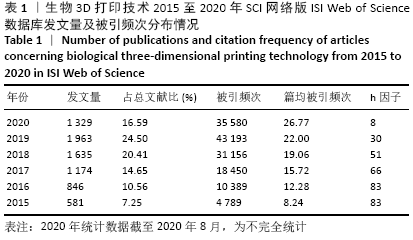
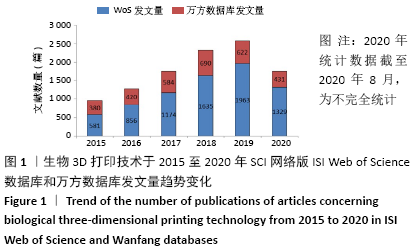
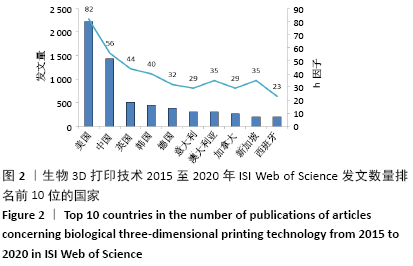
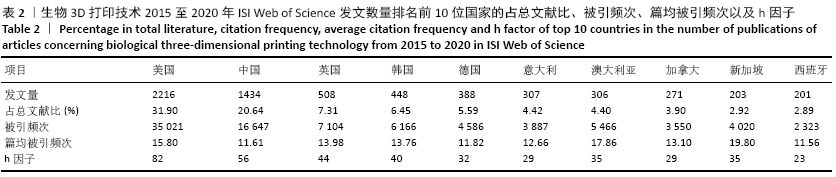
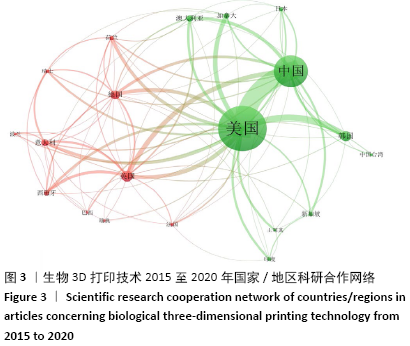
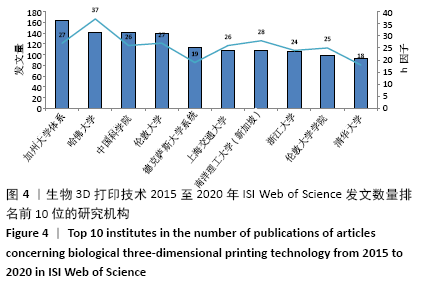
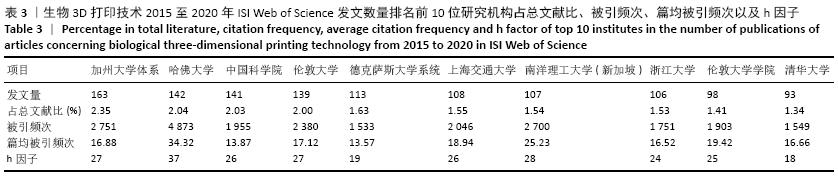
[1] NGO TD, KASHANI A, IMBALZANO G, et al. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos B Eng. 2018;143:172-196.
[2] MARTIN JH, YAHATA BD, HUNDLEY JM, et al. 3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys. Nature. 2017;549(7672):365-369.
[3] LIGON SC, LISKA R, STAMPFL J, et al. Polymers for 3D Printing and Customized Additive Manufacturing. Chem Rev. 2017;117(15): 10212-10290.
[4] ZAREK M, LAYANI M, COOPERSTEIN I, et al. 3D Printing of Shape Memory Polymers for Flexible Electronic Devices. Adv Mater. 2016; 28(22):4449-4454.
[5] WAHEED S, CABOT JM, MACDONALD NP, et al. 3D printed microfluidic devices: enablers and barriers. Lab Chip. 2016;16(11):1993-2013.
[6] LEE JY, AN J, CHUA CK. Fundamentals and applications of 3D printing for novel materials. Applied Materials Today. 2017;7:120-133.
[7] CHIMENE D, LENNOX KK, KAUNAS RR, et al. Advanced Bioinks for 3D Printing: A Materials Science Perspective. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016;44(6): 2090-2102.
[8] VADODARIA S, MILLS T. Jetting-based 3D printing of edible materials. Food Hydrocolloids. 2020;106:105857.
[9] WELCH JL, XIANG J, MACKIN SR, et al. Inactivation of Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus Virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Diverse RNA and DNA Viruses on Three-Dimensionally Printed Surgical Mask Materials. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2020. doi:10.1017/ice.2020.417.
[10] KOTZ F, HELMER D, RAPP BE. Emerging Technologies and Materials for High-Resolution 3D Printing of Microfluidic Chips. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2020. doi: 10.1007/10_2020_141.
[11] ZHANG Y, ZHANG F, YAN Z, et al. Printing, folding and assembly methods for forming 3D mesostructures in advanced materials. Nat Rev Mater. 2017;2(4):17019.
[12] HE R, LIU W, WU Z, et al. Fabrication of complex-shaped zirconia ceramic parts via a DLP- stereolithography-based 3D printing method. Ceram Int. 2018;44(3):3412-3416.
[13] BAGHERI SAED A, BEHRAVESH AH, HASANNIA S, et al. Functionalized poly l-lactic acid synthesis and optimization of process parameters for 3D printing of porous scaffolds via digital light processing (DLP) method. J Manuf Process. 2020;56:550-561.
[14] 张秀梅,翟运开,丁楠,等.精准医学决策支持知识组织研究[J].医学信息学杂志,2020,41(5):24-29,48.
[15] 赵晓宇,刁天喜,高云华,等.美国“精准医学计划”解读与思考[J].军事医学,2015(4):241-244.
[16] SAUNDERS RE, DERBY B. Inkjet printing biomaterials for tissue engineering: bioprinting. Inter Mater Rev. 2014;59(8):430-448.
[17] HEINRICH MA, LIU W, JIMENEZ A, et al. 3D Bioprinting: from Benches to Translational Applications. Small. 2019;15(23):e1805510.
[18] WU C, WANG B, ZHANG C, et al. Bioprinting: an assessment based on manufacturing readiness levels. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017;37(3): 333-354.
[19] JAMRÓZ W, SZAFRANIEC J, KUREK M, et al. 3D Printing in Pharmaceutical and Medical Applications - Recent Achievements and Challenges. Pharm Res. 2018;35(9):176.
[20] CUI H, NOWICKI M, FISHER JP, et al. 3D Bioprinting for Organ Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(1):10.1002/adhm.201601118.
[21] BIAZAR E, NAJAFI SM, HEIDARI KS, et al. 3D bio-printing technology for body tissues and organs regeneration. J Med Eng Technol. 2018;42(3): 187-202.
[22] AIMAR A, PALERMO A, INNOCENTI B. The Role of 3D Printing in Medical Applications: A State of the Art. J Healthc Eng. 2019;2019:5340616.
[23] HOSPODIUK M, DEY M, SOSNOSKI D, et al. The bioink: A comprehensive review on bioprintable materials. Biotechnol Adv. 2017;35(2):217-239.
[24] HÖLZL K, LIN S, TYTGAT L, et al. Bioink properties before, during and after 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication. 2016;8(3):032002.
[25] RASTOGI P, KANDASUBRAMANIAN B. Review of alginate-based hydrogel bioprinting for application in tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2019; 11(4):042001.
[26] VALOT L, MARTINEZ J, MEHDI A, et al. Chemical insights into bioinks for 3D printing. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(15):4049-4086.
[27] ARRIGONI C, GILARDI M, BERSINI S, et al. Bioprinting and Organ-on-Chip Applications Towards Personalized Medicine for Bone Diseases. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017;13(3):407-417.
[28] GOLD K, GAHARWAR AK, JAIN A. Emerging trends in multiscale modeling of vascular pathophysiology: Organ-on-a-chip and 3D printing. Biomaterials. 2019;196:2-17.
[29] YU F, CHOUDHURY D. Microfluidic bioprinting for organ-on-a-chip models. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24(6):1248-1257.
[30] MI S, DU Z, XU Y, et al. The crossing and integration between microfluidic technology and 3D printing for organ-on-chips. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(39):6191-6206.
[31] BHATTACHARJEE N, URRIOS A, KANG S, et al. The upcoming 3D-printing revolution in microfluidics. Lab Chip. 2016;16(10):1720-1742.
[32] RADHAKRISHNAN J, VARADARAJ S, DASH SK, et al. Organotypic cancer tissue models for drug screening: 3D constructs, bioprinting and microfluidic chips. Drug Discov Today. 2020;25(5):879-890.
[33] RICHARD C, NEILD A, CADARSO VJ. The emerging role of microfluidics in multi-material 3D bioprinting. Lab Chip. 2020;20(12):2044-2056.
[34] SANTANA HS, PALMA MSA, LOPES MGM, et al. Microfluidic Devices and 3D Printing for Synthesis and Screening of Drugs and Tissue Engineering. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2020;59(9):3794-3810.
[35] SKELLEY NW, HAGERTY MP, STANNARD JT, et al. Sterility of 3D-Printed Orthopedic Implants Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Orthopedics. 2020;43(1):46-51.
[36] FRIZZIERO L, LIVERANI A, DONNICI G, et al. New Methodology for Diagnosis of Orthopedic Diseases through Additive Manufacturing Models. Symmetry. 2019;11(4):27.
[37] DONG XP, ZHANG YW, PEI YJ, et al. Three-dimensional printing for the accurate orthopedics: clinical cases analysis. Biodes Manuf. 2020;3(2): 122-132.
[38] BRUNS N, KRETTEK C. 3D-printing in trauma surgery : Planning, printing and processing. Unfallchirurg. 2019;122(4):270-277.
[39] ALLEN B, MOORE C, SEYLER T, et al. Modulating antibiotic release from reservoirs in 3D-printed orthopedic devices to treat periprosthetic joint infection. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(10):2239-2249.
[40] HAN C, YAO Y, CHENG X, et al. Electrophoretic Deposition of Gentamicin-Loaded Silk Fibroin Coatings on 3D-Printed Porous Cobalt-Chromium-Molybdenum Bone Substitutes to Prevent Orthopedic Implant Infections. Biomacromolecules. 2017;18(11):3776-3787.
[41] VIJAYAVENKATARAMAN S, GOPINATH A, LU WF. A new design of 3D-printed orthopedic bone plates with auxetic structures to mitigate stress shielding and improve intra-operative bending. Biodes Manuf. 2020;3(2):98-108.
[42] 朱浩,郑孟杰,李延超,等.3D打印技术在颧上颌复合体骨折治疗中应用[J].创伤与急危重病医学,2020,8(5):335-337.
[43] 凌昊楠,李松军.3D打印复合支架修复软骨缺损的研究进展[J].医学综述,2020,26(18):3572-3576,3582.
[44] 李焕龙,耿承奎,陈帅,等.3D打印技术在骨盆手术中的应用[J].实用医学杂志,2020,36(17):2329-2333.
[45] 唐保明,李钊伟,杨爱荣,等.3D打印技术辅助治疗复杂髋臼骨折的疗效研究[J].中国医学装备,2020,17(9):107-110.
[46] 刘婷,杨德雨,刘莉,等.3D打印技术在脑血管病中的应用进展[J].中国卒中杂志,2020,15(8):916-920.
[47] CHEN H, HAN Q, WANG C, et al. Porous Scaffold Design for Additive Manufacturing in Orthopedics: A Review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:609.
[48] BARTOLOMEU F, DOURADO N, PEREIRA F, et al. Additive manufactured porous biomaterials targeting orthopedic implants: A suitable combination of mechanical, physical and topological properties. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;107:110342.
[49] GAO CH, WANG CY, JIN H, et al. Additive manufacturing technique-designed metallic porous implants for clinical application in orthopedics. RSC Adv. 2018;8(44):25210-25227.
[50] HAN X, YANG D, YANG C, et al. Carbon Fiber Reinforced PEEK Composites Based on 3D-Printing Technology for Orthopedic and Dental Applications. J Clin Med. 2019;8(2):240.
[51] BOSE S, BANERJEE D, SHIVARAM A, et al. Calcium phosphate coated 3D printed porous titanium with nanoscale surface modification for orthopedic and dental applications. Mater Des. 2018;151:102-112.
[52] NARITA M, TAKAKI T, SHIBAHARA T, et aI. Utilization of desktop 3D printer-fabricated “Cost-Effective” 3D models in orthognathic surgery. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;42(1):24.
[53] LOUVRIER A, MARTY P, BARRABÉ A, et al. How useful is 3D printing in maxillofacial surgery?. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;118(4):206-212.
[54] DATTA P, AYAN B, OZBOLAT IT. Bioprinting for vascular and vascularized tissue biofabrication. Acta Biomater. 2017;51:1-20.
[55] MONDSCHEIN RJ, KANITKAR A, WILLIAMS CB, et al. Polymer structure-property requirements for stereolithographic 3D printing of soft tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2017;140:170-188.
[56] ALI M, P R AK, LEE SJ, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinting for organ bioengineering: promise and pitfalls. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2018;23(6):649-656.
[57] WU Y, RAVNIC DJ, OZBOLAT IT. Intraoperative Bioprinting: Repairing Tissues and Organs in a Surgical Setting. Trends Biotechnol. 2020; 38(6):594-605.
[58] ESWARAMOORTHY SD, RAMAKRISHNA S, RATH SN. Recent advances in three-dimensional bioprinting of stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(6):908-924.
[59] LEI M, WANG X. Biodegradable Polymers and Stem Cells for Bioprinting. Molecules. 2016;21(5):539.
[60] AXPE E, OYEN ML. Applications of Alginate-Based Bioinks in 3D Bioprinting. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):1976.
[61] SHANJANI Y, KANG Y, ZARNESCU L, et al. Endothelial pattern formation in hybrid constructs of additive manufactured porous rigid scaffolds and cell-laden hydrogels for orthopedic applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;65:356-372.
[62] VITHANI K, GOYANES A, JANNIN V, et al. An Overview of 3D Printing Technologies for Soft Materials and Potential Opportunities for Lipid-based Drug Delivery Systems. Pharm Res. 2018;36(1):4.
[63] TRENFIELD SJ, AWAD A, MADLA CM, et al. Shaping the future: recent advances of 3D printing in drug delivery and healthcare. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019;16(10):1081-1094.
[64] MAZZOCCHI A, SOKER S, SKARDAL A. 3D bioprinting for high-throughput screening: Drug screening, disease modeling, and precision medicine applications. Applied Physics Reviews. 2019;6(1):011302.
[65] AFSANA, JAIN V, HAIDER N, et al. 3D Printing in Personalized Drug Delivery. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(42):5062-5071.
[66] GOOLE J, AMIGHI K. 3D printing in pharmaceutics: A new tool for designing customized drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2016;499(1-2): 376-394.
[67] YAN WC, DAVOODI P, VIJAYAVENKATARAMAN S, et al. 3D bioprinting of skin tissue: From pre-processing to final product evaluation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;132:270-295.
[68] MA X, LIU J, ZHU W, et al. 3D bioprinting of functional tissue models for personalized drug screening and in vitro disease modeling. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;132:235-251.
[69] 赵莹莹.3D打印技术在药物发展中的应用[J].河南科技,2020,(17): 70-71.
[70] 孙冲,刘堂义.3D打印技术在医学中的应用[J].中医学,2019,8(3): 197-202.
[71] 陈绍华,徐浩,王拥军,等.3D生物打印药物筛选生理病理模型平台建立的研究进展[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2019,21(9): 1902-1908.
[72] 石靖,王增明,郑爱萍.3D打印技术在药物制剂中的应用和挑战[J].药学进展,2019,43(3):164-173.
[73] 马薇.3D打印技术在药物制剂中的研究进展[J].今日药学,2018, 28(3):204-206.
[74] 陈国宁,舒花,余佩,等.3D打印技术在药学领域研究中的应用[J].中国药学杂志,2016,51(16):1353-1359.
[75] 王雪,张灿,平其能.3D打印技术在药物高端制剂中的研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2016,47(2):140-147. |