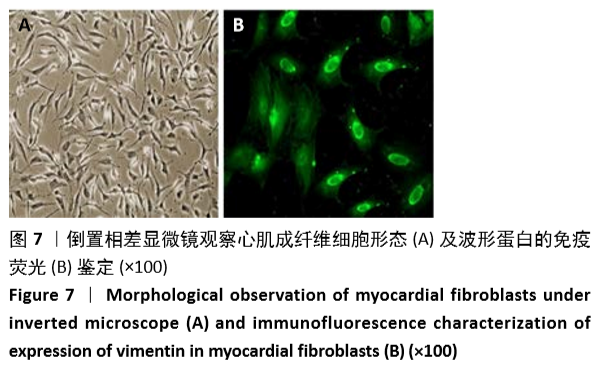
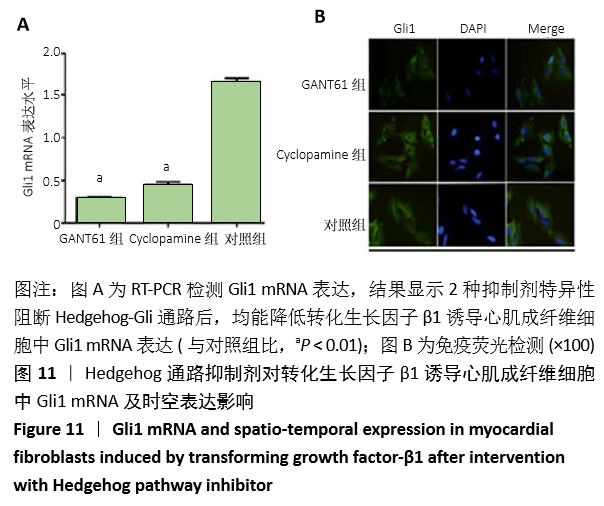
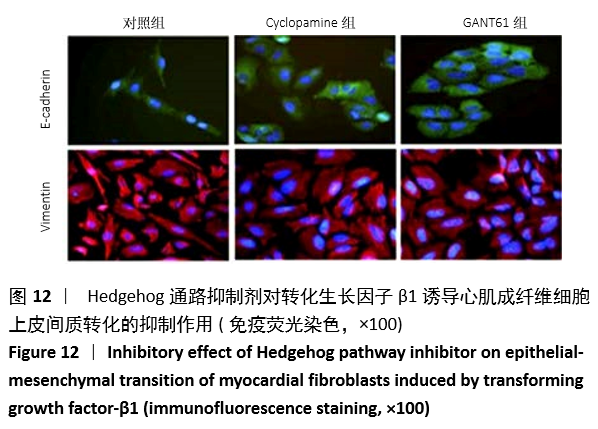
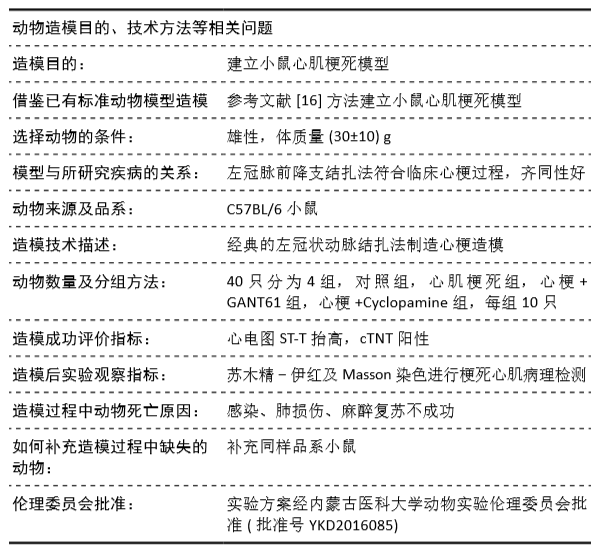
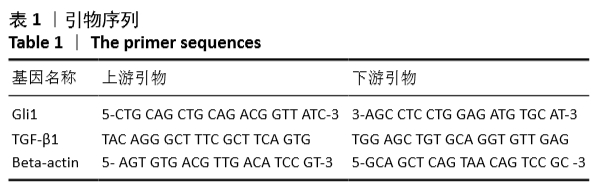
方法:①动物实验:左冠状动脉结扎法建立小鼠心肌梗死模型,苏木精-伊红和Masson染色法观察梗死后3,7,14 d心肌组织的病理改变,用RT-PCR、Western blot和免疫荧光法检测不同时段Gli1 mRNA及蛋白的时空表达,RT-PCR和免疫荧光定量检测加入特异性阻断剂后Gli1的mRNA及蛋白的时空表达变化。②细胞实验:差速贴壁法原代培养SD乳鼠心肌成纤维细胞,采用不同质量浓度(0,1,5,10 μg/L)转化生长因子β1刺激心肌成纤维细胞,RT-PCR、Western blot检测Gli1 mRNA及蛋白表达,选用10 μg/L的转化生长因子β1诱导心肌成纤维细胞24 h,免疫荧光法检测Gli1蛋白时空表达及上皮间质转分化标记物的表达。分别采用GANT61和Cyclopamine特异性阻断Hedgehog信号通路中的Gli1和Smo 24 h后,加入10 μg/L转化生长因子β1,RT-PCR检测Gli1 mRNA表达变化,荧光免疫法检测Gli1的时空表达以及上皮间质转分化标记物的表达变化。
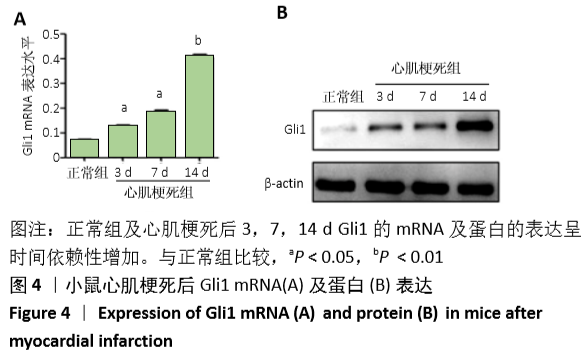
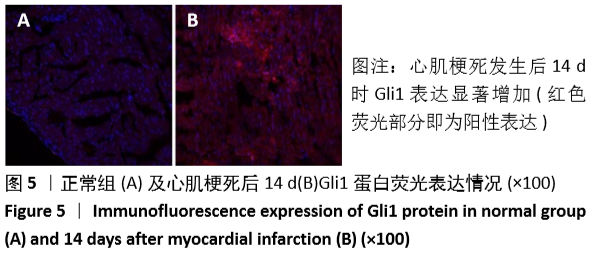
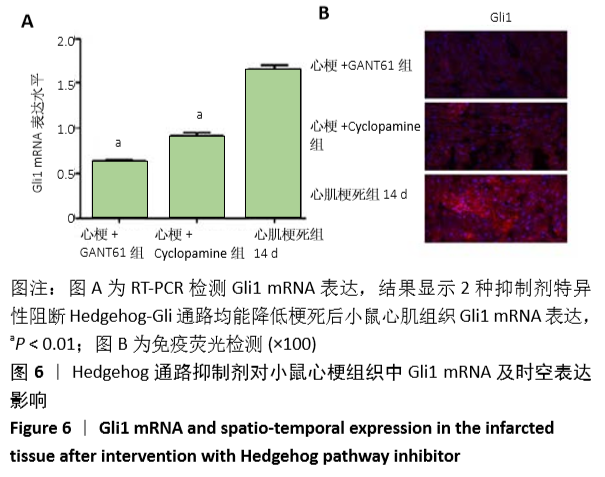
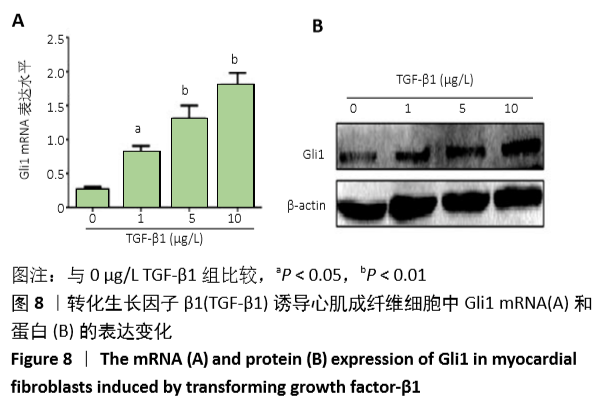
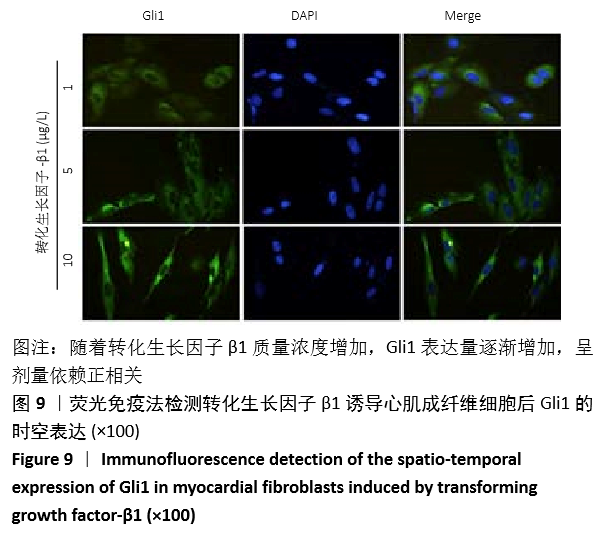
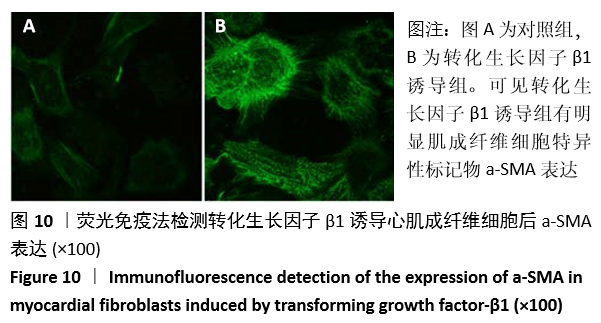
结果与结论:①动物实验结果:随着梗死后时间延长,小鼠心肌Gli1的mRNA和蛋白表达水平逐渐升高,而加入Hedgehog通路特异性阻断剂后梗死组织中Gli1的mRNA及蛋白表达均有下降。②细胞实验结果:采用转化生长因子β1刺激后,心肌成纤维细胞上皮间质转化为肌成纤维细胞(特异性标记物a-SMA阳性);随着转化生长因子β1干预剂量增加,Gli1的mRNA及蛋白表达逐渐增加。采用阻断剂特异性阻断Hedgehog信号通路中的Gli1和Smo 24 h后,Gli1的mRNA和蛋白表达均受抑制,同时伴有上皮间质转化发生的生物标记物E-Cadherin和Vimentin的表达改变,证实发生了上皮间质转化。③结合体内及体外实验,共同证实了Hedgehog-Gli信号通路参与心肌纤维化及心肌成纤维细胞转分化发生发展过程。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5878-9882 (聂慧娟)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: