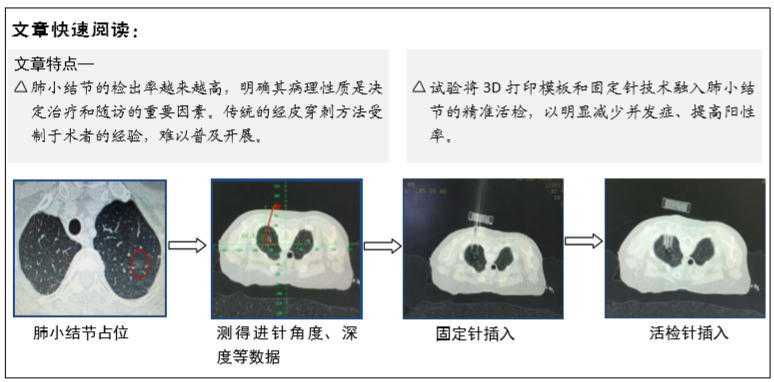
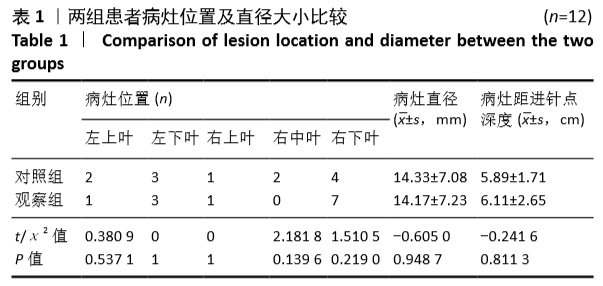
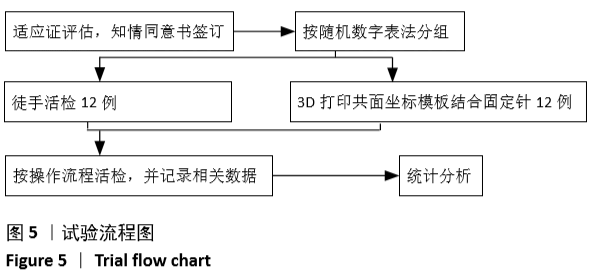
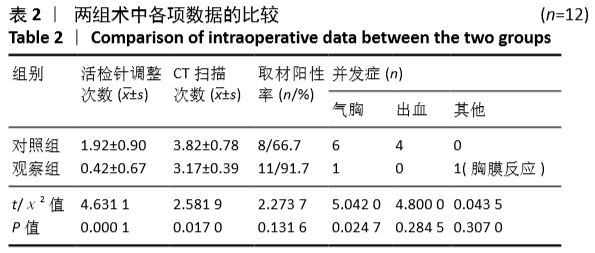
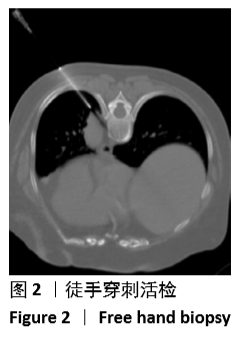
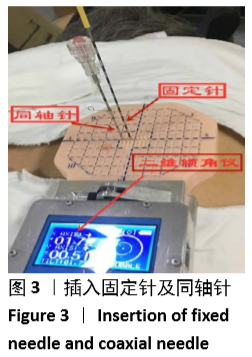
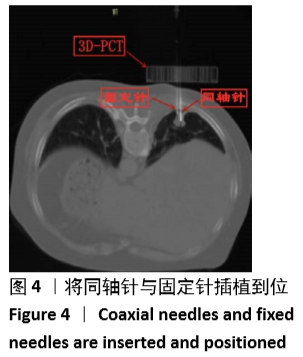
[1] 张迪,范丽,望云,等.低剂量CT肺癌筛查中肺癌危险因素及高危模型的单中心研究[J].中华放射学杂志,2018,52(5):369-373.
[2] 孙琦,黄遥,赵世俊,等.低剂量CT肺癌筛查中持续存在肺结节的CT体积和质量增长及其影响因素[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2018,40(4):274-279.
[3] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会肺癌学组,中国肺癌防治联盟专家组.肺结节诊治中国专家共识(2018年版)[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2018,41(10): 763-771.
[4] LEE KH, LIM KY, SUH YJ, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Lung Biopsies: A Multicenter Study.Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(8):1300-1310.
[5] 朱盈盈,周婷满,汪晓芹,等.电磁导航支气管镜下行肺部结节活检患者的护理[J].重庆医科大学学报,2017,42(9):1174-1177.
[6] 何杰,李小燕,余觅,等.电磁导航支气管镜引导冷冻肺活检对肺外周结节的诊断价值[J].中国内镜杂志,2019,25(4):54-59.
[7] 李静,徐维章,茅昌敏,等.电磁导航支气管镜引导下活检刷检联合肺泡灌洗对肺外周结节的诊断价值[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2018,38(8):1158-1160.
[8] 王东东,李晓光,李彬,等.经同轴套管穿刺活检同步微波消融治疗高度可疑恶性肺结节[J].介入放射学杂志,2018,27(11):1040-1044.
[9] 徐俊马,喻岳超,赵杰, 等.三维导航系统结合3D打印模板在精准穿刺及治疗中的临床应用[J].临床医学,2018,38(11):1-4,7.
[10] 王冠,陈宝明,张玉卫,等.3D打印共面穿刺模板辅助CT引导下肺原发小微结节穿刺临床研究[J].癌症进展,2017,15(9):1003-1007.
[11] 中国抗癌协会肿瘤介入学专业委员会,中国抗癌协会肿瘤介入学专业委员会青委会.胸部肿瘤经皮穿刺活检中国专家共识[J].中华介入放射学电子杂志,2018,6(3):188-194.
[12] 刘春全,崔永.肺结节评估四大指南比较分析[J].中国肺癌杂志,2017, 20(7):490-498.
[13] SÁNCHEZ M, BENEGAS M. Management of incidental lung nodules <8 mm in diameter.J Thorac Dis.2018;10(Suppl 22):S2611-S2627.
[14] LEMPEL JK. Intraoperative Percutaneous Microcoil Localization of Small Peripheral Pulmonary Nodules Using Cone-Beam CT in a Hybrid Operating Room.AJR Am J Roentgenol.2019;213(4):778-781.
[15] ALPERT JB. Management of Incidental Lung Nodules: Current Strategy and Rationale.Radiol Clin North Am.2018;56(3):339-351.
[16] TONGBAI T, MCDERMOTT S, FINTELMANN FJ, et al. Complications and Accuracy of Computed Tomography-guided Transthoracic Needle Biopsy in Patients Over 80 Years of Age.J Thorac Imaging.2019;34(3):187-191.
[17] 邹兰科,邓忠天.大孔径CT模拟机引导下经皮穿刺肺活检116例临床研究[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2019,36(4):453-456.
[18] 寇咏,王瑶.CT引导经皮肺穿刺活检对肺部病变的诊断意义及并发症原因分析[J].中国实验诊断学,2019,23(11):1896-1899.
[19] JIAO D,REN K,LI Z,et al.Clinical role of guidance by C-arm CT for I brachytherapy on pulmonary tumors.Radiol Med.2017;122(11):829-836.
[20] 王东旭,张啸波,肖越勇, 等.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检术并发症的影响因素及处理方法[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2019,16(9):522-526.
[21] SHIEKH Y, HASEEB WA, FEROZ I, et al. Evaluation of various patient-, lesion-, and procedure-related factors on the occurrence of pneumothorax as a complication of CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy.Pol J Radiol.2019;84(1):e73-e79.
[22] YOON SH, PARK CM, LEE KH, et al. Erratum: Analysis of Complications of Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Biopsy Using CT-Guidance Modalities In a Multicenter Cohort of 10568 Biopsies.Korean J Radiol.2019;20(3):531
[23] HAFFNER M, QUINN A, HSIEH TY, et al. Optimization of 3D Print Material for the Recreation of Patient-Specific Temporal Bone Models.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol.2018;127(5):338-343.
[24] OBASARE E, MELENDRES E, MORRIS DL, et al. Patient specific 3D print of left atrial appendage for closure device.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging.2016; 32(10):1495-1497.
[25] 靳一帆,万熠,刘新宇,等.基于FDM3D打印技术在医疗临床中的应用[J].实验室研究与探索,2016,35(6):9-12.
[26] 杨新宇.3D打印技术在医学中的应用进展[J].复旦学报(医学版),2016, 43(4):490-494.
[27] 许宁,郑磊,张杰,等.放射性粒子组织间植入近距离放疗在颅底腺源性恶性肿瘤治疗中的应用[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2017,33(6):798-801.
[28] 王俊杰.3D打印技术在精准粒子植入治疗中的应用[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2017,37(7):481-484.
[29] 王俊杰,柴树德,郑广钧,等.3D打印模板辅助CT引导放射性125I粒子植入治疗肿瘤专家共识[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2017,37(3): 161-170.
[30] 徐俊马,喻岳超,王俊杰.肺局灶性磨玻璃影三维导航支架结合3D-PCT引导穿刺一例报告并文献复习[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2018,25(14): 1042-1044.
[31] 吉喆,郭福新,姜玉良,等.3D打印共面模板辅助CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检技术的临床应用[J].癌症进展,2018,16(3):302-305.
[32] 徐俊马,喻岳超,刘智,等.3D打印模板结合CT引导125I放射性粒子精准植入治疗恶性肿瘤物理剂量学参数比较[J].江苏医药,2019,45(5): 492-496. |