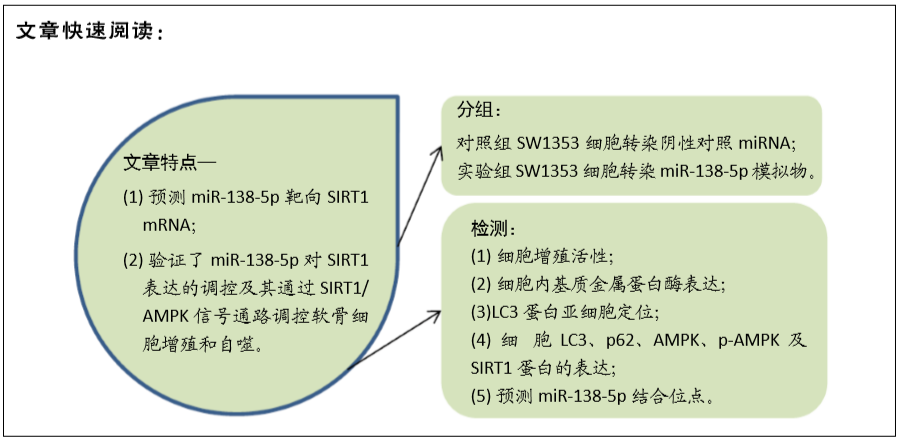
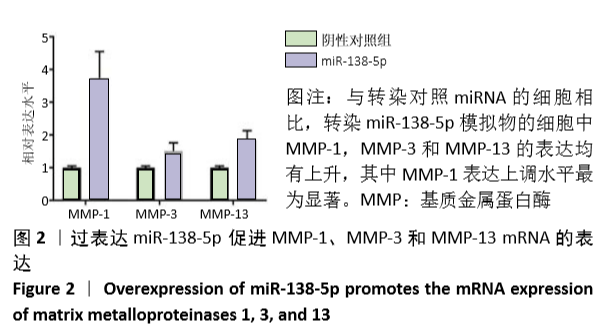
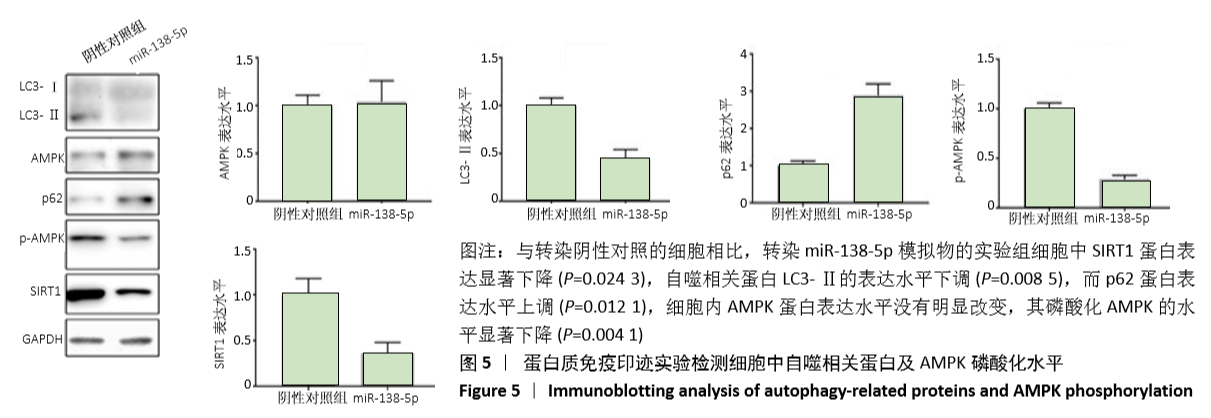
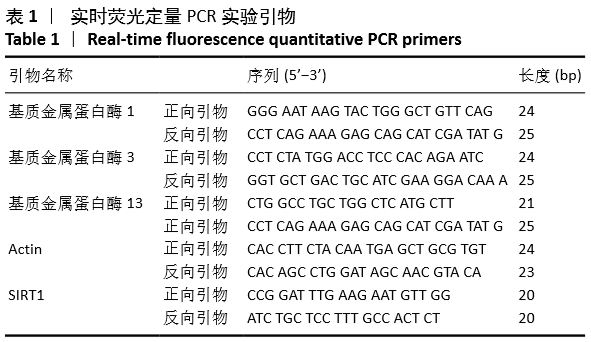
[1] VINA ER, KWOH CK. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: literature update. Curr Opin Rheumatol.2018; 30(2): 160-167.
[2] SILVERWOOD V, BLAGOJEVIC-BUCKNALL M, JINKS C, et al. Current evidence on risk factors for knee osteoarthritis in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2015; 23(4): 507-515.
[3] PALMIERI-SMITH RM, CAMERON KL, DISTEFANO LJ, et al. The Role of Athletic Trainers in Preventing and Managing Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis in Physically Active Populations: a Consensus Statement of the Athletic Trainers’ Osteoarthritis Consortium. J Athl Train. 2017; 52(6): 610-623.
[4] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR A J, CICUTTINI F M, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers.2016; 2: 16072.
[5] CHOI M C, JO J, PARK J, et al. NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways in Osteoarthritic Cartilage Destruction. Cells. 2019;8(7):734.
[6] ZHANG M, LYGRISSE K, WANG J. Role of MicroRNA in Osteoarthritis. J Arthritis. 2017;6(2):239.
[7] ZHOU ZB, DU D, HUANG GX, et al. Circular RNA Atp9b, a competing endogenous RNA, regulates the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting miR-138-5p. Gene.2018; 646: 203-209.
[8] DUAN L,DUAN D,WEI W,et al.MiR-19b-3p attenuates IL-1beta induced extracellular matrix degradation and inflammatory injury in chondrocytes by targeting GRK6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019; 459(1-2): 205-214.
[9] LI B, BAI L, SHEN P, et al. Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in knee anterior cruciate ligament tissues surgically removed from patients with osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med.2017; 40(4): 1105-1113.
[10] YUAN Y, ZHANG G Q, CHAI W, et al. Silencing of microRNA-138-5p promotes IL-1beta-induced cartilage degradation in human chondrocytes by targeting FOXC1: miR-138 promotes cartilage degradation. Bone Joint Res.2016;5(10): 523-530.
[11] CARBALLO CB, NAKAGAWA Y, SEKIYA I, et al. Basic Science of Articular Cartilage. Clin Sports Med.2017; 36(3): 413-425.
[12] KOPANSKA M, SZALA D, CZECH J, et al. MiRNA expression in the cartilage of patients with osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res.2017; 12(1): 51.
[13] CARAMES B, HASEGAWA A, TANIGUCHI N, et al. Autophagy activation by rapamycin reduces severity of experimental osteoarthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2012, 71(4): 575-581.
[14] CHENG NT, MENG H, MA LF, et al. Role of autophagy in the progression of osteoarthritis: The autophagy inhibitor, 3-methyladenine, aggravates the severity of experimental osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med.2017; 39(5): 1224-1232.
[15] QIN N, WEI L, LI W, et al. Local intra-articular injection of resveratrol delays cartilage degeneration in C57BL/6 mice by inducing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR pathway. J Pharmacol Sci.2017;134(3):166-174.
[16] GUILAK F, NIMS RJ, DICKS A, et al. Osteoarthritis as a disease of the cartilage pericellular matrix. Matrix Biol.2018;71-72:40-50.
[17] POSEY KL, COUSTRY F, HECHT JT. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein: COMPopathies and beyond. Matrix Biol.2018;71-72:161-173.
[18] LI H, WANG D, YUAN Y, et al. New insights on the MMP-13 regulatory network in the pathogenesis of early osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1): 248.
[19] MALEMUD CJ. Inhibition of MMPs and ADAM/ADAMTS[J]. Biochem Pharmacol.2019;165:33-40.
[20] WU GW, CHEN J,HUANG YM,et al.Electroacupuncture Delays Cartilage Degeneration by Modulating Nuclear Factor-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Chin J Integr Med.2019;25(9):677-683.
[21] WAN Y, LI W, LIAO Z, et al. Selective MMP-13 inhibitors: promising agents for the therapy of Osteoarthritis. Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(22): 3753-3769.
[22] LEI J, FU Y, ZHUANG Y, et al. LncRNA SNHG1 Alleviates IL-1beta-induced Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting miR-16-5p-mediated p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(9):BSR20191523.
[23] LI Y, XIAO W, WU P, et al. The expression of SIRT1 in articular cartilage of patients with knee osteoarthritis and its correlation with disease severity. J Orthop Surg Res.2016;11(1):144.
[24] SUN W, LI Y, WEI S. miR-4262 regulates chondrocyte viability, apoptosis, autophagy by targeting SIRT1 and activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in rats with osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med.2018; 15(1): 1119-1128.
[25] TIAN S, GUO X, YU C, et al. miR-138-5p suppresses autophagy in pancreatic cancer by targeting SIRT1. Oncotarget.2017; 8(7): 11071-11082.
[26] CETRULLO S, D’ADAMO S, TANTINI B, et al. mTOR, AMPK, and Sirt1: Key Players in Metabolic Stress Management. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr.2015;25(1): 59-75.
[27] VELAGAPUDI R, EL-BAKOUSH A, LEPIARZ I, et al. AMPK and SIRT1 activation contribute to inhibition of neuroinflammation by thymoquinone in BV2 microglia. Mol Cell Biochem.2017; 435(1-2): 149-162.
[28] CHEN H, LIU X, CHEN H, et al. Role of SIRT1 and AMPK in mesenchymal stem cells differentiation[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2014, 13: 55-64.
[29] PRESNEAU N, DUHAMEL LA, YE H, et al. Post-translational regulation contributes to the loss of LKB1 expression through SIRT1 deacetylase in osteosarcomas. Br J Cancer.2017;117(3):398-408.
[30] ZHANG X, HAN X, ZHANG P, et al.Morin attenuates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-mediated injury by inducing autophagy via activating AMPK signaling in HUVECs.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019;46(11): 1053-1060.
[31] XUE JF, SHI ZM, ZOU J, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother.2017;89: 1252-1261. |